-
摘要: 充填料漿的管道輸送是充填采礦法的一個重要環節,而充填料漿的流變參數是評價充填料漿管輸特性的重要指標,目前主要采用流變儀進行測定,但礦山現場通常不具備流變實驗條件,主要通過塌落度實驗來評價充填料漿的流動性能。本文采用微型塌落筒進行不同質量分數、灰砂比的充填料漿塌落度實驗,建立微型塌落筒擴展度與屈服應力之間的解析模型,根據料漿停止流動后的形態得到簡化計算模型,基于簡化模型理論計算料漿的屈服應力,并將理論值與流變儀測試同等配比條件下得到的屈服應力實驗值進行對比分析,同時通過雙因素方差分析研究了不同質量分數、灰砂比對充填料漿擴展度的影響規律。結果表明,擴展度主要受質量分數的影響,灰砂比對其影響不顯著,充填料漿的屈服應力隨質量分數的增大而增大。在質量分數較低時,理論值與實驗值的相對誤差范圍較大,二者的相對誤差在25%以內,平均誤差為16.79%;隨著質量分數增大,誤差逐漸減小至15%以內,平均誤差為8.81%。綜合考慮質量分數的影響,提出基于質量分數的修正系數,修正后的屈服應力理論值與實驗值的相對誤差降至10%以內,平均誤差為3.54%。本研究微型塌落筒實驗較傳統塌落度實驗不僅節省實驗用料和勞動強度,還可有效表征料漿屈服應力,對于礦山充填料的流動性能評價具有實際指導意義。Abstract: The backfill mining method is widely used in mines because of its advantages of environmental protection, safety, and efficiency and includes filling slurry pipeline transportation as an important part. The rheological parameters of filling slurry are important indicators for evaluating the characteristics of filling slurry pipeline transport; these parameters are mainly determined by rheometers at present, while the rheological experimental conditions are usually unavailable at the mine site. Because of its simplicity and speed, mines mainly use a slump test to evaluate the flow properties of a filling slurry. In this paper, we used a mini-slump cone to conduct a slump experiment of filling slurry with different mass fractions and cement–tailings ratios (the two most common variable parameters in filling slurry ratios), established an analytical model between the spread of a mini-slump cone and yield stress, obtained a simplified calculation model according to the shape of the filling slurry after flowing, calculated the yield stress of the slurry based on the simplified model, and compared the theoretical value with the experimental value of the yield stress of the filling slurry under the condition of the same ratio tested by a rheometer. At the same time, the influence law of different mass fractions and cement–sand ratios on the expansion degree of the filling slurry was studied using a two-factor analysis of variance. The results show that the spread is mainly influenced by the mass fraction and unsubstantially affected by the cement–sand ratio. The yield stress of the filling slurry increases with the mass fraction. When the mass fraction is low, the error in the theoretical value relative to the experimental value has a large range, and the error in the theoretical value is within 25%, averaging 16.79%; as the mass fraction increases, this error gradually decreases below 15%, averaging 8.81%. Considering its effect, a correction factor based on the mass fraction was proposed, and the error in the theoretical yield stress value after the correction was reduced below 10%, averaging 3.54%. In this study, the mini-slump cone test not only reduces the experimental material and labor intensity compared with the traditional slump test but also effectively characterizes the yield stress of the slurry, which provides practical guidance for evaluating the flowability of mine filling slurry.
-
Key words:
- filling slurry /
- spread /
- yield stress /
- analytical model /
- correction factor
-
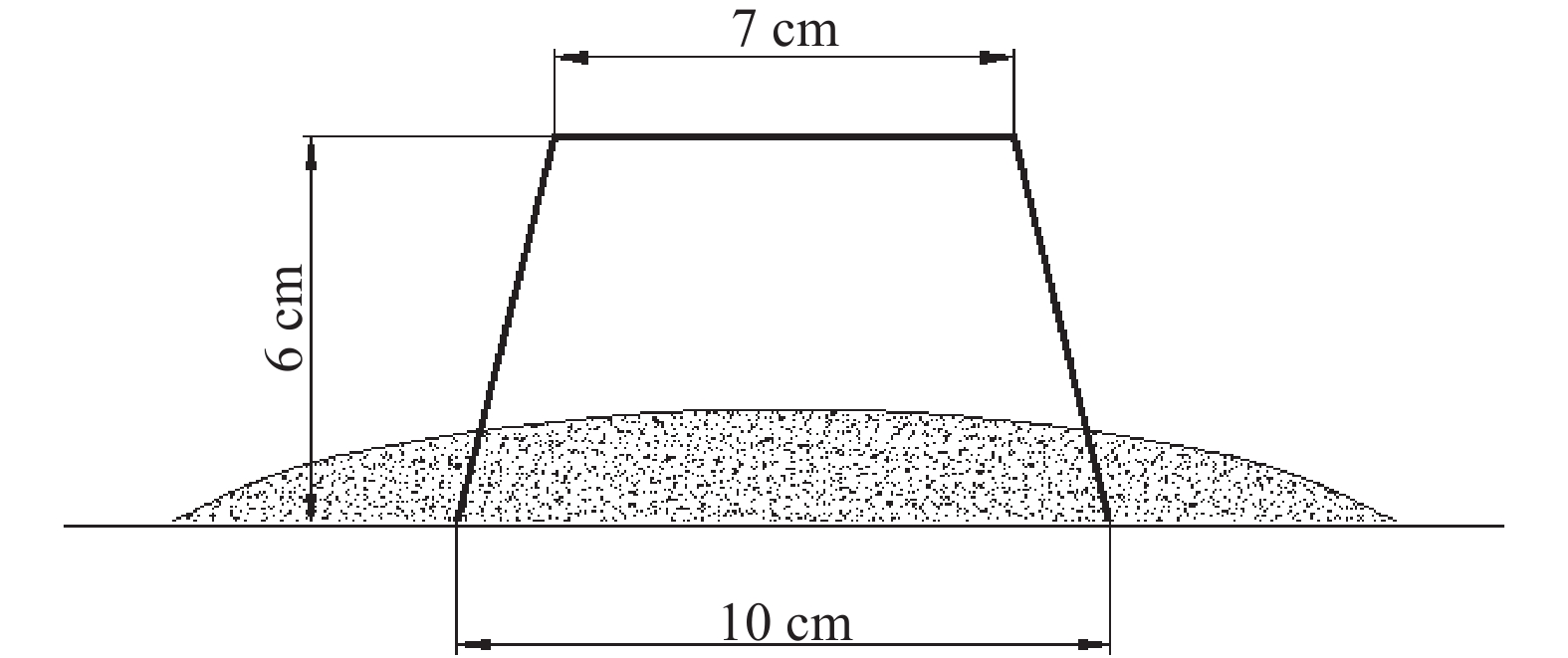
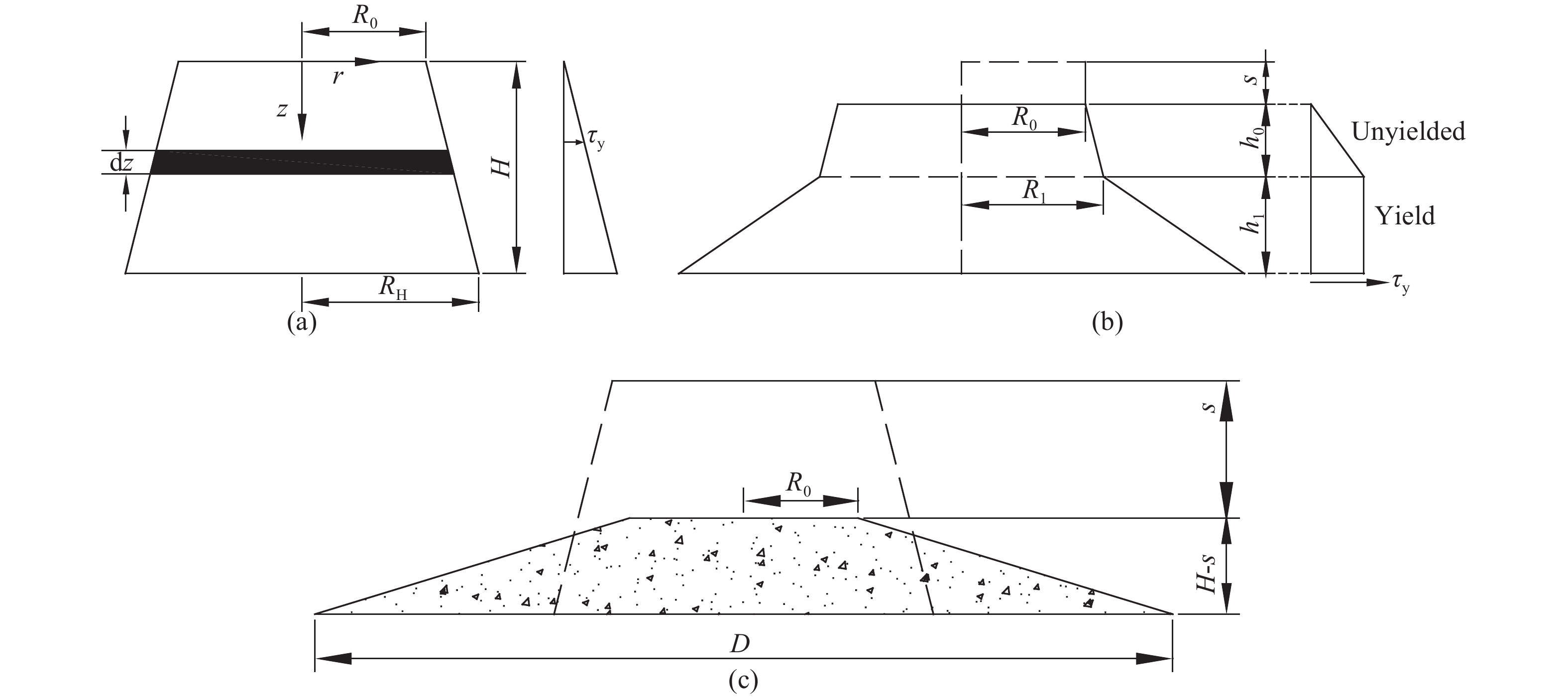
圖 4 微型塌落度實驗充填料受力分析圖(圖中R0為上口半徑,RH為下口半徑,H為高度,R1為未變形部分下口半徑,h0為未變形部分高度,h1為已屈服部分高度,s為塌落度,τy為料漿的屈服應力). (a)初始應力分析;(b)最終應力分析;(c)料漿最終擴展度形態
Figure 4. Mechanical analysis diagram of the filling slurry in a mini-slump cone test (in the figure, R0 is the upper radius, RH is the lower radius, H is the height, R1 is the radius of the lower plane of the undeformed part, h0 is the height of the undeformed part, h1 is the height of the yielded part, s is the slump, and τy is the yield stress of filling slurry): (a) initial stress analysis; (b) final stress analysis; (c) final spread shape of the slurry
表 1 擴展度與流變參數測試結果
Table 1. Results of the spread and rheological parameters test
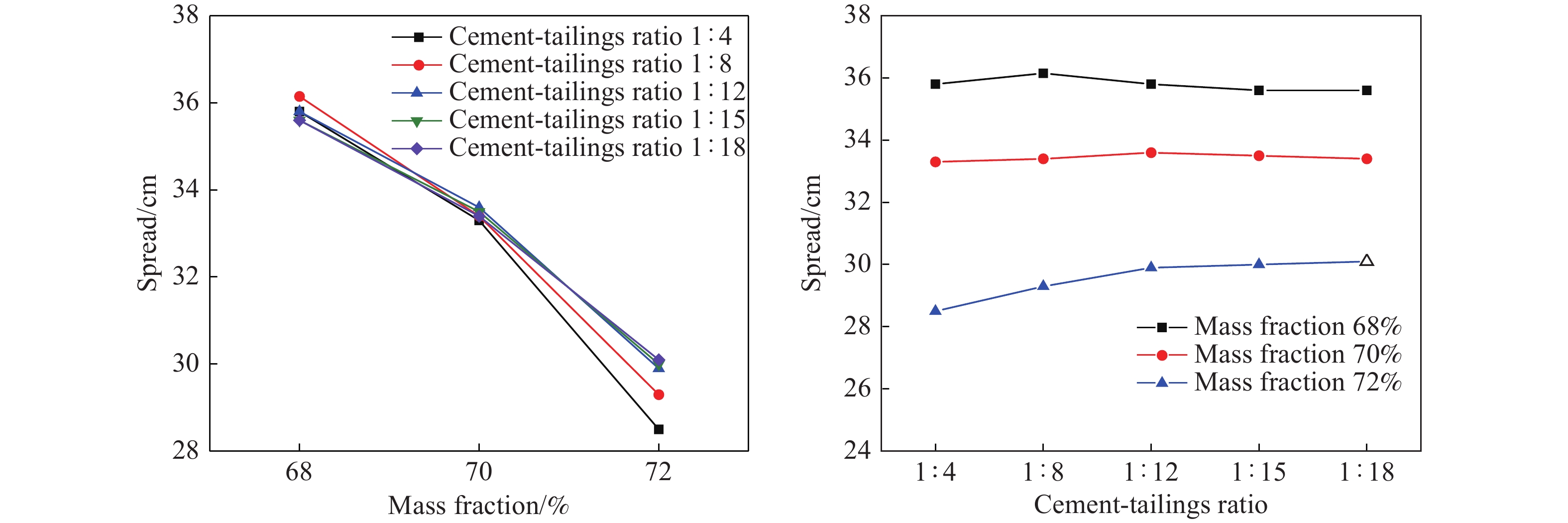
Mass fraction/% Cement–tailings ratio Spread/cm Yield stress/Pa Viscosity/
(Pa·s)68 1∶4 35.8 8.82 0.2782 68 1∶8 36.15 8.32 0.2769 68 1∶12 35.8 9.01 0.2583 68 1∶15 35.6 9.50 0.2535 68 1∶18 35.6 8.46 0.2804 70 1∶4 33.3 15.19 0.2435 70 1∶8 33.4 14.29 0.2687 70 1∶12 33.6 14.83 0.2940 70 1∶15 33.5 13.56 0.3008 70 1∶18 33.4 12.89 0.2882 72 1∶4 28.5 26.59 0.3337 72 1∶8 29.3 24.54 0.4039 72 1∶12 29.8 23.66 0.5445 72 1∶15 30 21.34 0.4652 72 1∶18 30.1 22.46 0.4523 表 2 方差分析結果
Table 2. Results of variance analysis
Source Type III sum of squares Df Mean square F Sig. Mass fraction 98.983 2 49.492 278.433 0.000 Cement–tailings ratio 0.624 4 0.156 0.878 0.518 Error 1.422 8 0.178 Total 101.029 14 表 3 解析模型計算屈服應力與測試屈服應力對比
Table 3. Comparison of yield stress calculated by an analytical model and measured yield stress
Mass fraction/% Cement–tailings ratio Spread/cm Test yield stress/Pa Calculation yield stress/Pa Absolute error Relative error/% 68 1∶4 35.8 8.82 10.216 1.3958 15.83 68 1∶8 36.15 8.32 9.892 1.5756 18.95 68 1∶12 35.8 9.01 10.216 1.20735 13.4 68 1∶15 35.6 9.50 10.546 1.04685 11.02 68 1∶18 35.6 8.46 10.546 2.0906 24.73 70 1∶4 33.3 15.19 14.152 ?1.0415 6.85 70 1∶8 33.4 14.29 14.029 ?0.2625 1.84 70 1∶12 33.6 14.83 13.897 ?0.9335 6.3 70 1∶15 33.5 13.56 13.717 0.16 1.18 70 1∶18 33.4 12.89 14.029 1.138 8.83 72 1∶4 28.5 26.59 22.532 ?4.056 15.26 72 1∶8 29.3 24.54 20.919 ?3.62 14.75 72 1∶12 29.8 23.66 20.506 ?3.1555 13.34 72 1∶15 30 21.34 19.892 ?1.4435 6.76 72 1∶18 30.1 22.46 19.529 ?2.93 13.04 表 4 修正后屈服應力對比
Table 4. Comparison of yield stress after correction
Mass fraction/% Cement–tailings ratio Test yield stress/Pa Corrected yield stress/Pa Correcting errors Corrected error rate/% 68 1∶4 8.82 8.814 0.0062 0.07 68 1∶8 8.32 8.535 ?0.2186 2.63 68 1∶12 9.01 8.814 0.1946 2.16 68 1∶15 9.50 9.099 0.4002 4.21 68 1∶18 8.46 9.099 ?0.6436 7.61 70 1∶4 15.19 14.251 0.9425 6.2 70 1∶8 14.29 14.127 0.1645 1.15 70 1∶12 14.83 13.994 0.8365 5.64 70 1∶15 13.56 13.813 ?0.2560 1.89 70 1∶18 12.89 14.127 ?1.2360 9.59 72 1∶4 26.59 25.939 0.6490 2.44 72 1∶8 24.54 24.082 0.4570 1.86 72 1∶12 23.66 23.607 0.0545 0.23 72 1∶15 21.34 22.9 ?1.5645 7.33 72 1∶18 22.46 22.482 ?0.0230 0.1 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Wu A X, Wang H J. Theory and Technology of Metal Ore Paste Filling. Beijing: Science Press, 2015吳愛祥, 王洪江. 金屬礦膏體充填理論與技術. 北京: 科學出版社, 2015 [2] Wu A X, Yang Y, Cheng H Y, et al. Status and prospects of paste technology in China. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(5): 517吳愛祥, 楊瑩, 程海勇, 等. 中國膏體技術發展現狀與趨勢. 工程科學學報, 2018, 40(5):517 [3] Aldhafeeri Z, Fall M. Time and damage induced changes in the chemical reactivity of cemented paste backfill. J Environ Chem Eng, 2016, 4(4): 4038 doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.09.006 [4] Ghirian A, Fall M. Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical–chemical behaviour of cemented paste backfill in column experiments. Part I: Physical, hydraulic and thermal processes and characteristics. Eng Geol, 2013, 164: 195 [5] Wu A X, Li H, Cheng H Y, et al. Status and prospects of research on the rheology of paste backfill using unclassified tailings (Part 2): Rheological measurement and prospects. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(4): 451吳愛祥, 李紅, 程海勇, 等. 全尾砂膏體流變學研究現狀與展望(下): 流變測量與展望. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(4):451 [6] Jiang H Q, Fall M. Yield stress and strength of saline cemented tailings in sub-zero environments: Portland cement paste backfill. Int J Miner Process, 2017, 160: 68 doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2017.01.010 [7] Deng D Q, Gao Y T, Wu S C. Liquidity detection based on the slump testing of coarse aggregate filling material. J Beijing Univ Civ Eng Archit, 2009, 25(1): 30鄧代強, 高永濤, 吳順川. 基于坍落度測試的粗骨料充填料漿流動性檢驗. 北京建筑工程學院學報, 2009, 25(1):30 [8] Saak A W, Jennings H M, Shah S P. A generalized approach for the determination of yield stress by slump and slump flow. Cem Concr Res, 2004, 34(3): 363 doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.08.005 [9] Roussel N. Correlation between yield stress and slump: Comparison between numerical simulations and concrete rheometers results. Mater Struct, 2006, 39(4): 501 [10] Tan Z J, Bernal S A, Provis J L. Reproducible mini-slump test procedure for measuring the yield stress of cementitious pastes. Mater Struct, 2017, 50(6): 235 doi: 10.1617/s11527-017-1103-x [11] Wallevik J E. Relationship between the Bingham parameters and slump. Cem Concr Res, 2006, 36(7): 1214 doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.03.001 [12] Li L, Zhang J, Hassani F, et al. Slump tests for yield stress of paste tailings. Met Mine, 2017(1): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2017.01.007李亮, 張柬, Hassani F, 等. 膏體尾礦屈服應力的塌落度試驗研究. 金屬礦山, 2017(1):30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2017.01.007 [13] Pei D F, Song Z P, Qi Z J, et al. Prediction on rheological parameters of pasty backfilling slurry based on mini-slump mould and consistency funnel. Met Mine, 2020(4): 15裴佃飛, 宋澤普, 齊兆軍, 等. 基于微型塌落筒和稠度漏斗的膏體充填料漿流變參數預測研究. 金屬礦山, 2020(4):15 [14] Zhou H, Zhang X W, Jiang H Q, et al. Relation between slump and yield stress of tailing slurry with different particle sizes. J Guangxi Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2022, 47(1): 103 doi: 10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2022.0103周晃, 張希巍, 姜海強, 等. 不同粒徑尾砂料漿塌落度和屈服應力關系. 廣西大學學報(自然科學版), 2022, 47(1):103 doi: 10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2022.0103 [15] Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, People’s Republic of China. GB/T 50080—2016 Standard for Test Method of Performance on Ordinary Fresh Concrete. Beijing: China Architecture Publishing, 2016中華人民共和國住房與城鄉建設部. GB/T 50080—2016普通混凝土拌合物性能試驗方法標準. 北京: 中國建筑工業出版社, 2016 [16] Chen X Z, Yang X C, Guo L J, et al. Rheological properties of tailings paste based on a spread test. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(10): 1299陳鑫政, 楊小聰, 郭利杰, 等. 基于擴散度的尾砂膏體流變特性. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(10):1299 [17] Wu A X, Jiao H Z, Wang H J, et al. Yield stress measurements and optimization of Paste tailings. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol), 2013, 44(8): 3370吳愛祥, 焦華喆, 王洪江, 等. 膏體尾礦屈服應力檢測及其優化. 中南大學學報(自然科學版), 2013, 44(8):3370 [18] Hou Y Q, Yin S H, Dai C Q, et al. Rheological properties and pipeline resistance calculation model in tailings paste. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2021, 31(2): 510 doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35800侯永強, 尹升華, 戴超群, 等. 尾礦膏體流變特性和管輸阻力計算模型. 中國有色金屬學報, 2021, 31(2):510 doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35800 [19] Kou Y P, Jiang H Q, Ren L, et al. Rheological properties of cemented paste backfill with alkali-activated slag. Minerals, 2020, 10(3): 288 doi: 10.3390/min10030288 [20] Wang M M. Construction and application of two-factor analysis of variance model. Stat Decis, 2015(18): 72 doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2015.18.020王苗苗. 雙因素方差分析模型的構建及應用. 統計與決策, 2015(18):72 doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2015.18.020 [21] Dai J H, Han C. A comparative study on two-way ANOVA. Stat Decis, 2018, 34(4): 30 doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2018.04.006戴金輝, 韓存. 雙因素方差分析方法的比較. 統計與決策, 2018, 34(4):30 doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2018.04.006 [22] Li W C, Guo L J, Liu G S, et al. Analytical and experimental investigation of the relationship between spread and yield stress in the mini-cone test for cemented tailings backfill. Constr Build Mater, 2020, 260: 119770 doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119770 [23] Clayton S, Grice T G, Boger D V. Analysis of the slump test for on-site yield stress measurement of mineral suspensions. Int J Miner Process, 2003, 70(1-4): 3 doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(02)00148-5 [24] Shen H M, Wu A X, Jiang L C, et al. Small cylindrical slump test for unclassified tailings paste. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol), 2016, 47(1): 204沈慧明, 吳愛祥, 姜立春, 等. 全尾砂膏體小型圓柱塌落度檢測. 中南大學學報(自然科學版), 2016, 47(1):204 [25] Wu F, Yang F G, Xiao B L, et al. Characterization of rheological property and its application of high concentration and mixed aggregate filling slurry based on spread. J Central South Univ (Sci Technol), 2022, 53(8): 3104吳凡, 楊發光, 肖柏林, 等. 基于擴展度表征高濃度混合骨料充填料漿流變特性及應用. 中南大學學報(自然科學版), 2022, 53(8):3104 -




 下載:
下載: