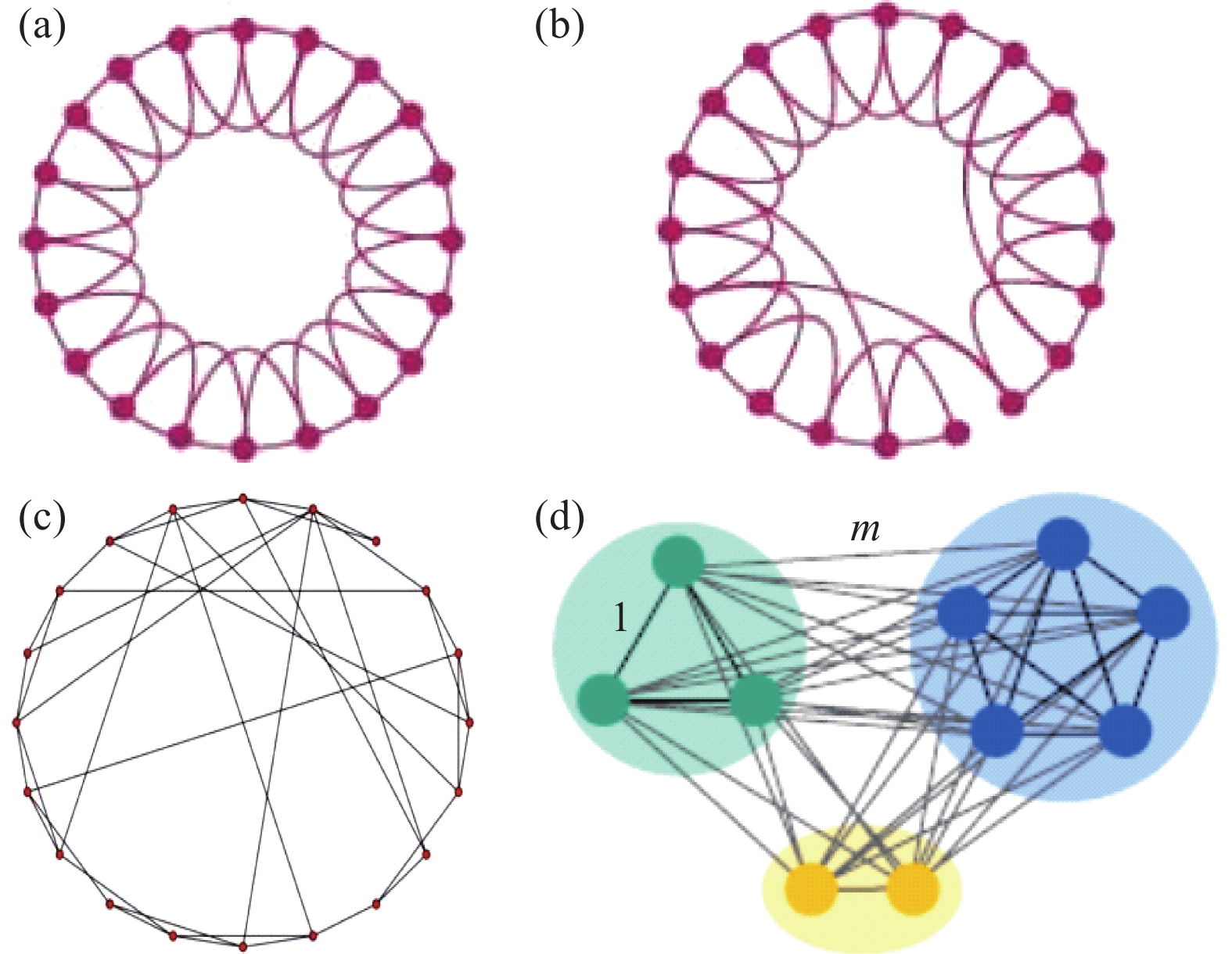
| [1] |
Barabási A L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 1999, 286(5439): 509 doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.509
|
| [2] |
Wang L, Wu T, Zhang Y L. Feedback mechanism in coevolutionary games. Control Theory Appl, 2014, 31(7): 823 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40059王龍, 吳特, 張艷玲. 共演化博弈中的反饋機制. 控制理論與應用, 2014, 31(7):823 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40059
|
| [3] |
Gallo E, Yan C. The effects of reputational and social knowledge on cooperation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(12): 3647 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415883112
|
| [4] |
Li X, Cao L. Largest Laplacian eigenvalue predicts the emergence of costly punishment in the evolutionary ultimatum game on networks. Phys Rev E, 2009, 80(6): 066101 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.066101
|
| [5] |
Doebeli M, Ispolatov Y, Simon B. Point of view: Towards a mechanistic foundation of evolutionary theory. Elife, 2019, 6: e23804
|
| [6] |
Goswami A, Gupta R, Parashari G S. Reputation-based resource allocation in P2P systems: A game theoretic perspective. IEEE Commun Lett, 2017, 21(6): 1273 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2675900
|
| [7] |
Hilbe C, Wu B, Traulsen A, et al. Cooperation and control in multiplayer social dilemmas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(46): 16425 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407887111
|
| [8] |
Tan S L, Wang Y N. Graphical Nash equilibria and replicator dynamics on complex networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst, 2020, 31(6): 1831 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2927233
|
| [9] |
Julou T, Mora T, Guillon L, et al. Cell-cell contacts confine public goods diffusion inside pseudomonas aeruginosa clonal microcolonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(31): 12577 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301428110
|
| [10] |
Qi S, Footer O, Camerer C F, et al. A collaborator's reputation can bias decisions and anxiety under uncertainty. J Neurosci, 2018, 38(9): 2262 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2337-17.2018
|
| [11] |
Feng C, Luo Y J, Krueger F. Neural signatures of fairness-related normative decision making in the ultimatum game: A coordinate-based meta-analysis. Hum Brain Mapp, 2015, 36(2): 591 doi: 10.1002/hbm.22649
|
| [12] |
Duradoni M, Paolucci M, Bagnoli F, et al. Fairness and trust in virtual environments: The effects of reputation. Future Internet, 2018, 10(6): 50 doi: 10.3390/fi10060050
|
| [13] |
Jeong H C, Oh S Y, Allen B, et al. Optional games on cycles and complete graphs. J Theor Biol, 2014, 356: 98 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.04.025
|
| [14] |
Melamed D, Harrell A, Simpson B. Cooperation, clustering, and assortative mixing in dynamic networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(5): 951 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715357115
|
| [15] |
Adami C, Schossau J, Hintze A. Evolutionary game theory using agent-based methods. Phys Life Rev, 2016, 19: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2016.08.015
|
| [16] |
Débarre F. Fidelity of parent-offspring transmission and the evolution of social behavior in structured populations. J Theor Biol, 2017, 420: 26 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.02.027
|
| [17] |
McAvoy A, Fraiman N, Hauert C, et al. Public goods games in populations with fluctuating size. Theor Popul Biol, 2018, 121: 72 doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2018.01.004
|
| [18] |
Szabó G, Borsos I. Evolutionary potential games on lattices. Phys Rep, 2016, 624: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.02.006
|
| [19] |
Lessard S, Soares C D. Frequency-dependent growth in class-structured populations: Continuous dynamics in the limit of weak selection. J Math Biol, 2018, 77(1): 229 doi: 10.1007/s00285-017-1195-5
|
| [20] |
Smith J M, Price G R. The logic of animal conflict. Nature, 1973, 246(5427): 15 doi: 10.1038/246015a0
|
| [21] |
Khoo T, Fu F, Pauls S. Spillover modes in multiplex games: Double-edged effects on cooperation and their coevolution. Sci Rep, 2018, 8: 6922 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25025-3
|
| [22] |
Wang Q, He N R, Chen X J. Replicator dynamics for public goods game with resource allocation in large populations. Appl Math Comput, 2018, 328: 162
|
| [23] |
Perc M, Jordan J J, Rand D G, et al. Statistical physics of human cooperation. Phys Rep, 2017, 687: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2017.05.004
|
| [24] |
Hilbe C, Martinez-Vaquero L A, Chatterjee K, et al. Memory-n strategies of direct reciprocity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(18): 4715 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621239114
|
| [25] |
Cheng D Z, Liu Z Q. Application of semi-tensor product of matrices to finite games. Control Theory Appl, 2019, 36(11): 1812 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90595程代展, 劉澤群. 有限博弈的矩陣半張量積方法. 控制理論與應用, 2019, 36(11):1812 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90595
|
| [26] |
Deng Z H, Nian X H. Distributed generalized Nash equilibrium seeking algorithm design for aggregative games over weight-balanced digraphs. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst, 2019, 30(3): 695 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850763
|
| [27] |
Zhang R, Zhu Q Y. A game-theoretic approach to design secure and resilient distributed support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst, 2018, 29(11): 5512 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2802721
|
| [28] |
Chotibut T, Nelson D R. Population genetics with fluctuating population sizes. J Stat Phys, 2017, 167(3-4): 777 doi: 10.1007/s10955-017-1741-y
|
| [29] |
Constable G W, Rogers T, McKane A J, et al. Demographic noise can reverse the direction of deterministic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(32): 4745 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603693113
|
| [30] |
Liu Y, Zhang J, An B, et al. A simulation framework for measuring robustness of incentive mechanisms and its implementation in reputation systems. Auton Agents Multi Agent Syst, 2016, 30(4): 581 doi: 10.1007/s10458-015-9296-2
|
| [31] |
Zhang Y L, Liu A Z, Sun C Y. Development of several studies on indirect reciprocity and the evolution of cooperation. Acta Autom Sin, 2018, 44(1): 1張艷玲, 劉愛志, 孫長銀. 間接互惠與合作演化的若干問題研究進展. 自動化學報, 2018, 44(1):1
|
| [32] |
Rong Z H, Xu X R, Wu Z X. Experiment research on the evolution of cooperation and network game theory. Sci Sin Phys Mech Astron, 2020, 50(1): 118榮智海, 許雄銳, 吳枝喜. 合作演化與網絡博弈實驗研究進展. 中國科學:物理學 力學 天文學, 2020, 50(1):118
|
| [33] |
Perc M, Gómez-Garde?es J, Szolnoki A, et al. Evolutionary dynamics of group interactions on structured populations: A review. J R Soc Interface, 2013, 10(80): 20120997 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0997
|
| [34] |
Nowak M A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1560 doi: 10.1126/science.1133755
|
| [35] |
Van Cleve J. Building a synthetic basis for kin selection and evolutionary game theory using population genetics. Theor Popul Biol, 2020, 133: 65 doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2020.03.001
|
| [36] |
Allen B, Nowak M A. There is no inclusive fitness at the level of the individual. Curr Opin Behav Sci, 2016, 12: 122 doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.10.002
|
| [37] |
Hilbe C, Chatterjee K, Nowak M A. Partners and rivals in direct reciprocity. Nat Hum Behav, 2018, 2(7): 469 doi: 10.1038/s41562-018-0320-9
|
| [38] |
Donahue K, Hauser O P, Nowak M A, et al. Evolving cooperation in multichannel games. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 3885 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17730-3
|
| [39] |
Hilbe C, Schmid L, Tkadlec J, et al. Indirect reciprocity with private, noisy, and incomplete information. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(48): 12241 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810565115
|
| [40] |
Clark D, Fudenberg D, Wolitzky A. Indirect reciprocity with simple records. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(21): 11344 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921984117
|
| [41] |
Hauert C, Saade C, McAvoy A. Asymmetric evolutionary games with environmental feedback. J Theor Biol, 2019, 462: 347 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.11.019
|
| [42] |
Szolnoki A, Perc M. Second-order free-riding on antisocial punishment restores the effectiveness of prosocial punishment. Phys Rev X, 2017, 7(4): 041027
|
| [43] |
Cooney D B. Analysis of multilevel replicator dynamics for general two-strategy social dilemma. Bull Math Biol, 2020, 82(6): 66 doi: 10.1007/s11538-020-00742-x
|
| [44] |
McAvoy A, Allen B, Nowak M A. Social goods dilemmas in heterogeneous societies. Nat Hum Behav, 2020, 4(8): 819 doi: 10.1038/s41562-020-0881-2
|
| [45] |
Su Q, Li A, Wang L. Evolutionary dynamics under interactive diversity. New J Phys, 2017, 19: 103023 doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa8feb
|
| [46] |
Su Q, Zhou L, Wang L. Evolutionary multiplayer games on graphs with edge diversity. PLoS Comput Biol, 2019, 15(4): e1006947 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006947
|
| [47] |
Zhou L, Li A M, Wang L. Evolution of cooperation on complex networks with synergistic and discounted group interactions. EPL, 2015, 110(6): 60006 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/110/60006
|
| [48] |
Su Q, Li A, Wang L. Evolution of cooperation with interactive identity and diversity. J Theor Biol, 2018, 442: 149 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.01.021
|
| [49] |
Hauser O P, Hilbe C, Chatterjee K, et al. Social dilemmas among unequals. Nature, 2019, 572(7770): 524 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1488-5
|
| [50] |
Szolnoki A, Chen X J. Environmental feedback drives cooperation in spatial social dilemmas. EPL, 2017, 120(5): 58001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/120/58001
|
| [51] |
Ak?ay E. Collapse and rescue of cooperation in evolving dynamic networks. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 2692 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05130-7
|
| [52] |
Stewart A J, Plotkin J B. Collapse of cooperation in evolving games. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(49): 17558 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1408618111
|
| [53] |
Hilbe C, ?imsa ?, Chatterjee K, et al. Evolution of cooperation in stochastic games. Nature, 2018, 559(7713): 246 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0277-x
|
| [54] |
Su Q, McAvoy A, Wang L, et al. Evolutionary dynamics with game transitions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(51): 25398 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908936116
|
| [55] |
Weitz J S, Eksin C, Paarporn K, et al. An oscillating tragedy of the commons in replicator dynamics with game-environment feedback. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(47): E7518 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604096113
|
| [56] |
Chen P, Li Q, Zhang D Z, et al. A survey of multimodal machine learning. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(5): 557陳鵬, 李擎, 張德政, 等. 多模態學習方法綜述. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(5):557
|
| [57] |
Lin Y H, Weitz J S. Spatial interactions and oscillatory tragedies of the commons. Phys Rev Lett, 2019, 122(14): 148102 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.148102
|
| [58] |
Chen X, Szolnoki A. Punishment and inspection for governing the commons in a feedback-evolving game. PLoS Comput Biol, 2018, 14(7): e1006347 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006347
|
| [59] |
Nowak M A, May R M. Evolutionary games and spatial chaos. Nature, 1992, 359(6398): 826 doi: 10.1038/359826a0
|
| [60] |
Barabási A L. Scale-free networks: A decade and beyond. Science, 2009, 325(5939): 412 doi: 10.1126/science.1173299
|
| [61] |
McAvoy A, Adlam B, Allen B, et al. Stationary frequencies and mixing times for neutral drift processes with spatial structure. Proc R Soc A, 2018, 474(2218): 20180238 doi: 10.1098/rspa.2018.0238
|
| [62] |
Liu J Z, Meng H R, Wang W, et al. Evolution of cooperation on independent networks: The influence of asymmetric information sharing updating mechanism. Appl Math Comput, 2019, 340: 234
|
| [63] |
Deng Z H, Huang Y J, Gu Z Y, et al. Multi-games on interdependent networks and the evolution of cooperation. Phys A, 2018, 510: 83 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.06.120
|
| [64] |
Zhao J Q, Luo C, Zheng Y J. Evolutionary dynamics of the cooperation clusters on interdependent networks. Phys A, 2019, 517: 132 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.11.018
|
| [65] |
Chu C, Hu X, Shen C, et al. Self-organized interdependence among populations promotes cooperation by means of coevolution. Chaos, 2019, 29(1): 013139 doi: 10.1063/1.5059360
|
| [66] |
Szolnoki A, Perc M. Information sharing promotes prosocial behaviour. New J Phys, 2013, 15(5): 053010 doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/15/5/053010
|
| [67] |
Szolnoki A, Chen X. Reciprocity-based cooperative phalanx maintained by overconfident players. Phys Rev E, 2018, 98(2-1): 022309
|
| [68] |
Xia C Y, Li X P, Wang Z, et al. Doubly effects of information sharing on interdependent network reciprocity. New J Phys, 2018, 20(7): 075005 doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aad140
|
| [69] |
Ibsen-Jensen R, Chatterjee K, Nowak M A. Computational complexity of ecological and evolutionary spatial dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(51): 15636 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511366112
|
| [70] |
Tarnita C E, Wage N, Nowak M A. Multiple strategies in structured populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(6): 2334 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016008108
|
| [71] |
Antal T, Ohtsuki H, Wakeley J, et al. Evolution of cooperation by phenotypic similarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(21): 8597 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902528106
|
| [72] |
Zhang Y, Liu A, Sun C. Impact of migration on the multi-strategy selection in finite group-structured populations. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 35114 doi: 10.1038/srep35114
|
| [73] |
Ohtsuki H, Hauert C, Lieberman E, et al. A simple rule for the evolution of cooperation on graphs and social networks. Nature, 2006, 441(7092): 502 doi: 10.1038/nature04605
|
| [74] |
Allen B, Lippner G, Chen Y T, et al. Evolutionary dynamics on any population structure. Nature, 2017, 544(7649): 227 doi: 10.1038/nature21723
|
| [75] |
Allen B, McAvoy A. A mathematical formalism for natural selection with arbitrary spatial and genetic structure. J Math Biol, 2019, 78(4): 1147 doi: 10.1007/s00285-018-1305-z
|
| [76] |
Allen B, Nowak M. Games on graphs. EMS Surv Math Sci, 2014, 1(1): 113 doi: 10.4171/EMSS/3
|
| [77] |
Zhang Y L, Fu F, Wu T, et al. A tale of two contribution mechanisms for nonlinear public goods. Sci Rep, 2013, 3: 2021 doi: 10.1038/srep02021
|
| [78] |
Debove S, Baumard N, André J B. Models of the evolution of fairness in the ultimatum game: A review and classification. Evol Hum Behav, 2016, 37(3): 245 doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2016.01.001
|
| [79] |
Santos F P, Santos F C, Paiva A, et al. Evolutionary dynamics of group fairness. J Theor Biol, 2015, 378: 96 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.04.025
|
| [80] |
Takesue H, Ozawa A, Morikawa S. Evolution of favoritism and group fairness in a co-evolving three-person ultimatum game. EPL, 2017, 118(4): 48002 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/118/48002
|
| [81] |
Page K M, Nowak M A, Sigmund K. The spatial ultimatum game. Proc R Soc Lond B, 2000, 267(1458): 2177 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2000.1266
|
| [82] |
Alexander J M K. The Structural Evolution of Morality. Cambridge University Press, 2007
|
| [83] |
Iranzo J, Román J, Sánchez A. The spatial Ultimatum game revisited. J Theor Biol, 2011, 278(1): 1 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.02.020
|
| [84] |
Gao J, Li Z, Wu T, et al. The coevolutionary ultimatum game. EPL, 2011, 93(4): 48003 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/93/48003
|
| [85] |
Wang X F, Chen X J, Wang L. Evolutionary dynamics of fairness on graphs with migration. J Theor Biol, 2015, 380: 103 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.05.020
|
| [86] |
Szolnoki A, Perc M, Szabó G. Accuracy in strategy imitations promotes the evolution of fairness in the spatial ultimatum game. EPL, 2012, 100(2): 28005 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/100/28005
|
| [87] |
Han X, Cao S, Bao J Z, et al. Equal status in Ultimatum Games promotes rational sharing. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 1222 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19503-x
|
| [88] |
Rand D G, Tarnita C E, Ohtsuki H, et al. Evolution of fairness in the one-shot anonymous Ultimatum Game. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(7): 2581 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214167110
|
| [89] |
Killingback T, Studer E. Spatial Ultimatum Games, collaborations and the evolution of fairness. Proc Biol Sci, 2001, 268(1478): 1797 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1697
|
| [90] |
Wu T, Fu F, Zhang Y, et al. Adaptive role switching promotes fairness in networked ultimatum game. Sci Rep, 2013, 3: 1550 doi: 10.1038/srep01550
|
| [91] |
Yang Z H, Li Z, Wu T, et al. Effects of partner choice and role assignation in the spatial ultimatum game. EPL, 2015, 109(4): 40013 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/109/40013
|
| [92] |
Forber P, Smead R. The evolution of fairness through spite. Proc Biol Sci, 2014, 281(1780): 20132439
|
| [93] |
Zhang Y L, Fu F. Strategy intervention for the evolution of fairness. PLoS One, 2018, 13(5): e0196524 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196524
|
| [94] |
Szolnoki A, Perc M, Szabó G. Defense mechanisms of empathetic players in the spatial ultimatum game. Phys Rev Lett, 2012, 109(7): 078701 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.078701
|
| [95] |
Page K M, Nowak M A. Empathy leads to fairness. Bull Math Biol, 2002, 64(6): 1101 doi: 10.1006/bulm.2002.0321
|
| [96] |
Zhang Y L, Liu J, Li A M. Effects of empathy on the evolutionary dynamics of fairness in group-structured systems. Complexity, 2019, 2019: 2915020
|
| [97] |
Wang X, Chen X, Wang L. Random allocation of pies promotes the evolution of fairness in the Ultimatum Game. Sci Rep, 2014, 4: 4534
|
| [98] |
Chen W, Wu T, Li Z W, et al. Heterogenous allocation of chips promotes fairness in the Ultimatum Game. EPL, 2015, 109(6): 68006 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/109/68006
|
| [99] |
Zhang Y L, Chen X J, Liu A Z, et al. The effect of the stake size on the evolution of fairness. Appl Math Comput, 2018, 321: 641
|
| [100] |
Deng L L, Lin Y, Wang C, et al. Effects of coupling strength and coupling schemes between interdependent lattices on the evolutionary ultimatum game. Phys A, 2020, 540: 123173 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.123173
|
| [101] |
Zhao Y K, Xiong T, Zheng L, et al. The effect of similarity on the evolution of fairness in the ultimatum game. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2020, 131: 109494 doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2019.109494
|





 下載:
下載: