-
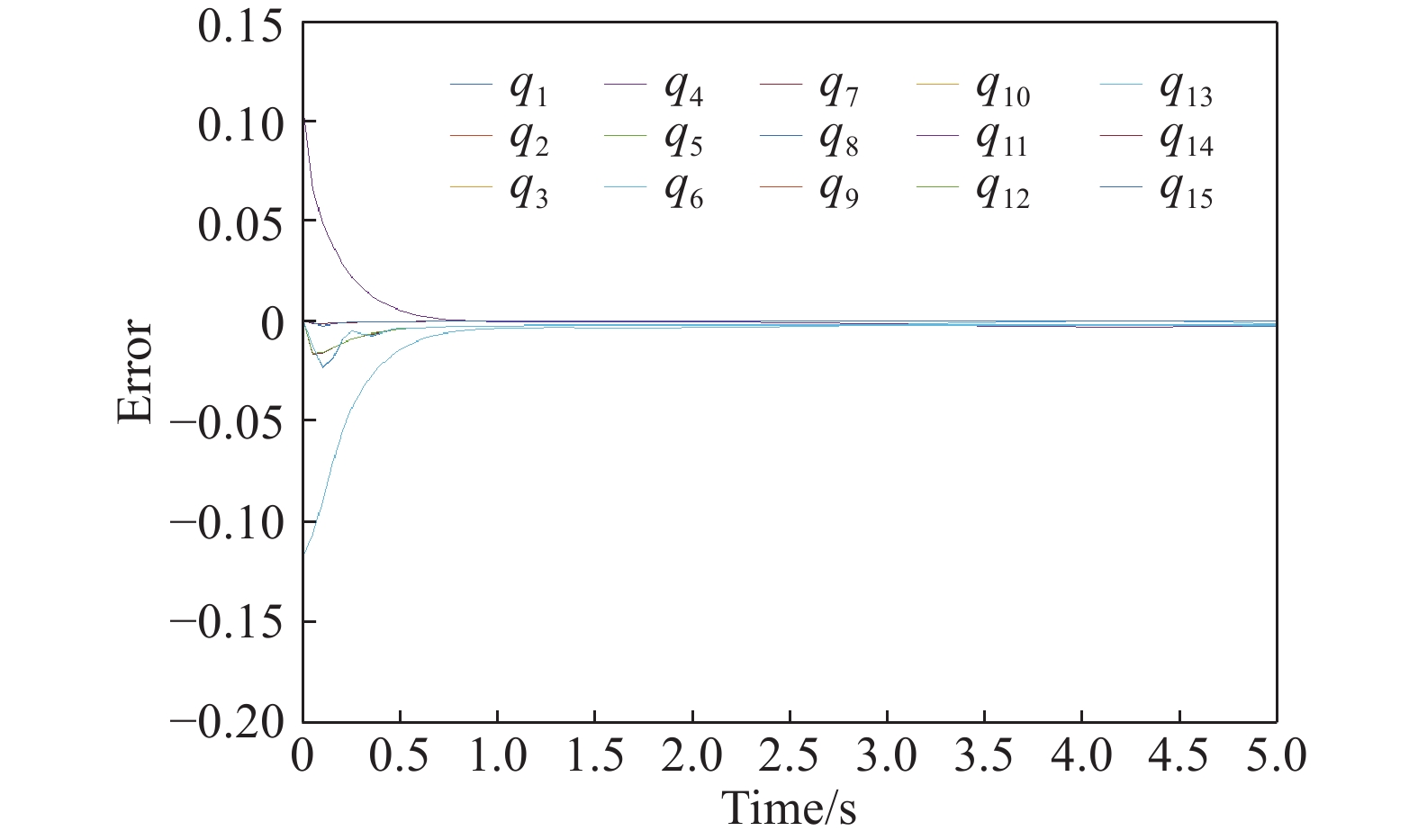
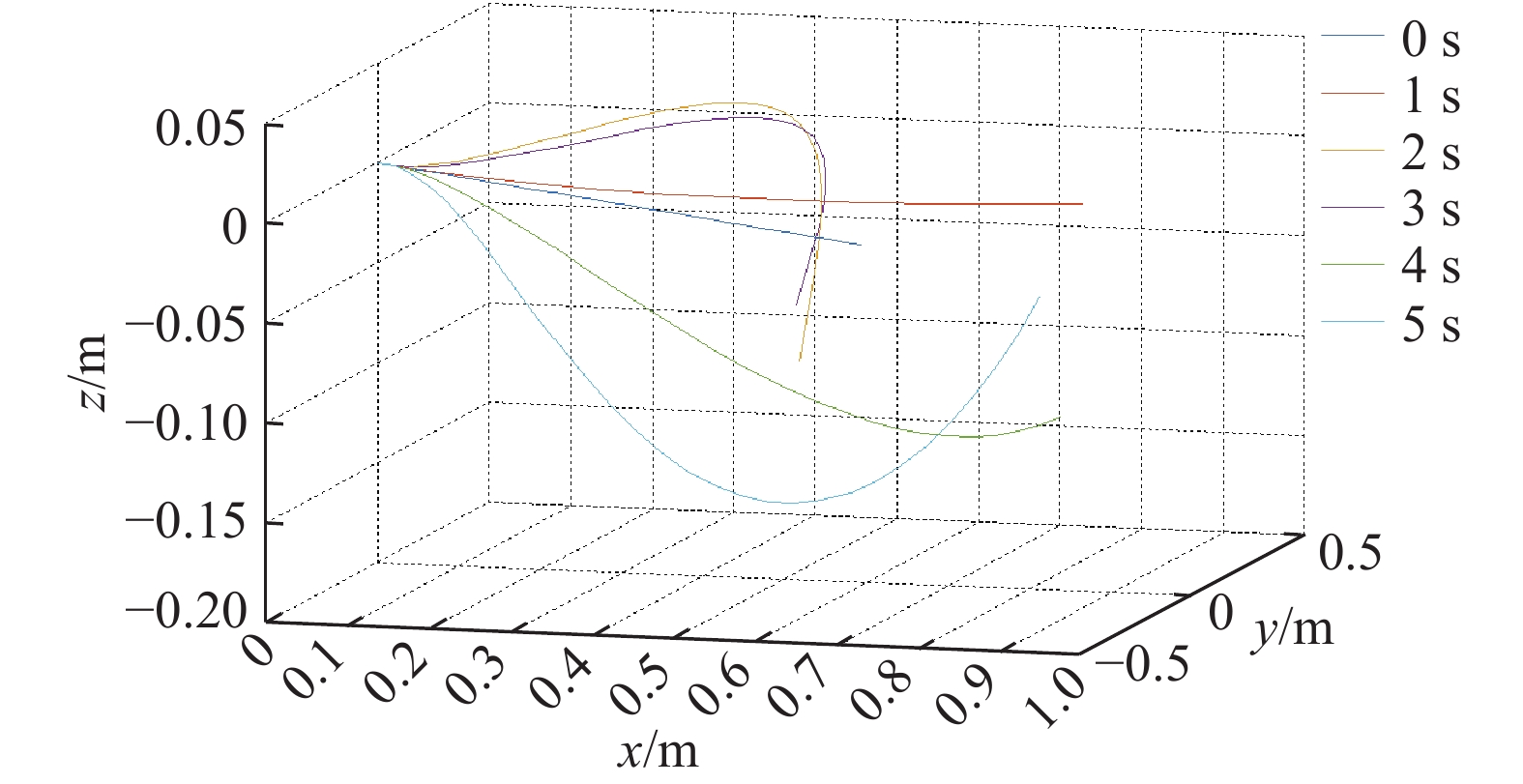
摘要: 軟體機械臂因其出色的環境適應能力以及安全的人機交互使其在醫療、航天航空等領域有著廣闊的應用前景。但由于軟體機械臂是一類連續體裝置,不能采用傳統的剛體機械臂的建模和控制方法,需要一種新的建模方法。針對一類線驅動軟體機械臂,本文提出一種基于應變參數化方法的軟體機械臂建模方法,能夠描述軟體機械臂在三維空間下在不同布線方式下的運動。首先把整個軟體機械臂當作一個Cosserat梁,利用成熟的Cosserat梁理論進行建模,其核心思想是利用Ritz方法對軟體機械臂應變場進行離散化,得到一組常微分方程組,其次利用反向傳播(Back propagation,BP)神經網絡完成形狀空間與驅動器空間的驅動力轉換。針對軟體機械臂模型中存在的未知動態,利用徑向基函數(Radial basis function,RBF)神經網絡進行逼近和補償。然后基于Lyapunov穩定理論證明了引入自適應神經網絡控制器后閉環系統的穩定性。最后,針對模型與自適應神經網絡控制器進行了一系列的仿真實驗,驗證了模型和控制算法的有效性。因此,可以實現對一類軟體機械臂的建模控制。
-
關鍵詞:
- 軟體機械臂 /
- Ritz方法 /
- 神經網絡控制 /
- Cosserat梁理論 /
- Lyapunov穩定理論
Abstract: With the vigorous development of material synthesis, mechanical manufacturing, and computer technology, as well as the in-depth study of control theory and bionics, robotics has undergone tremendous changes in recent decades. From rigid robots to discrete redundancy robots, from continuum robots to soft robots, the application of robots has long been beyond traditional industrial fields such as assembly, welding, and painting. It has expanded to medicine, education, agriculture, the military, etc., covering almost every aspect of people's lives. Soft manipulators have broad application prospects in medicine, aerospace engineering, and other fields due to their excellent environmental adaptability and safe human–machine interaction. However, soft robots comprise flexible materials and often have no internal support structure, so their ends have a very limited carrying capacity. To compensate for this inadequacy, soft robots usually use the bending of the entire body to grasp objects or operate underwater to partially counteract gravity. In addition, the deformation state of a soft robot is difficult to estimate when it is affected by external force or in contact with the environment, which also causes many difficulties in the modeling and control of soft robots. In the case of inaccurate modeling and poor controllability, the accessibility and accuracy of its end are bound to be greatly compromised. For a class of line-driven soft manipulators, a modeling method based on strain parameterization is proposed that can describe the motion of soft manipulators in three-dimensional space under different wiring methods. First, the entire soft manipulator is treated as a Cosserat beam and modeled by the mature Cosserat beam theory, wherein the strain field of the soft manipulator is discretized using the Ritz method to obtain a set of ordinary differential equations, and then a back propagation (BP) neural network is used to complete the drive force conversion between the shape and driver spaces. A radial basis function (RBF) neural network is used to approximate and compensate for the unknown dynamics present in the soft manipulator model. The stability of the closed-loop system after introducing the adaptive neural network controller is then demonstrated on the basis of Lyapunov's stability theory. Finally, a series of simulation experiments are performed for the model and the adaptive neural network controller to verify the effectiveness of the model and the control algorithm. Therefore, the modeling control of a type of soft manipulator is realized. -
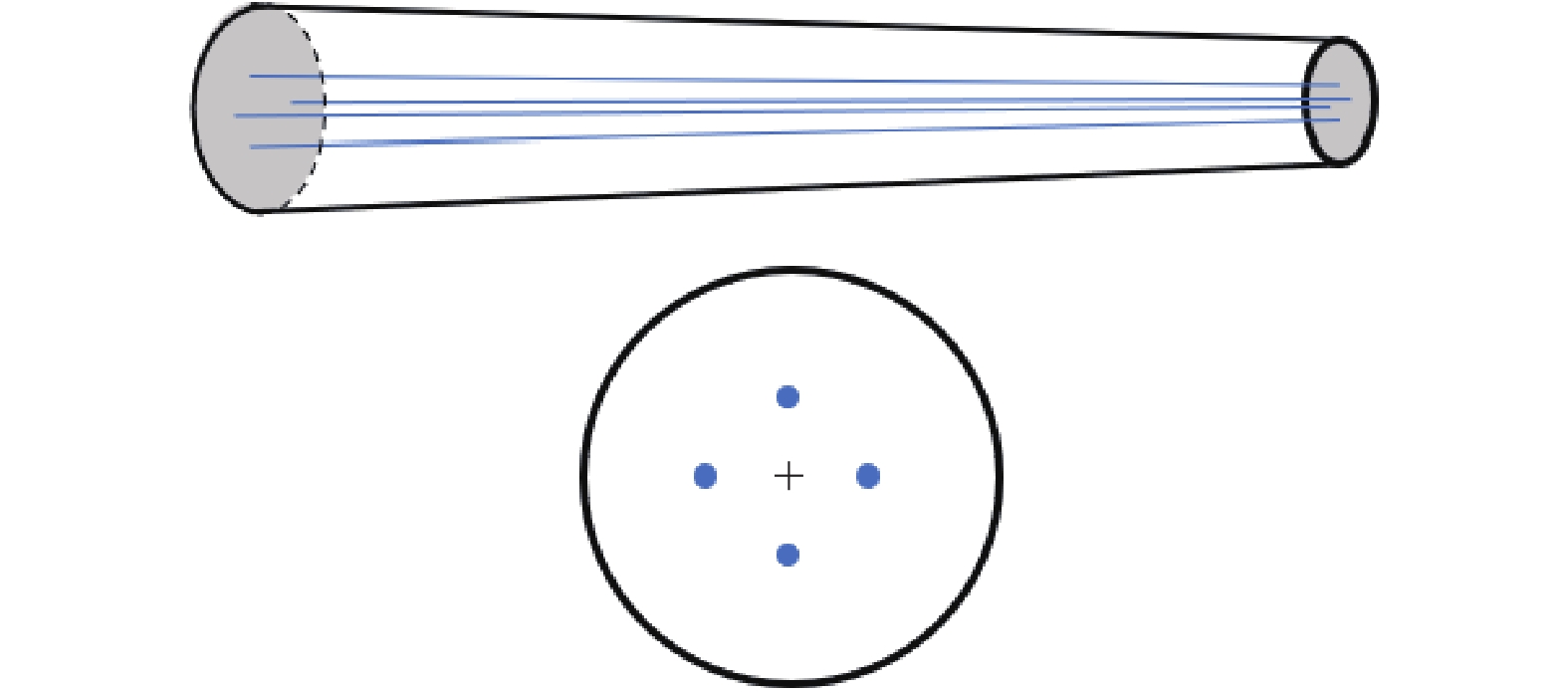
表 1 驅動線布線方式與
${\boldsymbol{P}}(X)$ 關系表Table 1. Relationship between the driving wire and
${\boldsymbol{P}}(X)$ Wiring method $ {P_Y} $ $ {P_Z} $ Parallel wiring $\sqrt 2 {R_{\rm{b}}}/4$ $\sqrt 2 {R_{\rm{b}}}/4$ Bundle wiring ${R_{{\rm{b}}} }(1 - X)/2$ 0 Cross wiring ${R_{{\rm{b}}} }(1 - X)/2$ 0 表 2 軟體機械臂的物理參數
Table 2. Physical parameters of the soft manipulator
Name Numerical size Radius/ m 0.005 Degrees of freedom 30 Number of drive lines 4 Material density of the body of the soft
manipulator/( kg?m?3)2000 Elastic modulus/( N?m?2) 106 Shear modulus/( N?m?2) 5 × 105 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Chinkjian G S, Burdick J W. The kinematics of hyper-redundant manipulator locomotion. IEEE Trans Manipul Autom, 1995, 11(6): 781 doi: 10.1109/70.478426 [2] Xie Z X, Domel A G, An N, et al. Octopus arm-inspired tapered soft actuators with suckers for improved grasping. Soft Robot, 2020, 7(5): 639 doi: 10.1089/soro.2019.0082 [3] Hawkes E, Blumenschein L H, Greer J D, et al. A soft robot that navigates its environment through growth. Sci Robot, 2017, 2(8): eaan3028 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aan3028 [4] Yang Y, Liu Z, Han J T, et al. Research development on actuators, modeling and control of soft manipulator. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(12): 2124楊妍, 劉志杰, 韓江濤, 等. 軟體機械臂的驅動方式及建模和控制研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(12):2124 [5] Connolly F, Walsh C J, Bertoldi K. Automatic design of fiber-reinforced soft actuators for trajectory matching. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(1): 51 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615140114 [6] Yang J K. Simulation and Optimization of Hook-Lift Self-Loading Truck's Hook-Lift Mechanism [Dissertation]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2015楊健侃. 拉臂式自裝卸車拉臂機構的仿真分析與優化[學位論文]. 重慶: 重慶交通大學, 2015 [7] Boyer F, Primault D. Finite element of slender beams in finite transformations: A geometrically exact approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng, 2004, 59(5): 669 doi: 10.1002/nme.879 [8] Largilliere F, Verona V, Coevoet E, et al. Real-time control of soft-robots using asynchronous finite element modeling // 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Seattle, 2015: 2550 [9] Boyer F, Porez M, Khalil W. Macro-continuous computed torque algorithm for a three-dimensional eel-like robot. IEEE Trans Robotics, 2006, 22(4): 763 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.875492 [10] Rucker D C, Webster III R J. Statics and dynamics of continuum robots with general tendon routing and external loading. IEEE Trans Robotics, 2011, 27(6): 1033 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2160469 [11] Boyer F, Porez M. Multibody system dynamics for bio-inspired locomotion: From geometric structures to computational aspects. Bioinspir Biomim, 2015, 10(2): 025007 doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/10/2/025007 [12] Webster R J. Design and kinematic modeling of constant curvature continuum robots: A review. Int J Robotics Res, 2010, 29(13): 1661 doi: 10.1177/0278364910368147 [13] Godage I S, Medrano-Cerda G A, Branson D T, et al. Dynamics for variable length multisection continuum arms. Int J Robotics Res, 2016, 35(6): 695 doi: 10.1177/0278364915596450 [14] Falkenhahn V, Mahl T, Hildebrandt A, et al. Dynamic modeling of bellows-actuated continuum robots using the Euler-Lagrange formalism. IEEE Trans Robotics, 2015, 31(6): 1483 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2496826 [15] Bertails F. Linear time super-helices. Comput Graph Forum, 2009, 28(2): 417 doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01381.x [16] Renda F, Boyer F, Dias J, et al. Discrete cosserat approach for multisection soft manipulator dynamics. IEEE Trans Robotics, 2018, 34(6): 1518 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2868815 [17] Zhu J W, Wang H S, Chen W D, et al. The three-dimensional shape control for a soft manipulator // 13th IEEE International Conference on Control & Automation (ICCA). Ohrid, 2017: 385 [18] Wang H S, Chen W D, Yu X J, et al. Visual servo control of cable-driven soft robotic manipulator // 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, 2013: 57 [19] Yu Y, Qi P, Althoefer K, et al. Lagrangian dynamics and nonlinear control of a continuum manipulator // 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Zhuhai, 2015: 1912 [20] Fu Q, Zhang S Y, Wang J B, et al. Indoor fixed-height control for bio-inspired flapping-wing aerial vehicles based on offboard monocular vision. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(2): 249付強, 張樹禹, 王久斌, 等. 基于外部單目視覺的仿生撲翼飛行器室內定高控制. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(2):249 [21] Kong L H, He W, Dong Y T, et al. Asymmetric bounded neural control for an uncertain robot by state feedback and output feedback. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2019, 51(3): 1 [22] Xu Z, Zhang G, Wang H M, et al. Error compensation of collaborative robot dynamics based on deep recurrent neural network. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(7): 995徐征, 張弓, 汪火明, 等. 基于深度循環神經網絡的協作機器人動力學誤差補償. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(7):995 [23] He W, Jing Z, He X Y, et al. Robust adaptive vibration control for a string with time-varying output constraint. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control, 2018, 28(17): 5213 doi: 10.1002/rnc.4300 [24] Zhang T, Ge S S, Hang C C. Adaptive neural network control for strict-feedback nonlinear systems using backstepping design. Automatica, 2000, 36(12): 1835 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(00)00116-3 [25] Gander M, Wanner G. From Euler, Ritz, and Galerkin to modern computing. SIAM Rev, 2012, 54(4): 627 doi: 10.1137/100804036 [26] Boyer F, Renda F. Poincaré's equations for cosserat media: Application to shells. J Nonlinear Sci, 2017, 27(1): 1 doi: 10.1007/s00332-016-9324-7 [27] Walker M W,. On-line computational scheme for mechanical manipulators. J Dyn Syst Meas Control, 1980, 102(2): 69 doi: 10.1115/1.3149599 [28] Renda F, Cacucciolo V, Dias J, et al. Discrete Cosserat approach for soft robot dynamics: A new piece-wise constant strain model with torsion and shears // 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, 2016: 5495 -




 下載:
下載: