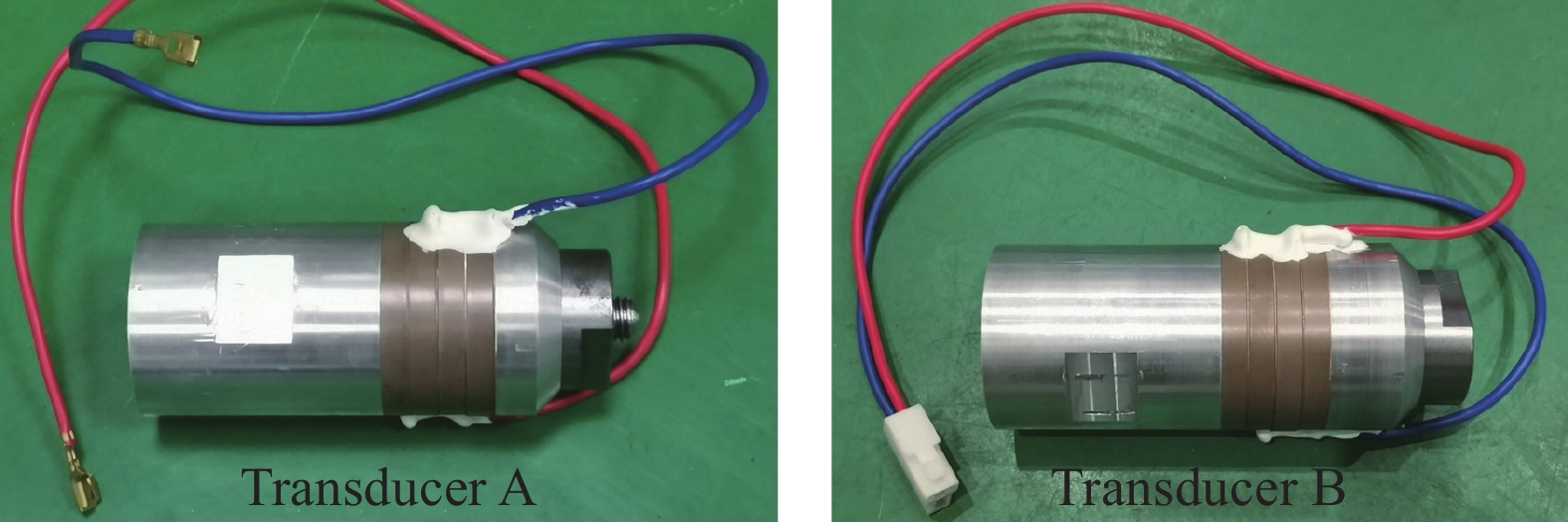
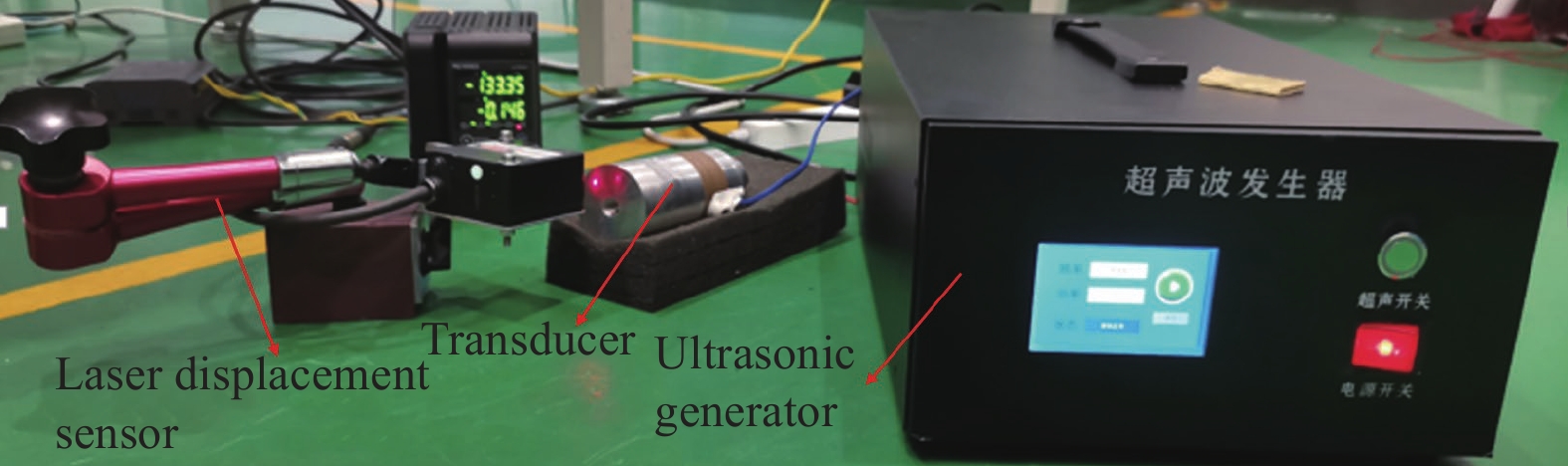
Optimized design for a piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer based on the six-terminal network
-
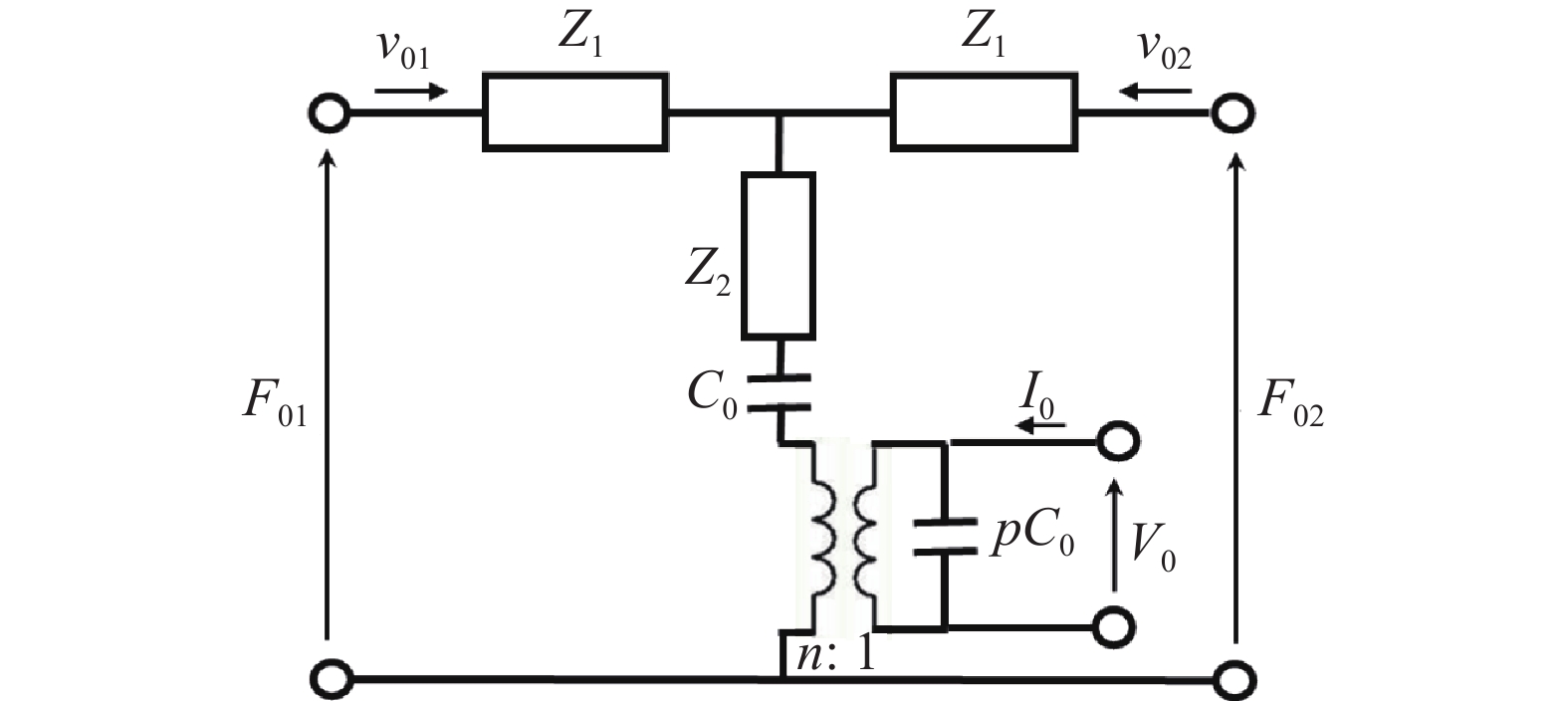
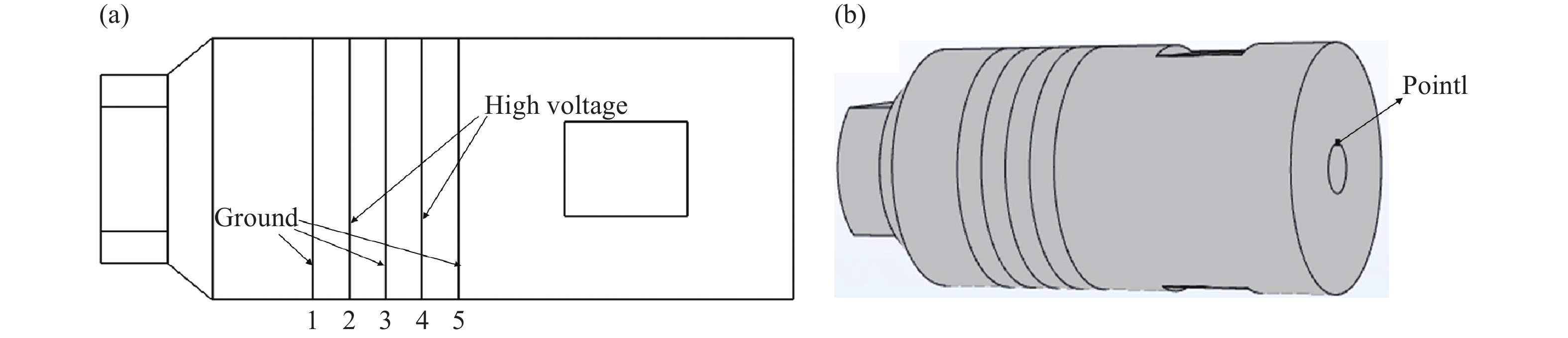
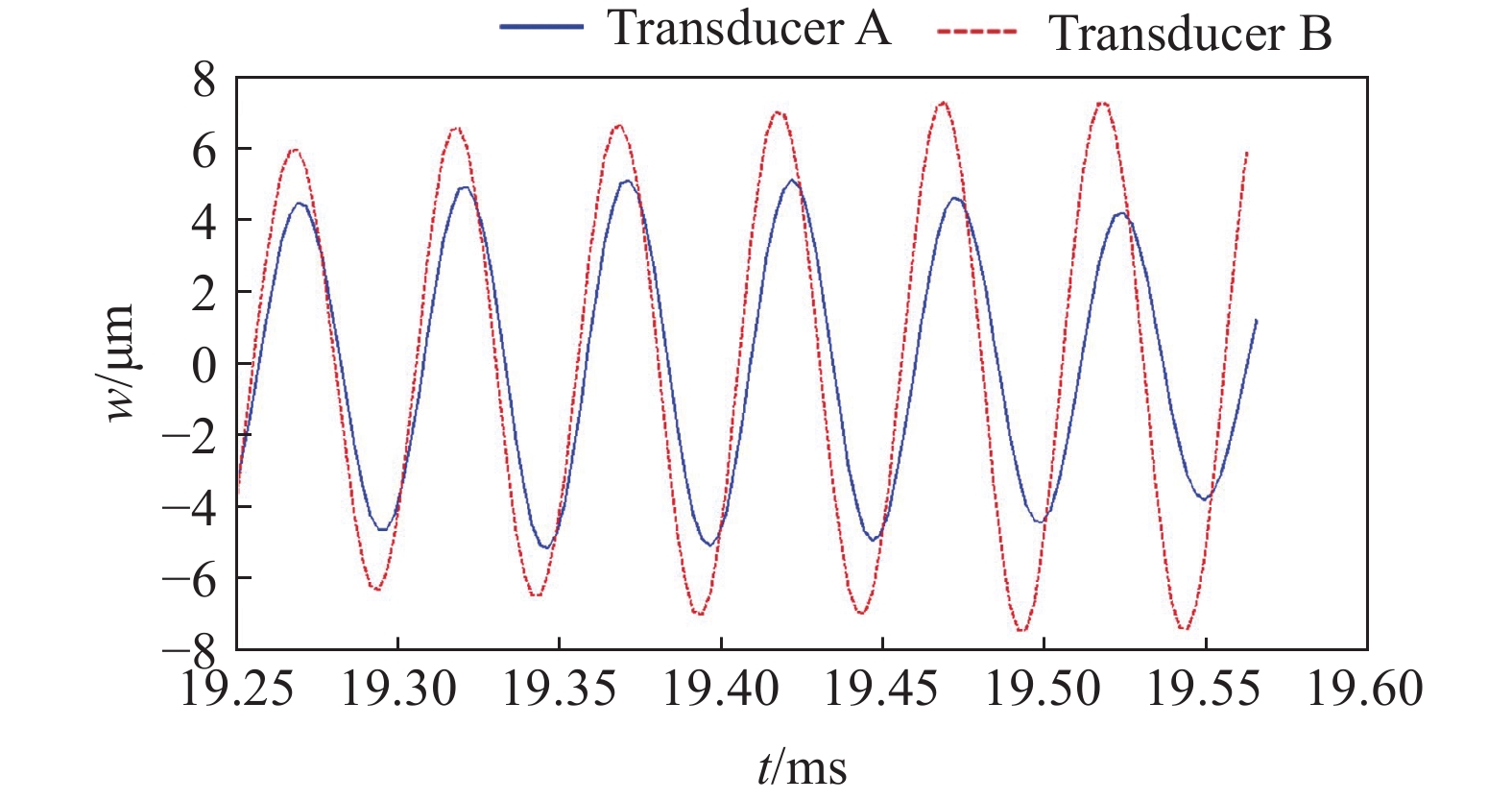
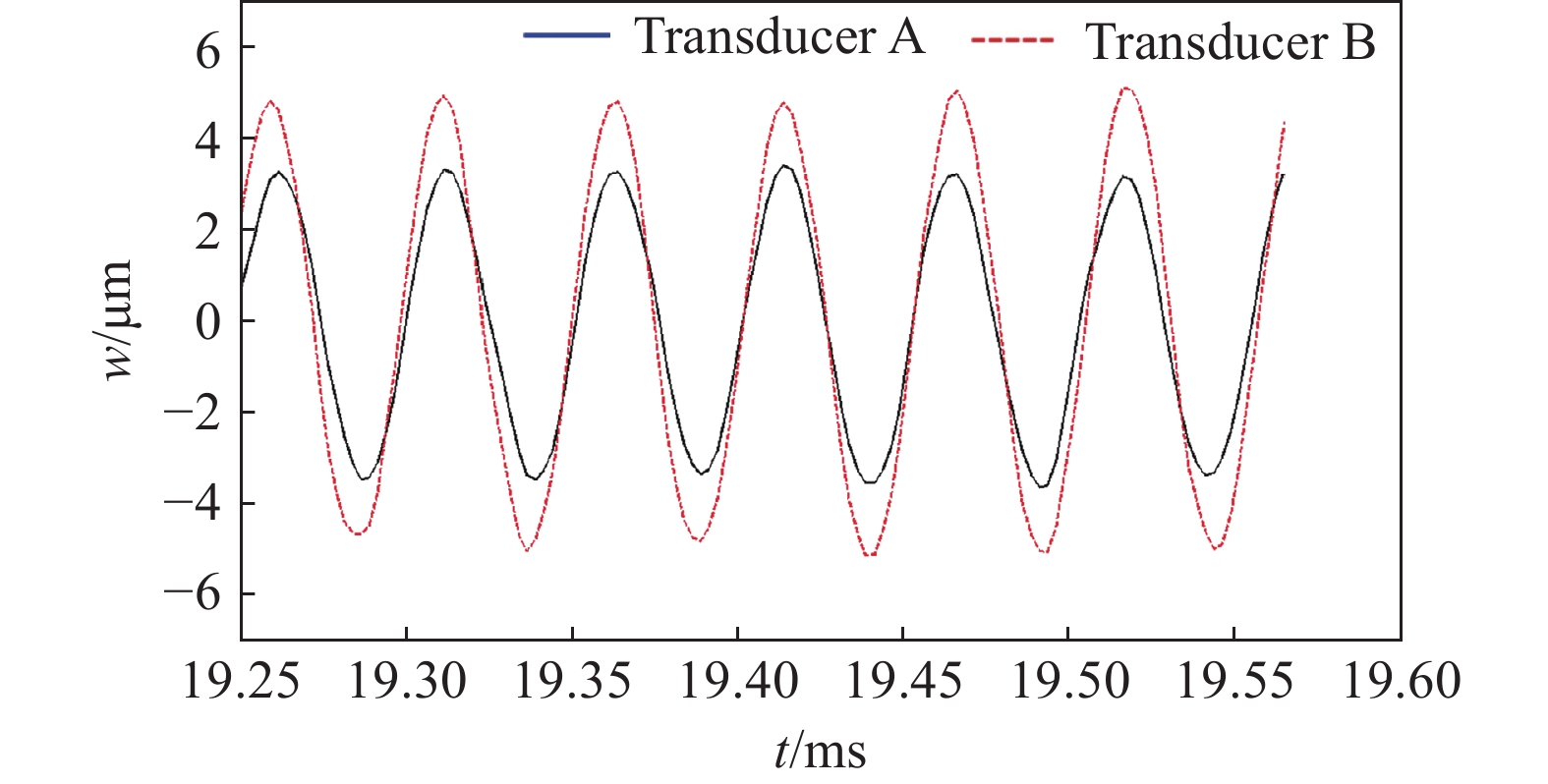
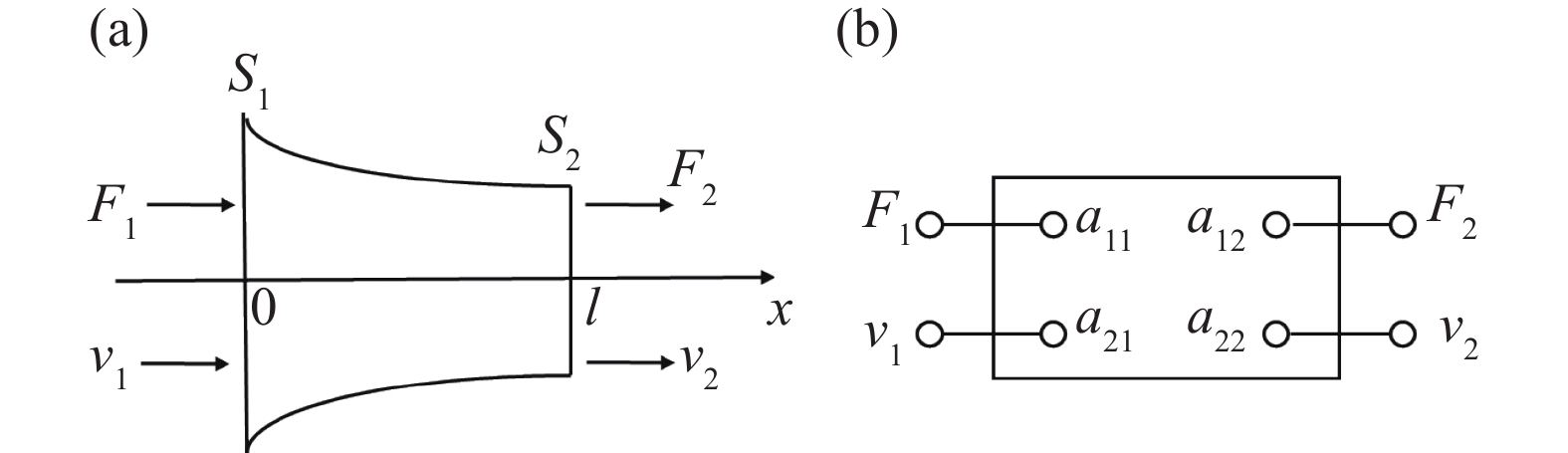
摘要: 壓電超聲換能器傳統四端網絡設計方法忽略了壓電陶瓷晶堆內部的機電耦合過程,使用該方法所設計的壓電超聲換能器尺寸誤差大,輸出的超聲振幅較小。為了提高壓電超聲換能器尺寸設計精度、增大換能器輸出的超聲振幅,本文將考慮壓電陶瓷晶堆內部機電耦合作用的六端網絡引入到壓電超聲換能器的設計中,分別采用四端網絡法和六端網絡法設計得到兩個不同尺寸的壓電超聲換能器A和B,通過有限元方法對比分析了兩個換能器的固有頻率和輸出振幅,并進一步通過實驗驗證了設計理論與仿真分析的有效性。研究結果表明,在相同激勵電壓下,采用六端網絡法設計得到的壓電超聲換能器B輸出的超聲振幅是換能器A輸出振幅的1.5倍,六端網絡法設計壓電超聲換能器可以提高所設計換能器的振動性能。Abstract: As an effective method for efficient precision machining of hard and brittle materials, ultrasonic-assisted machining has been widely researched and applied over the past years. As a result, higher requirements are put forward for the performance of ultrasonic-assisted machining equipment. The ultrasonic transducer is one of the core components of an ultrasonic-assisted machining system, which determines its machining performance. The study on the design method of an ultrasonic transducer is necessary for the establishment of an ultrasonic-assisted machining system. The four-terminal network method based on mechanic-electric analogies is an effective design method, which regards the mechanical vibration system as an electrical four-terminal network. The wave velocity of the mechanical wave in the vibration system can be equivalent to the current in the equivalent circuit, and the force impedance at both ends of the vibration system can be equivalent to the electrical impedance at both ends of the equivalent circuit. The size of the ultrasonic transducer can be calculated according to the electromechanical similarity theory and vibration boundary conditions. However, the conventional four-terminal network design method of the piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer (PUT) neglects the electromechanical coupling process inside the stacked piezoelectric ceramics (SPCs). The PUT designed by this method has a big size error and low output amplitude. Aimed to obtain a higher ultrasonic amplitude of PUT, the equivalent six-terminal network of SPCs considering electromechanical coupling is introduced into the traditional design method, and two PUTs of different sizes are designed by the four-terminal network and the six-terminal network, named transducer A and transducer B, respectively. The natural frequency and output amplitudes of the two PUTs are analyzed and compared by the finite element method, and the experiments further verified the validity of the theory and the simulation analysis. When the excitation voltage is the same, results show that the output amplitude of transducer B (designed by the six-terminal network) is 1.5 times higher than that of transducer A. Finally, applying a six-terminal network to the PUT designing can improve the vibration performance of the PUT effectively.
-
表 1 壓電超聲換能器各部分材料參數
Table 1. Material parameters of each part of the PUT
Materials Density/
(kg·m?3)Young’s modulus, E/
(N·m?2)Poisson’s ratio Aluminum alloy 6061 2700 7.07×1010 0.33 PZT-8 7600 x: 7.407×1010 xy: 0.303 y: 8.696×1010 yz: 0.356 z: 8.696×1010 xz: 0.322 45 Steel 7850 7.07×1011 0.31 表 2 壓電超聲換能器設計尺寸
Table 2. Designed dimensions of each part of the PUTs
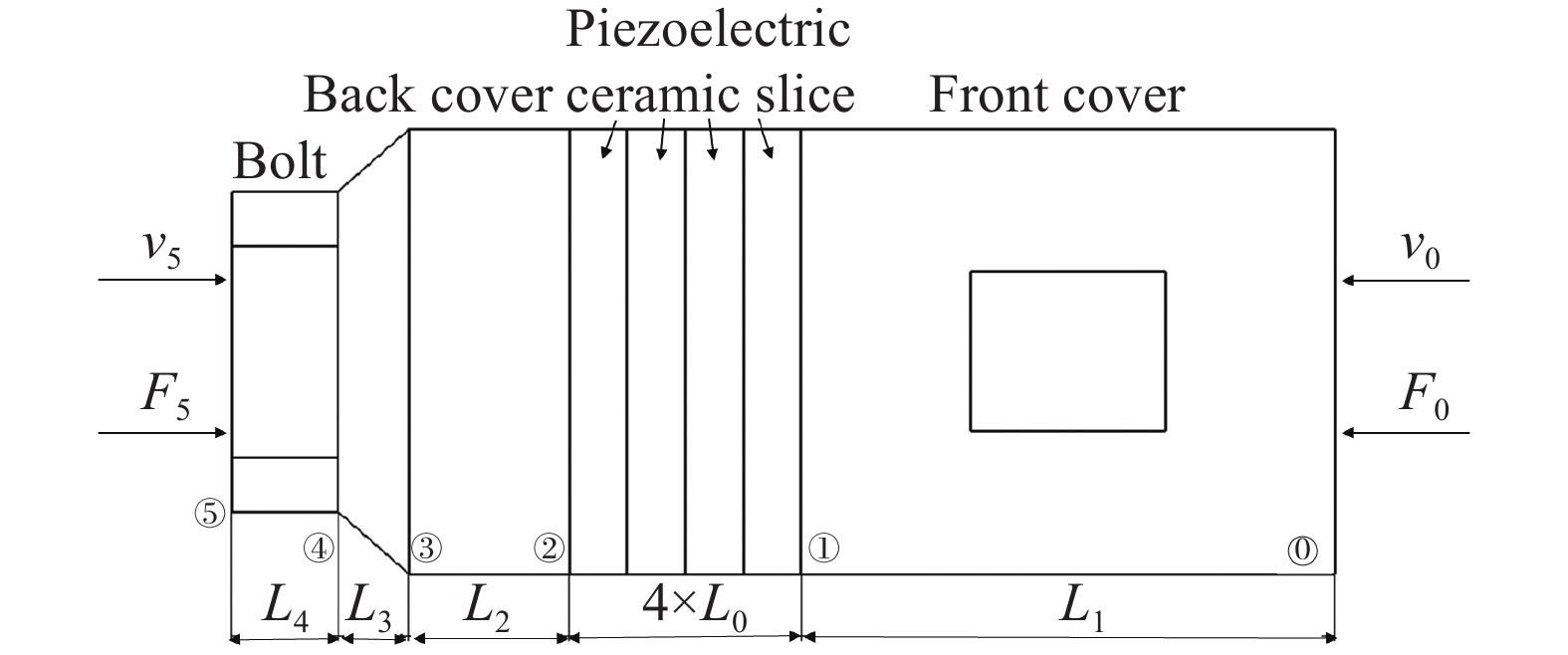
Parts Length/mm Diameter/mm Front cover 58.63 50 piezoelectric ceramic slice 6.5 50 Cylindrical section of the back cover
(four-terminal network method)9.95 50 Cylindrical section of the back cover
(six-terminal network method)15.78 50 Conic section of back cover 8 Bottom surface: 50
Top surface: 36Bolt 12 36 表 3 壓電超聲換能器縱振固有頻率仿真分析
Table 3. Natural frequency of the longitudinal vibration of the PUTs by FEM
Transducer Natural frequency/Hz Design error/% Modal solution Transducer A 20074 0.37 
Transducer B 19270 3.65  www.77susu.com
www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Shih A J, Denkena B, Grove T, et al. Fixed abrasive machining of non-metallic materials. CIRP Ann, 2018, 67(2): 767 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2018.05.010 [2] Wu H. Wire sawing technology: A state-of-the-art review. Precis Eng, 2016, 43: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.08.008 [3] Ohmori H, Ebizuka N, Morita S, et al. Ultraprecision micro-grinding of germanium immersion grating element for mid-infrared super dispersion spectrograph. CIRP Ann, 2001, 50(1): 221 doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62109-X [4] Zhang Y. Studies on the Preparation and Properties of CoTiNb2O8-Based Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017張云. 鈮酸鈦鈷基微波介質陶瓷的制備與性能研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2017 [5] Brinksmeier E, Mutlugunes Y, Klocke F, et al. Ultra-precision grinding. Cirp Annals, 2010, 59(2): 652 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.05.001 [6] Zhou M, Wang X J, Ngoi B K A, et al. Brittle-ductile transition in the diamond cutting of glasses with the aid of ultrasonic vibration. J Mater Process Technol, 2002, 121(2-3): 243 doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01262-6 [7] Thoe T B, Aspinwall D K, Wise M L H. Review on ultrasonic machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 1998, 38(4): 239 doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(97)00036-9 [8] Ibrahim M R, Rahim Z, Rahim E, et al. An experimental investigation of cutting temperature and tool wear in 2 dimensional ultrasonic vibrations assisted micro-milling // 2016 the 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Mechanical Engineering (ICMME 2016). Chongqing, 2016: 07005 [9] Feng P F, Wang J J, Zhang J F, et al. Research status and future prospects of rotary ultrasonic machining of hard and brittle materials. J Mech Eng, 2017, 53(19): 3 doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.003馮平法, 王健健, 張建富, 等. 硬脆材料旋轉超聲加工技術的研究現狀及展望. 機械工程學報, 2017, 53(19):3 doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.003 [10] Zhang C L, Feng P F, Zhang J F. Surface properties of optical glass processed with rotary ultrasonic face milling. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci Technol) , 2012, 52(11): 1616張承龍, 馮平法, 張建富. 光學玻璃旋轉超聲端面銑削表面特性. 清華大學學報(自然科學版), 2012, 52(11):1616 [11] Zhou M, Wang M, Dong G J. Experimental investigation on rotary ultrasonic face grinding of SiCp/Al composites. Mater Manuf Process, 2016, 31(5): 673 doi: 10.1080/10426914.2015.1025962 [12] He X P, Gao J. A review of ultrasonic solid horn design. Tech Acoust, 2006, 25(1): 82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.018賀西平, 高潔. 超聲變幅桿設計方法研究. 聲學技術, 2006, 25(1):82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.018 [13] Lesniewski P. Discrete component equivalent circuit for Webster’s horns. Appl Acoust, 1995, 44(2): 117 doi: 10.1016/0003-682X(95)91367-C [14] Gao J, He X P, Hu J. Unified treatment of ultrasonic horn characteristics based on four-end network approach. Tech Acoust, 2006, 25(1): 87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.019高潔, 賀西平, 胡靜. 四端網絡法統一變幅桿的性能參量. 聲學技術, 2006, 25(1):87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.019 [15] Qi H Q, Shan X B, Xie T. Wire drawing with orthogonal composite ultrasonic vibration. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2010, 32(1): 89齊海群, 單小彪, 謝濤. 正交復合超聲振動拉絲. 北京科技大學學報, 2010, 32(1):89 [16] Huang Y C, Ding G Z, Chen B H, et al. Simulation and experiment of Langevin-type piezoelectric ultrasonic horn for micro tool motion. Intell Technol Eng Syst, 2013, 234: 967 [17] Guo P, Ehmann K F. Development of a New Vibrator for Elliptical Vibration Texturing // ASME 2011 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference. Corvallis, 2011: 13 [18] Zhao F L, Feng D J, Guo D M, et al. Design of horn using four-end network method. Acta Acustica, 2002, 27(6): 554 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2002.06.015趙福令, 馮冬菊, 郭東明, 等. 超聲變幅桿的四端網絡法設計. 聲學學報, 2002, 27(6):554 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-0025.2002.06.015 [19] Huang D Z. Design of vibration system for ultrasonic wave vibrator. J Vib Shock, 2005, 24(5): 107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2005.05.032黃德中. 超聲波振動器四端網絡設計. 振動與沖擊, 2005, 24(5):107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2005.05.032 [20] Jiao F Y. Study on Elastic Waves Propagation in Piezoelectric and Piezoelectric Semiconductor Layer Structures [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019焦鳳瑀. 壓電和壓電半導體層狀結構中彈性波傳播研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2019 [21] Lin S Y. Theory and design of Ultrasonic Transducer. Beijing: Science Press, 2004林書玉. 超聲換能器的原理及設計. 北京: 科學出版社, 2004 [22] Martin G E. Vibrations of coaxially segmented, longitudinally polarized ferroelectric tubes. J Acoust Soc Am, 1964, 36(8): 1496 doi: 10.1121/1.1919233 [23] Zuo W K, Zhou W G, Wei M Y, et al. Formation and mechanism analysis of half-wave loss. Phys Bull, 2019(1): 33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0509-4038.2019.01.010左武魁, 周惟公, 魏民云, 等. 半波損失的形成和機理分析. 物理通報, 2019(1):33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0509-4038.2019.01.010 [24] He L P, Ren X M. Study on finite element modeling method of bolted joints. Trans Beijing Inst Technol, 2020, 40(12): 1275賀李平, 任雪梅. 螺栓聯接的有限元建模方法研究. 北京理工大學學報, 2020, 40(12):1275 [25] Qiao J P. Study on the influencing factors of frequency of transducer vibrator [Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011喬家平. 換能器振子頻率的影響因素研究[學位論文]. 長沙: 中南大學, 2011 -




 下載:
下載: