-
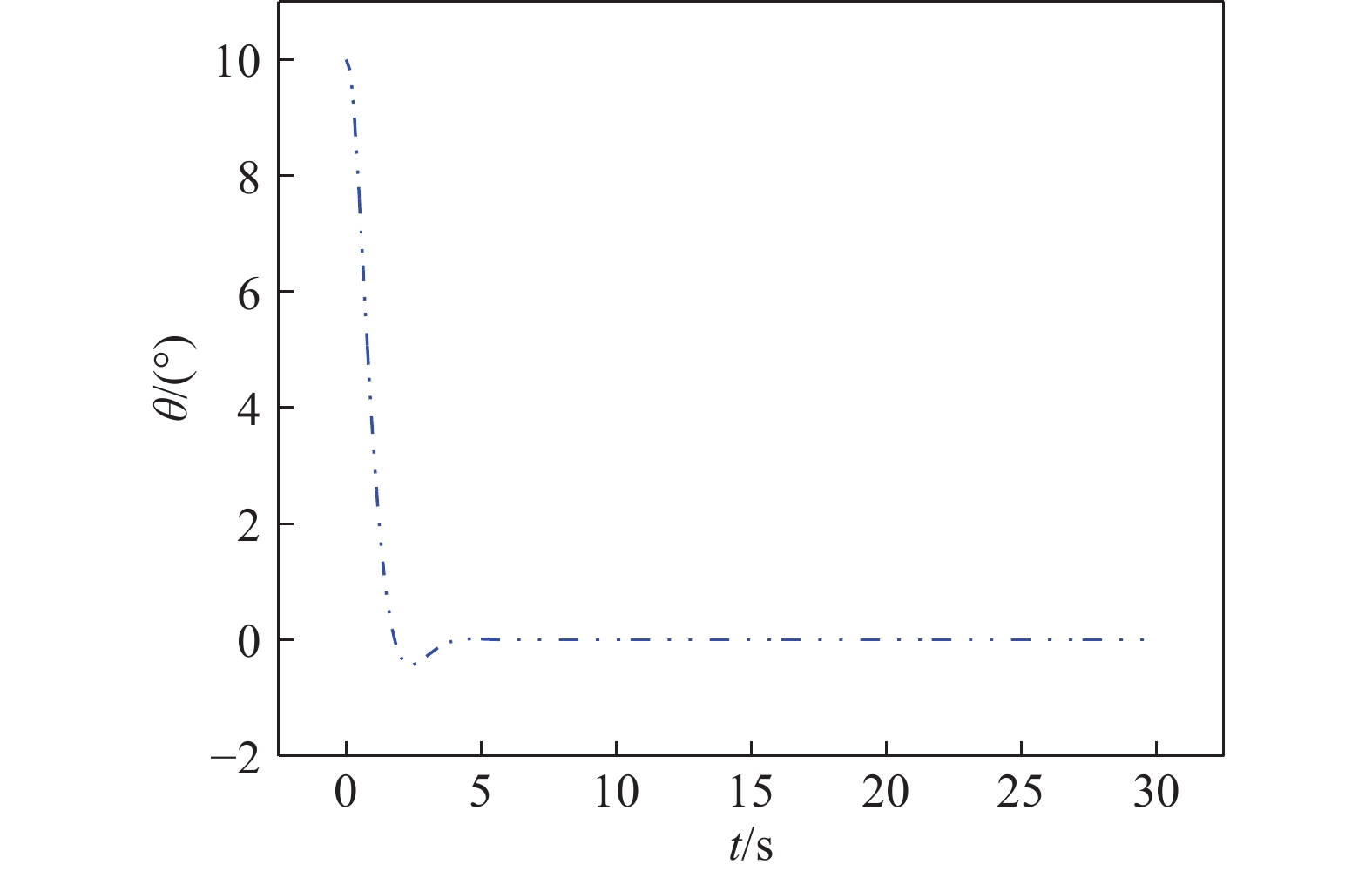
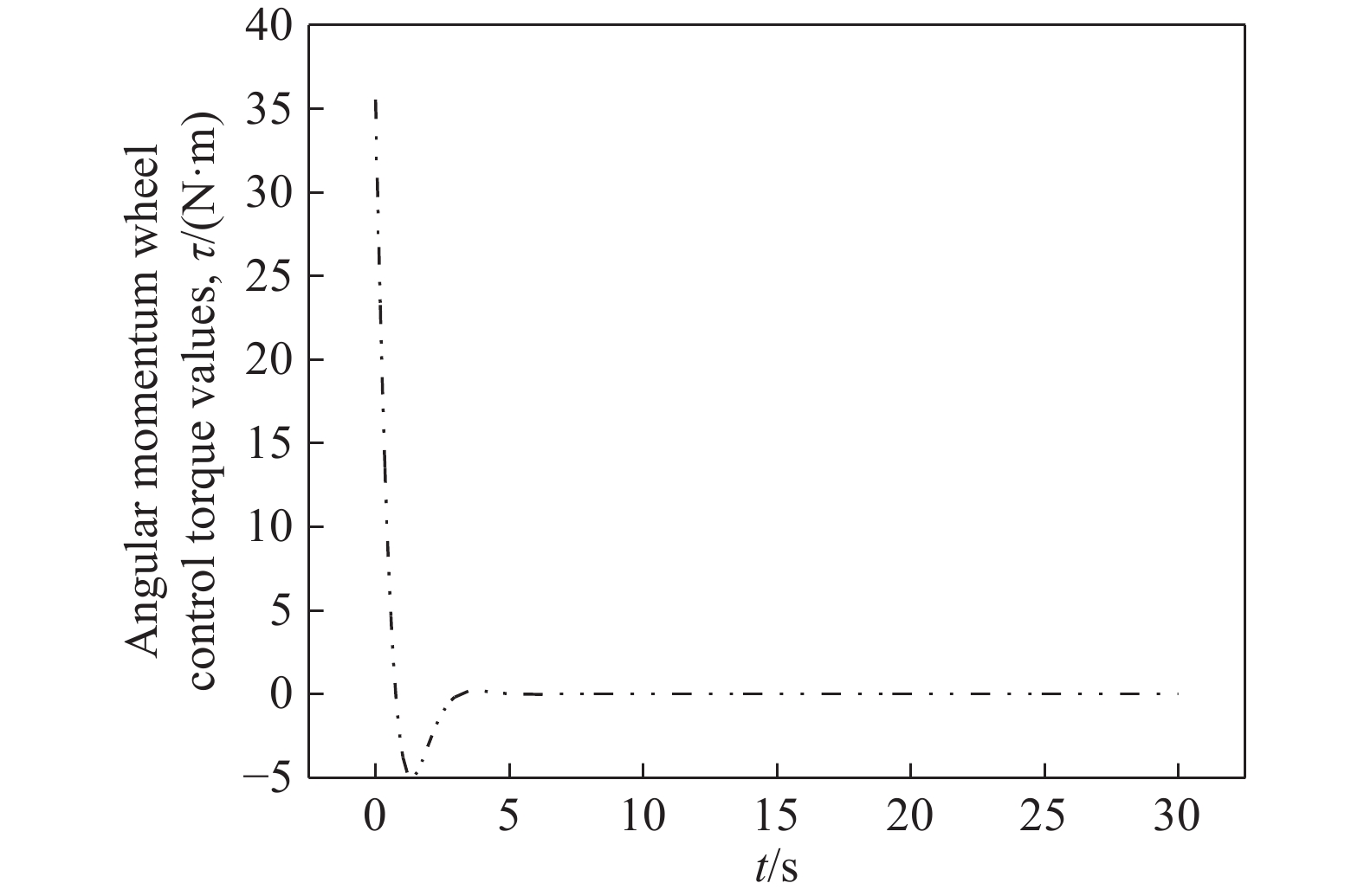
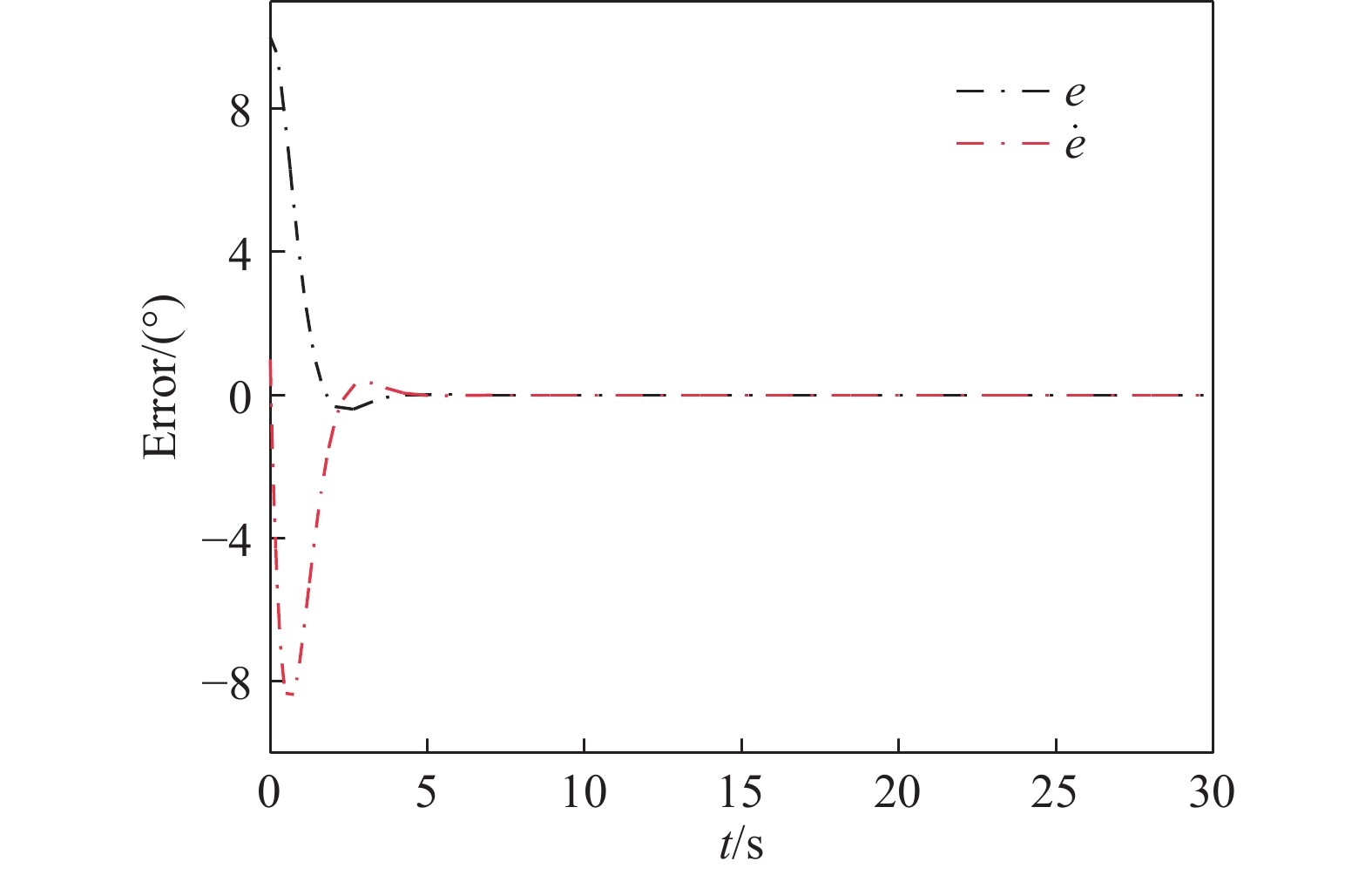
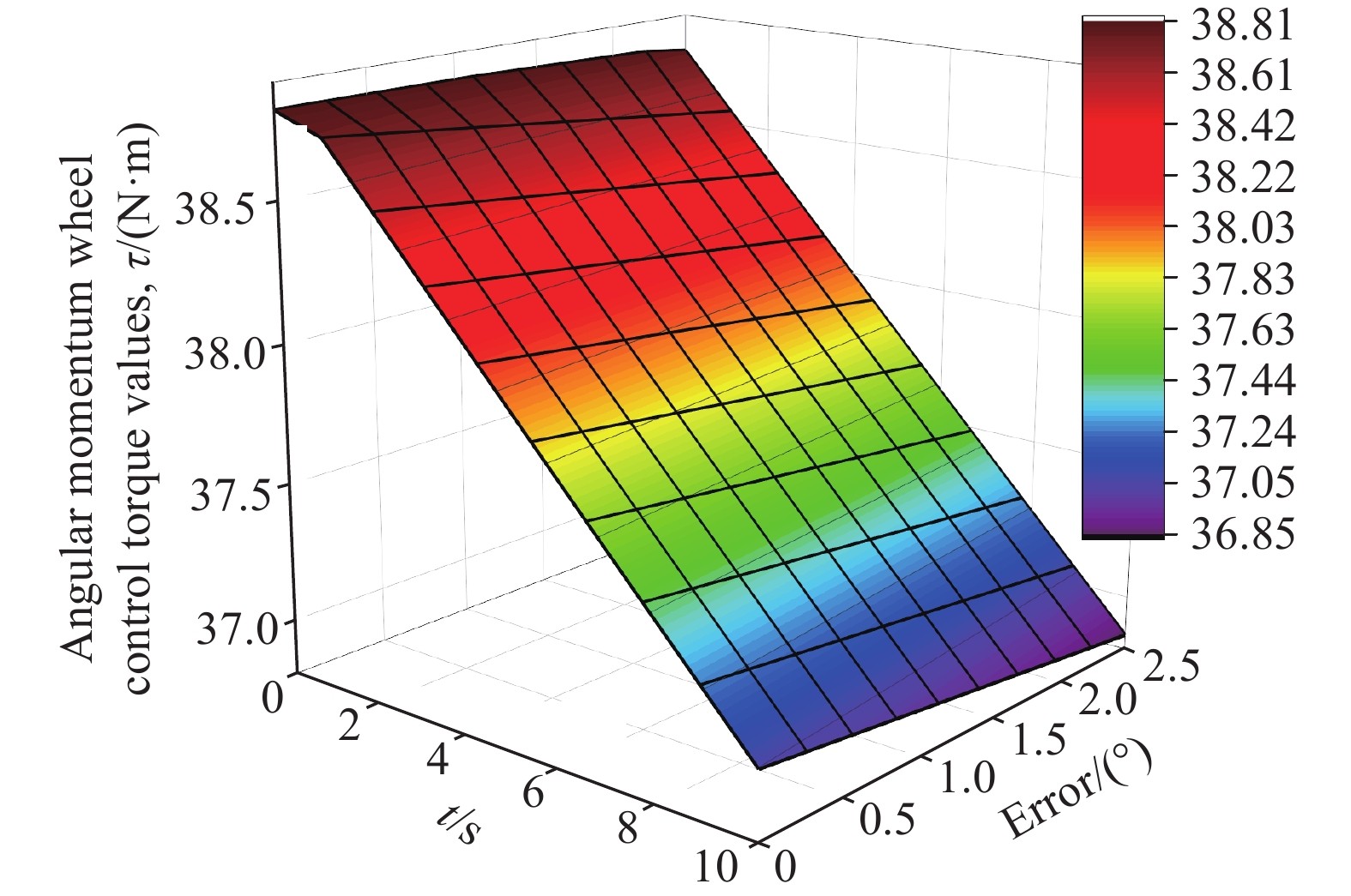
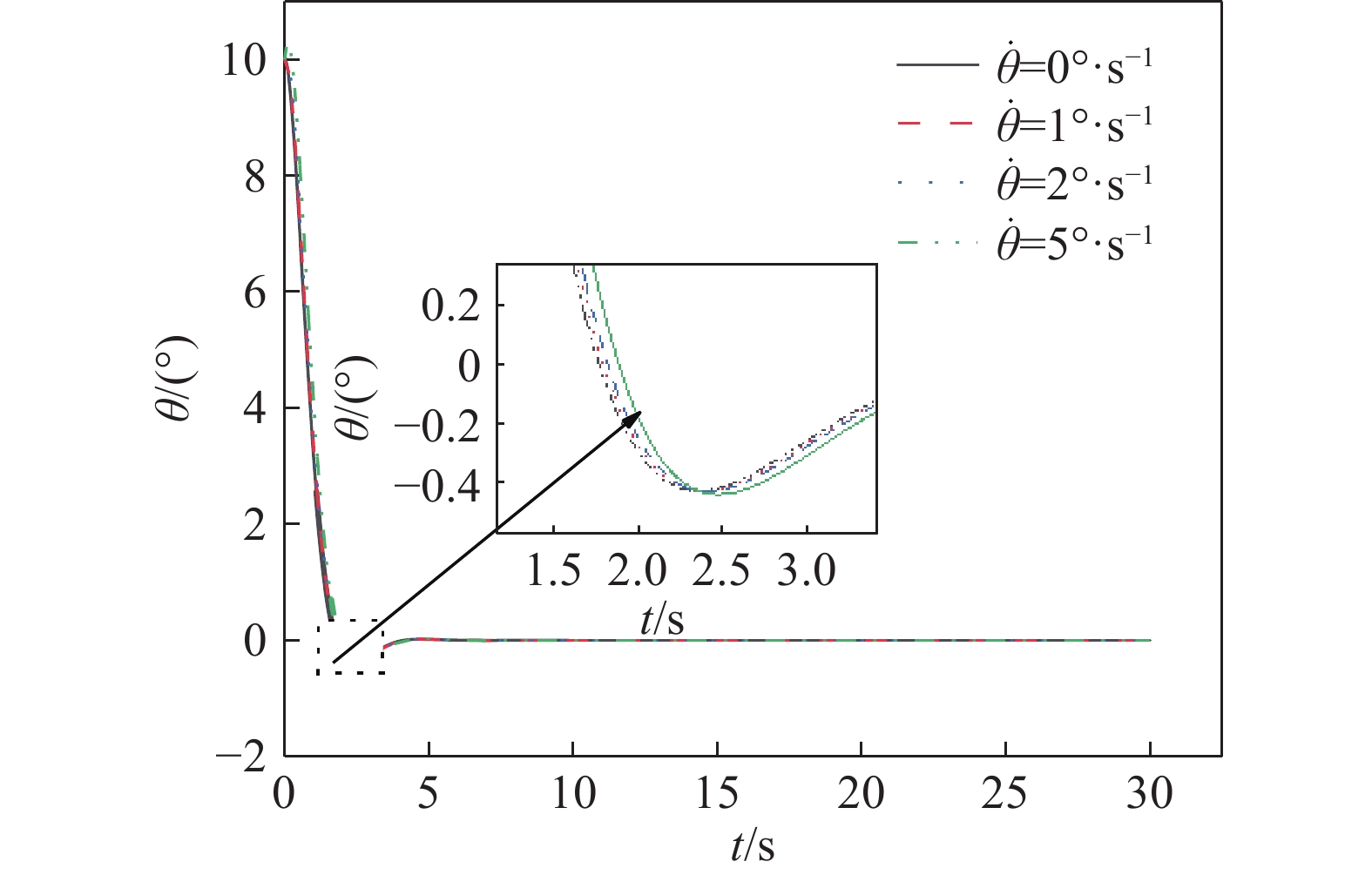
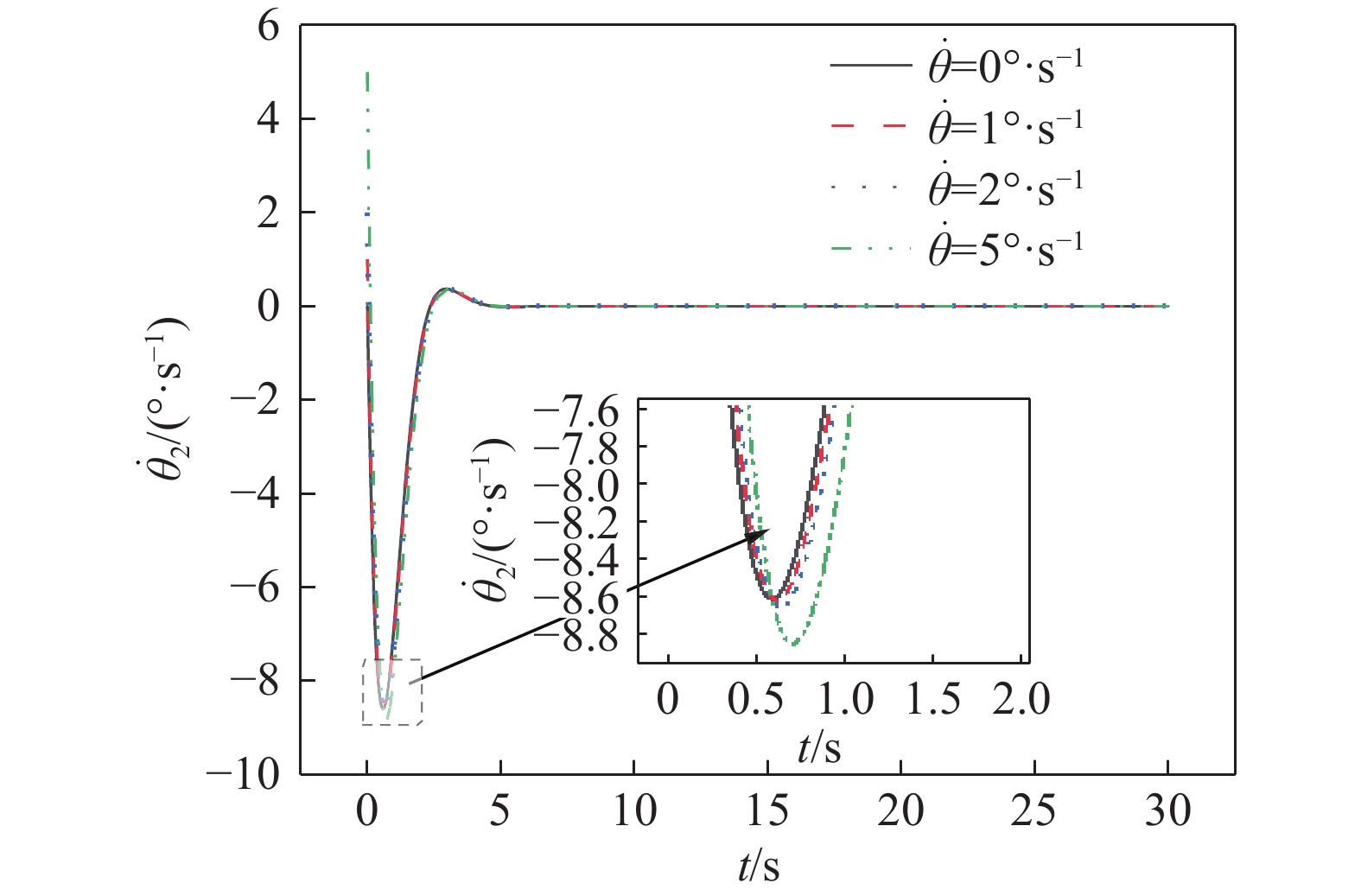
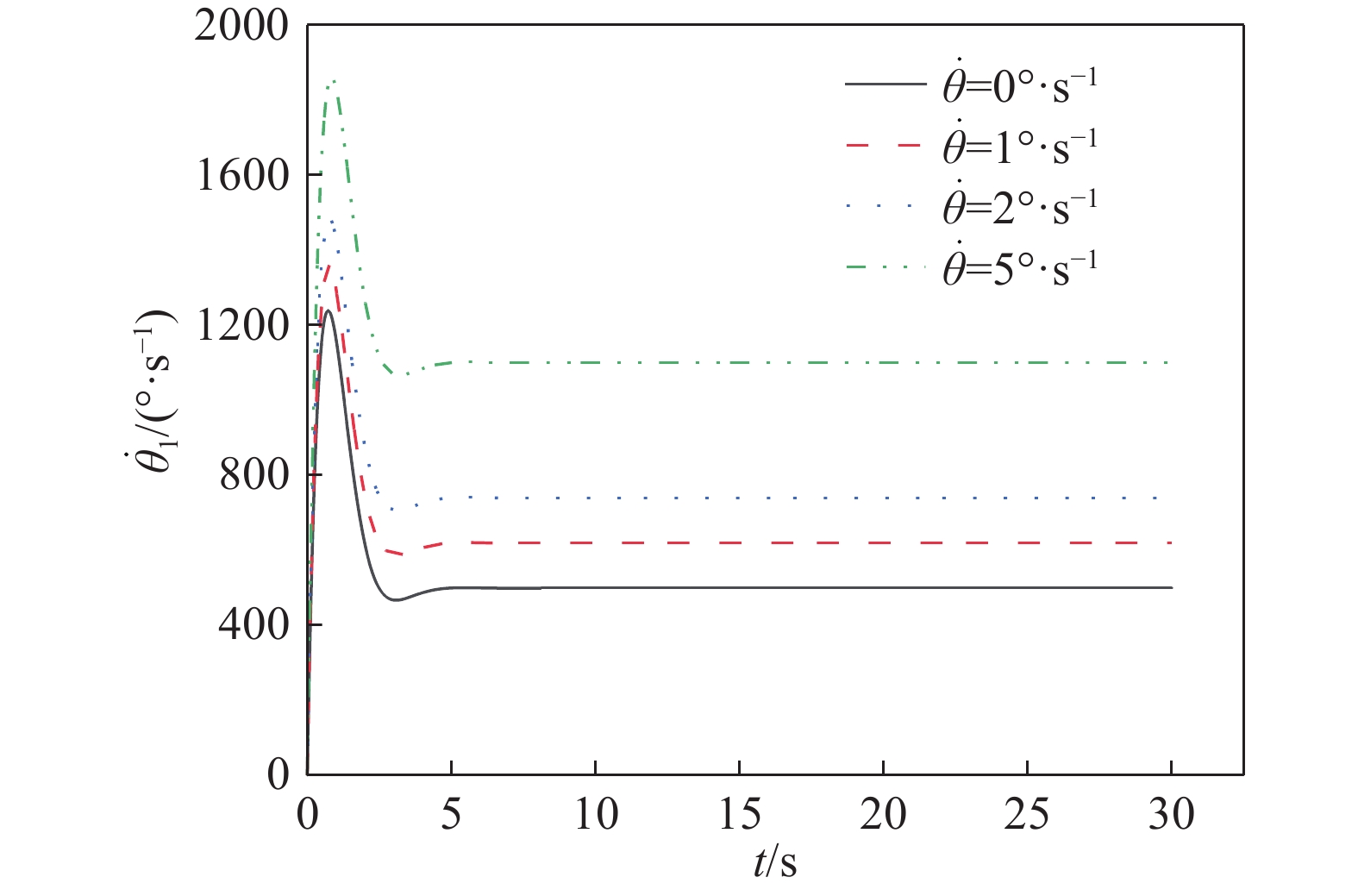
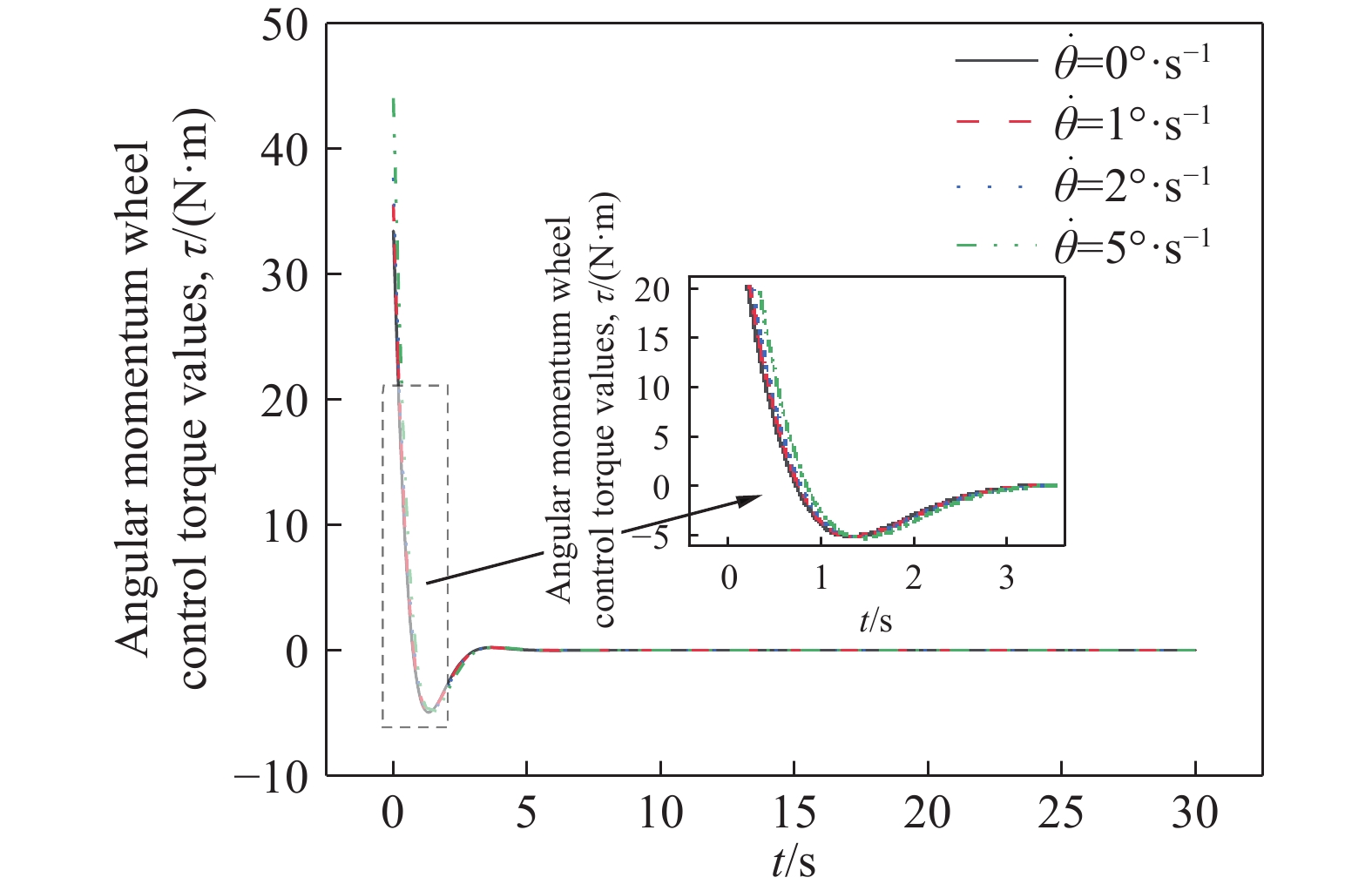
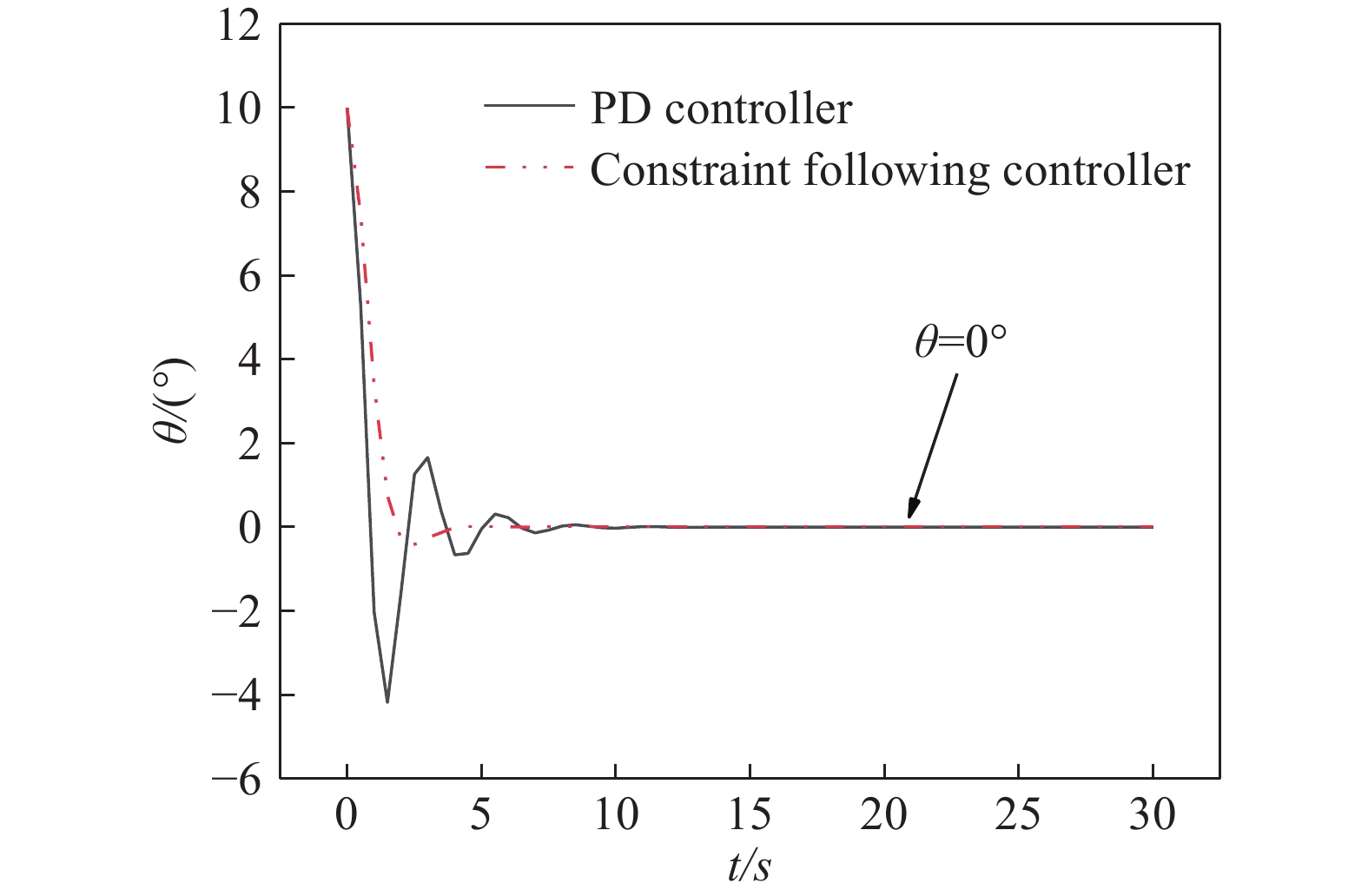
摘要: 針對自行車機器人側向自平衡問題,以一類裝有角動量輪的自行車機器人為研究對象,提出一種新的平衡控制方法。該方法根據自行車機器人靜止時刻的側向平衡條件,構造機器人平衡控制的運動學約束,并將平衡約束視為控制目標。基于Udwadia?Kalaba(U?K)理論,建立滿足機器人側向平衡的扭矩解析模型,設計基于模型的平衡約束跟隨控制器。研究結果表明,所提控制方法能夠實現自行車機器人的側向平衡,克服機器人側向橫滾角θ初始偏差的干擾,通過對平衡扭矩模型的計算,對自行車機器人進行主動平衡控制。相較于傳統PD反饋控制方法,該種基于模型設計的控制方法,具有系統響應速度快、超調量小和控制扭矩易于優化等特點。借助MATLAB軟件,對所提控制方法進行了仿真驗證,實現了初始橫滾角速度分別為0、1、2、5°·s?1條件下的自行車機器人側向自平衡控制,仿真結果驗證了控制系統的穩定性和有效性,為無人駕駛自行車機器人的平衡控制領域提供了一個新的思路。
-
關鍵詞:
- 自行車機器人 /
- 角動量輪 /
- Udwadia-Kalaba理論 /
- 自平衡控制 /
- PD控制
Abstract: In the 21st century, with the rapid development of computing and sensing technology, autonomous driving has become a hot and important research topic. The vast market for bicycles has created numerous opportunities for driverless bikes. An unmanned bicycle robot has the characteristics of flexible movement and narrow body, thus it can be widely used in disaster area-rescue operations, entertainment performances, and transportation scenes. Therefore, several scholars have studied and focused on this type of bicycle. For the lateral self-balancing problem of bicycle robots, a new balance control method has been studied for a class of bicycle robots that are equipped with an angular momentum wheel. The kinematics constraint of the robot balance control is constructed based on the lateral balance condition of the bicycle robot, and the balance constraint is regarded as the control target. Based on the Udwadia–Kalaba (U–K) theory, a torque analytical model satisfying the lateral balance of the robot was established, and a balance constraint following the controller based on the model was designed. The findings show that the proposed control method can achieve the lateral balance of the bicycle robot and overcome the disturbance caused by the initial deviation of the lateral roll angle θ. Through the calculation of the balance torque model, the bicycle robot is actively balanced. Compared with the traditional PD feedback control method, the control method based on the model design has the characteristics and advantages of fast system response, low overshoot, and ease of optimization of the control torque. The proposed control method is simulated and confirmed using MATLAB, and lateral self-balancing control of the bicycle robot is achieved at the initial roll angular velocities of 0, 1, 2, and 5°·s?1. The simulation results confirm the stability and effectiveness of the control system. This study proposes a novel idea for the balance control of unmanned bicycle robots.-
Key words:
- bicycle robot /
- angular momentum wheel /
- Udwadia–Kalaba theory /
- self-balancing control /
- PD control
-
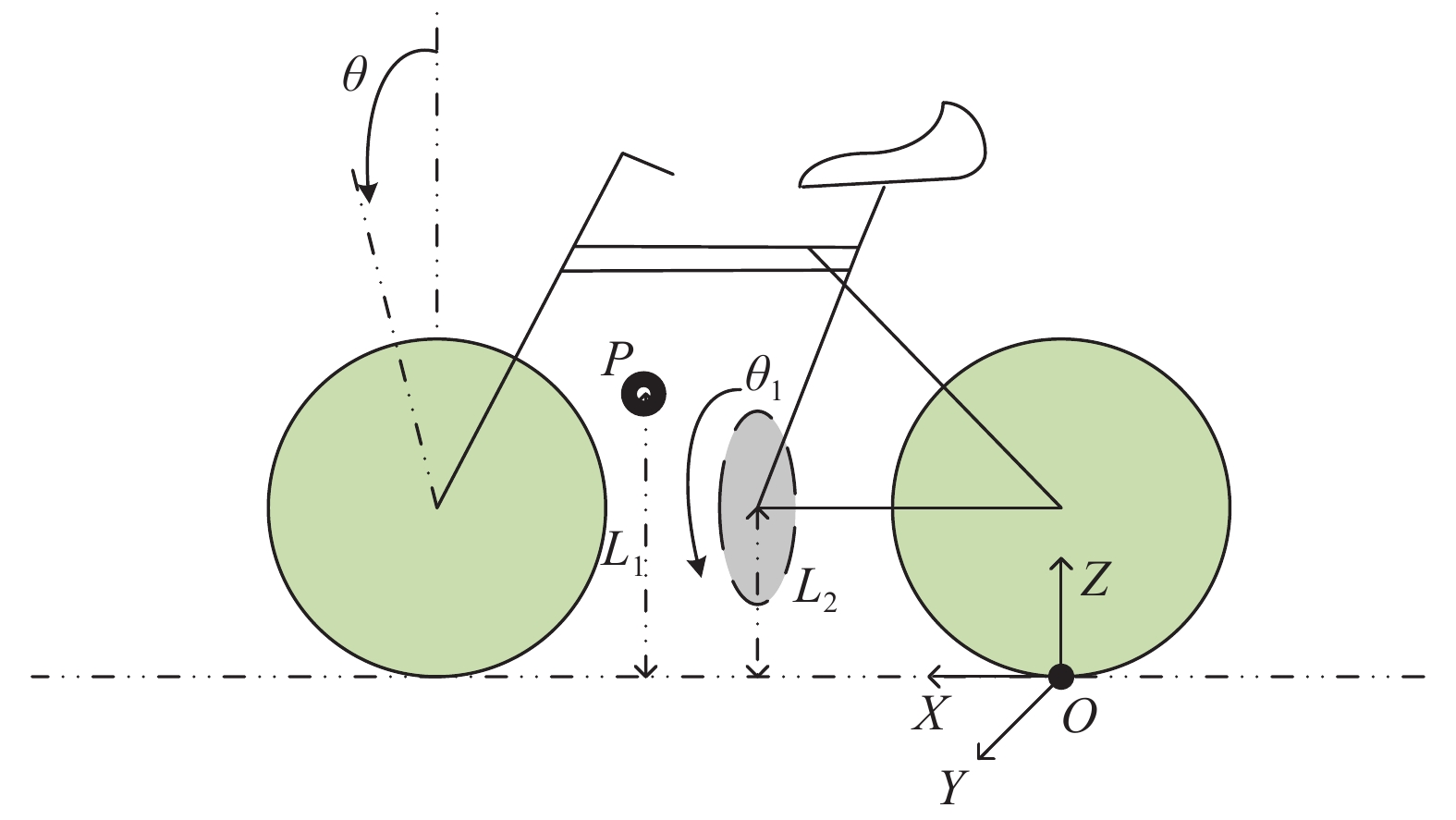
表 1 自行車機器人參數表
Table 1. Bicycle robot parameters
Parameter Value Parameter Value m1/kg 11 I2/(kg·m2) 0.007882 m2/kg 3.5 L1/m 0.2316 I1/(kg·m2) 0.12418 L2/m 0.15 g/(m·s-2) 9.8 K1 3 K2 4 HP 4 L0/m 0 HD 3 h 0 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Wang H. Research on Balance Control Method of the Bicycle Robot [Dissertation]. Xi’an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2019王涵. 自行車機器人平衡控制方法研究[學位論文]. 陜西: 陜西科技大學, 2019 [2] Bai G X, Meng Y, Liu L, et al. Current status of path tracking control of unmanned driving vehicles. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(4): 475白國星, 孟宇, 劉立, 等. 無人駕駛車輛路徑跟蹤控制研究現狀. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(4):475 [3] Hou S. The Study and Control of Unmanned Bicycle Based on Variable Universe Fuzzy Controller [Dissertation]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020侯帥. 基于變論域模糊控制的無人自行車控制研究[學位論文]. 大連: 大連理工大學, 2020 [4] Tanaka Y, Murakami T. Self sustaining bicycle robot with steering controller // The 8th IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control. Kawasaki, 2004: 193 [5] Lee S, Ham W. Self stabilizing strategy in tracking control of unmanned electric bicycle with mass balance // IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Lausanne, 2002: 2200 [6] Schwab A L, Meijaard J P. A review on bicycle dynamics and rider control. Veh Syst Dyn, 2013, 51(7): 1059 doi: 10.1080/00423114.2013.793365 [7] Vu N K, Nguyen H Q. Balancing control of two-wheel bicycle problems. Math Probl Eng, 2020, 2020: 6724382 [8] Lam P Y. Gyroscopic stabilization of a kid-size bicycle // 2011 IEEE 5th International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems. Qingdao, 2011: 247 [9] Lee S I, Lee I W, Kim M S, et al. Balancing and driving control of a bicycle robot. J Inst Control Robotics Syst, 2012, 18(6): 532 doi: 10.5302/J.ICROS.2012.18.6.532 [10] Chen C K, Chu T D, Zhang X D. Modeling and control of an active stabilizing assistant system for a bicycle. Sensors, 2019, 19(2): 248 doi: 10.3390/s19020248 [11] Spry S C, Girard A R. Gyroscopic stabilisation of unstable vehicles: Configurations, dynamics, and control. Veh Syst Dyn, 2008, 46(Suppl 1): 247 [12] Cui L L, Wang S, Lai J, et al. Nonlinear balance control of an unmanned bicycle: Design and experiments // 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas, 2021: 7279 [13] Zhang Y Z, Wang P C, Yi J G, et al. Stationary balance control of a bikebot // 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, 2014: 6706 [14] Beznos A V, Formal’sky A M, Gurfinkel E V, et al. Control of autonomous motion of two-wheel bicycle with gyroscopic stabilization // Proceedings of the I998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automatlon. Leuven, 1998: 2670 [15] Chen C K, Dao T K. Speed-adaptive roll-angle-tracking control of an unmanned bicycle using fuzzy logic. Veh Syst Dyn, 2010, 48(1): 133 doi: 10.1080/00423110903085872 [16] Zhang X R, Chen Y, Ping Z Q. Mechanical manipulator tracking control based on Udwadia and Kalaba equation. J Chang'an Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2014, 34(1): 115 doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2014.01.019張新榮, Chen Yehwa, 平昭琪. 基于Udwadia和Kalaba方程的機械臂軌跡跟蹤控制. 長安大學學報(自然科學版), 2014, 34(1):115 doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1671-8879.2014.01.019 [17] Udwadia F E, Kalaba R E. Analytical Dynamics: a New Approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996 [18] Chen Y H. Constraint-following servo control design for mechanical systems. J Vib Control, 2009, 15(3): 369 doi: 10.1177/1077546307086895 [19] Zhao H, Zhao F M, Huang K, et al. Position control of mechanical manipulator based on Udwadia-Kalaba theory. J Hefei Univ Technol Nat Sci, 2018, 41(4): 433趙韓, 趙福民, 黃康, 等. 基于Udwadia-Kalaba理論的機械臂位置控制. 合肥工業大學學報(自然科學版), 2018, 41(4):433 [20] Zhao R Y, Wu L L, Chen Y H. Robust control for nonlinear delta parallel robot with uncertainty: An online estimation approach. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 97604 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2997093 [21] Chen X L, Sun H, Zhen S C. A novel adaptive robust control approach for underactuated mobile robot // 2018 3rd International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM). Singapore, 2018: 642 [22] Han J, Wang P, Dong F F, et al. Robust servo constrained control of parallel robots based on the udwadia-kalaba method. Appl Math Mech, 2021, 42(3): 264韓江, 汪鵬, 董方方, 等. 基于Udwadia-Kalaba方法的并聯機器人魯棒伺服約束控制. 應用數學和力學, 2021, 42(3):264 [23] Yin H, Chen Y H, Yu D J. Vehicle motion control under equality and inequality constraints: A diffeomorphism approach. Nonlinear Dyn, 2019, 95(1): 175 doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4558-6 [24] Dong F F, Zhao X M. Underactuated Flexible Mechanical Arm System Based on Constraint Force Robust Servo Control: China Patent, 201810739283X. 2018-12-7董方方, 趙曉敏. 一種基于約束力魯棒伺服控制的欠驅動柔性機械臂系統: 中國專利, 201810739283X. 2018-12-7 [25] Bellman R. Introduction to Matrix Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1970 [26] Zhao R Y. Research on Extended Cascading Modeling and the Constraint-Following Control of Multi-Body Systems [Dissertation]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015趙睿英. 多剛體系統擴展層級建模與約束跟隨控制方法研究[學位論文]. 西安: 長安大學, 2015 [27] Zhang T, Qin B B, Zou Y B. Identification methods for robot payload dynamical parameters. Chin J Eng, 2017, 39(12): 1907張鐵, 覃彬彬, 鄒焱飚. 機器人負載的動力學參數辨識. 工程科學學報, 2017, 39(12):1907 [28] Udwadia F E. A new perspective on the tracking control of nonlinear structural and mechanical systems. Proc R Soc Lond A, 2003, 459(2035): 1783 doi: 10.1098/rspa.2002.1062 [29] Yu R R, Chen Y H, Zhao H, et al. Uniform ultimate boundedness for underactuated mechanical systems as mismatched uncertainty disappeared. Nonlinear Dyn, 2019, 95(4): 2765 doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4721-0 [30] Wang S, Cui L L, Lai J, et al. Gain scheduled controller design for balancing an autonomous bicycle // 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas, 2020: 7595 [31] Cui X D, Deng S F, Wang P J. Position domain control technology for six-joint robots. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(2): 244崔旭東, 鄧少豐, 王平江. 面向六關節機器人的位置域控制. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(2):244 -




 下載:
下載: