-
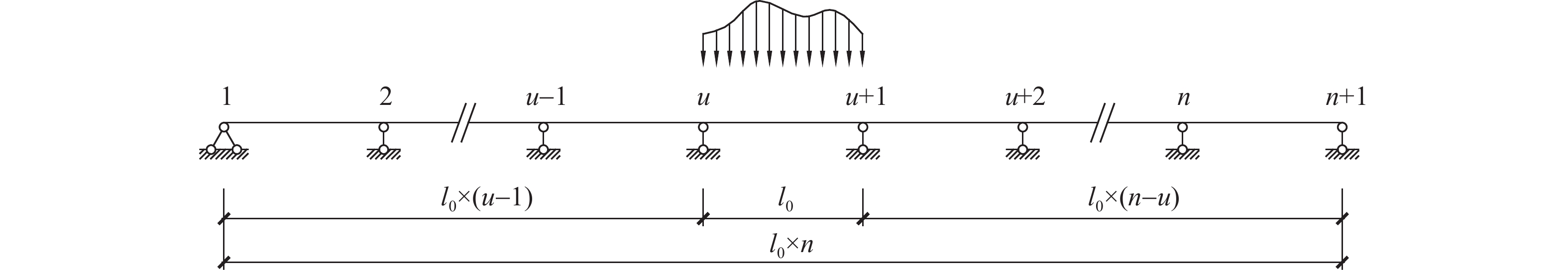
摘要: 求解等跨等截面連續梁的變形和內力是土木工程領域的典型問題. 基于Euler–Bernoulli梁理論,利用位移法和輔助數列推導出任意跨數的等跨等截面連續梁梁端轉動剛度的解析表達式,進而得到連續梁支點轉角、彎矩在跨中集中荷載、滿跨均布荷載、豎向溫差作用下的通用計算公式. 研究表明:當跨數趨于無窮大時,等跨等截面連續梁的梁端轉動剛度上限值為單跨梁抗彎線剛度的
$ 2\sqrt{\text{3}} $ 倍. 不同跨數的等跨等截面連續梁可采用形式統一的解析公式計算支點轉角和彎矩,不同靜力荷載作用結果的區別僅由單跨梁的固端彎矩決定. 所得公式形式簡潔、通用性強、應用方便,能揭示跨數對連續梁力學特性的影響規律,亦可用于分析頂推施工導梁參數優化等實際工程問題.Abstract: Solving the deformation and internal force of a prismatic multispan continuous beam of equal spans is a fundamental and classic problem in the area of civil engineering. Based on the Euler–Bernoulli beam theory, this paper presents unified analytical formulas to calculate the member-end rotation and bending moment of prismatic continuous beams of equal spans. First, simple closed-form expressions to determine the beam-end rotational stiffness of an equal-span prismatic continuous beam comprising any number of spans are derived using the displacement method in structural mechanics and the auxiliary series in mathematics. Furthermore, the rotational stiffness formulas are used to derive the analytical formulas for determining the joint rotation and bending moment at the supports of continuous beams subjected to various types of static loads and actions, such as a single point load applied at mid-span, distributed load applied over the span length, and differential temperature change between the top and bottom surfaces of the beam. Moreover, the implications of the proposed formulas on some interesting academic problems are thoroughly discussed. It is observed that as the number of spans goes infinity, the beam-end rotational stiffness of an equal-span prismatic continuous beam approaches the upper limit of$ 2\sqrt{\text{3}} $ i0, where i0 denotes the linear stiffness, which is the product of the modulus of elasticity (E) and the moment of inertia (I) divided by the length (l0) of the member of single-span beams. For equal-span prismatic continuous beams with various spans, the analytical formulas of the joint rotation and bending moment at the supports have unified expressions, while the difference between formulas for different static loads and actions is solely dependent on the fixed-end bending moment of single-span beams. This set of formulas reveals the advantages of concise form, general applicability, and convenient calculation. They can reveal the influence of the number of spans on the mechanical characteristics of continuous beams and analyze real-world engineering problems, such as optimization of the launching noses for incrementally launched bridges. Additionally, the proposed formulas in this paper can serve as an important reference for course teaching in the area of structural mechanics.-
Key words:
- continuous beams /
- rotation /
- bending moment /
- analytical formula /
- structural mechanics
-
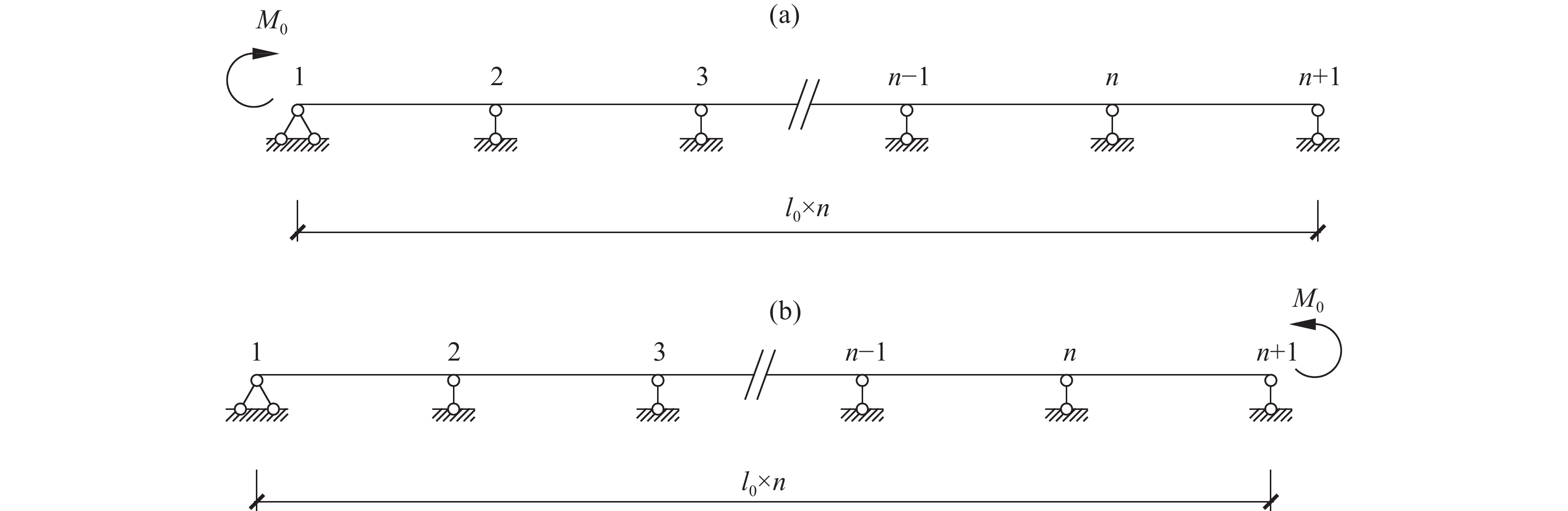
表 1 等跨等截面梁的計算公式
Table 1. Formulas for a prismatic continuous beam of equal spans
Case No. Analytical model Rotation, $ {z_k} $ Moment, $ {M_k} $ Parameter, $ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} $ 1 
Eq. 23 Eq. 24 $ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{ - F{l_0}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - F{l_0}} 8}} \right. } 8} $ 2 
$ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{ - ql_0^2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - ql_0^2} {12}}} \right. } {12}} $ 3 
$ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{EI\alpha \cdot \Delta T} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{EI\alpha \cdot \Delta T} h}} \right. } h} $ 4 
Eq. 25 Eq. 26 $ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{ - F{l_0}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - F{l_0}} 8}} \right. } 8} $ 5 
$ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{ - ql_0^2} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{ - ql_0^2} {12}}} \right. } {12}} $ 6 
$ M_1^{{\text{fix}}} = {{EI\alpha \cdot \Delta T} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{EI\alpha \cdot \Delta T} h}} \right. } h} $ Note: α and h are the linear expansion coefficient and the cross-sectional depth of the beam, respectively. The temperature changes in the top and bottom surfaces of the beam are denoted as t1 and t2, respectively. www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Xu Y, Shen C Y, Shao G T, et al. Continuous Beam Bridges. 3rd Ed. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2022徐岳, 申成岳, 邵國濤, 等. 連續梁橋. 3版. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2022 [2] Shao X D. Bridge Engineering. 5th Ed. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2019邵旭東. 橋梁工程. 5版. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2019 [3] Zhang H J, Pan D G. Semi-analytic solution to dynamic characteristics of non-uniform continuous beams. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2008, 30(6): 590 doi: 10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2008.06.019張懷靜, 潘旦光. 變截面連續梁動力特性的半解析解法. 北京科技大學學報, 2008, 30(6):590 doi: 10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2008.06.019 [4] Li L K. Structural Mechanics (I). 6th Ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2017李廉錕. 結構力學(上冊). 6版. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2017 [5] Long Y Q, Bao S H, Yuan S. Structural Mechanics (I) Basic Course. 4th Ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2018龍馭球, 包世華, 袁駟. 結構力學I——基礎教程. 4版. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2018 [6] Hibbeler R C. Structural Analysis. 9th Ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2015 [7] Leet K M, Uang C, Lanning J T, et al. Fundamentals of Structural Analysis. 5th Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2018 [8] Zuraski P D. Continuous-beam analysis for highway bridges. J Struct Eng, 1 991, 117(1): 80 [9] Compiling Group for “Manual of Static Calculation of Building Structures”. Manual of Static Calculation of Building Structures. 2nd Ed. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1998建筑結構靜力計算手冊編寫組. 建筑結構靜力計算手冊. 2版. 北京:中國建筑工業出版社, 1998 [10] Li Y C. Calculation of continuous beams with any number of spans. Bridge Constr, 1990, 20(4): 23李瀛滄. 任意多跨連續梁的計算. 橋梁建設, 1990, 20(4):23 [11] Dowell R K. Closed-form moment solution for continuous beams and bridge structures. Eng Struct, 2009, 31(8): 1880 doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2009.03.012 [12] Dowell R K, Johnson T P. Shear and bending flexibility in closed-form moment solutions for continuous beams and bridge structures. Eng Struct, 2011, 33(12): 3238 doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.08.016 [13] Hosseini-Tabatabaei M R, Rezaiee-Pajand M, Mollaeinia M R. Bridge-type structures analysis using RMP concept considering shear and bending flexibility. Struct Eng Mech, 2020, 74(2): 189 [14] Hosseini-Tabatabaei M R, Mollaeinia M R. Exact closed-form equations for internal forces functions of bridge-type structures. Struct Eng Mech, 2021, 80(2): 211 [15] Rosignoli M. Bridge Launching. London: Thomas Telford, 2002 [16] Zhou J X. Mechanical analysis for incrementally launched prismatic continuous beam bridges. Highway, 1994(11): 20周季湘. 等截面連續梁橋頂推施工的受力分析. 公路, 1994(11):20 [17] Dong C W, Li C X. Method for determination of reasonable parameters of launching nose for continuous beam. J Highw Transp Res Dev, 2010, 27(9): 55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2010.09.010董創文, 李傳習. 連續梁頂推導梁合理參數的確定方法. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(9):55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2010.09.010 [18] Rosignoli M. Nose-deck interaction in launched prestressed concrete bridges. J Bridge Eng, 1998, 3(1): 21 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(1998)3:1(21) [19] Wang W F, Lin J F, Ma W T. Optimum analysis of launching nose during incremental launching construction of bridge. Eng Mech, 2007, 24(2): 132 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.02.023王衛鋒, 林俊鋒, 馬文田. 橋梁頂推施工導梁的優化分析. 工程力學, 2007, 24(2):132 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.02.023 [20] Ji W, Shao T Y, Yu H F. Optimizing double launching noses for incrementally launched equal-span continuous girder bridges. J Bridge Eng, 2021, 26(7): 06021006 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001746 [21] Lee H W, Jang J Y. Simplified analysis formula for the interaction of the launching nose and the superstructure of ILM bridge. J Comput Struct Eng Inst Korea, 2012, 25(3): 245 doi: 10.7734/COSEIK.2012.25.3.245 [22] Wang L. A new method for solving static problems and influence lines of beams, continuous beams and rigid frames. J Hunan Univ, 1983, 10(2): 58王磊. 梁、連續梁、剛架靜力及影響線的新解法. 湖南大學學報, 1983, 10(2):58 [23] Sun X S, Zhang F C. Solving statically indeterminate continuous beams by “directly writing method”. J Shandong Univ Tech, 1999, 29(2): 197孫仙山, 張方春. “直寫法”求解靜不定連續梁. 山東工業大學學報, 1999, 29(2):197 [24] Yu X J. Conversion method for calculation of statically indeterminate straight beams with uniform cross-section. Eng Mech, 2007, 24(S1): 66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.z1.008喻曉今. 求超靜定等直梁的置換法. 工程力學, 2007, 24(增刊1):66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.z1.008 [25] Wu Y Y, Li Y S, Wei J W, et al. A subsection independently systematic integral method for solving problems of statically indeterminate beam. Eng Mech, 2013, 30(S1): 11 doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2012.04.S006吳艷艷, 李銀山, 魏劍偉, 等. 求解超靜定梁的分段獨立一體化積分法. 工程力學, 2013, 30(S1):11 doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2012.04.S006 [26] Jiang C Z, Huang J Q, Tang Z H. Distributed transfer function method for multi span statically indeterminate beam. J Xiangnan Univ, 2018, 39(2): 29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8173.2018.02.006蔣純志, 黃健全, 唐政華. 多跨超靜定梁的分布傳遞函數方法. 湘南學院學報, 2018, 39(2):29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8173.2018.02.006 [27] Wang Y J, Di J. A reasonable length ratio between side span and mid-span of continuous beams with uniform section. J Lanzhou Univ Nat Sci, 2016, 52(3): 320王亞軍, 狄謹. 等截面連續梁合理邊中跨跨徑比. 蘭州大學學報(自然科學版), 2016, 52(3):320 [28] Ji W, Shao T Y. Optimization analysis of double launching noses during launching construction of multi-span continuous girder bridge. J Zhejiang Univ Eng Sci, 2021, 55(7): 1289冀偉, 邵天彥. 多跨連續梁橋頂推施工雙導梁的優化分析. 浙江大學學報(工學版), 2021, 55(7):1289 -






 下載:
下載: