Calculation of continuous casting billet solidification based on element-free Galerkin method
-
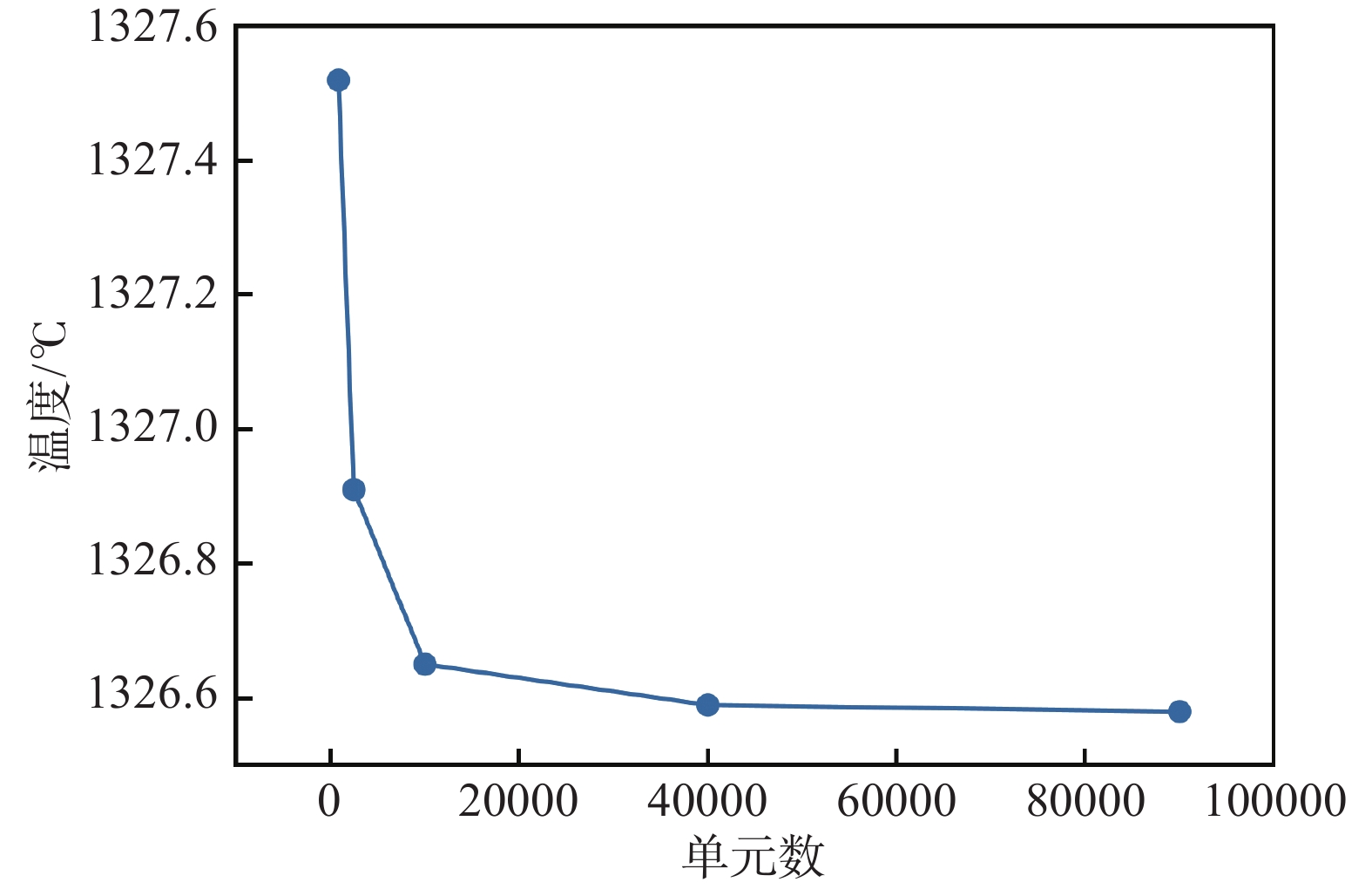
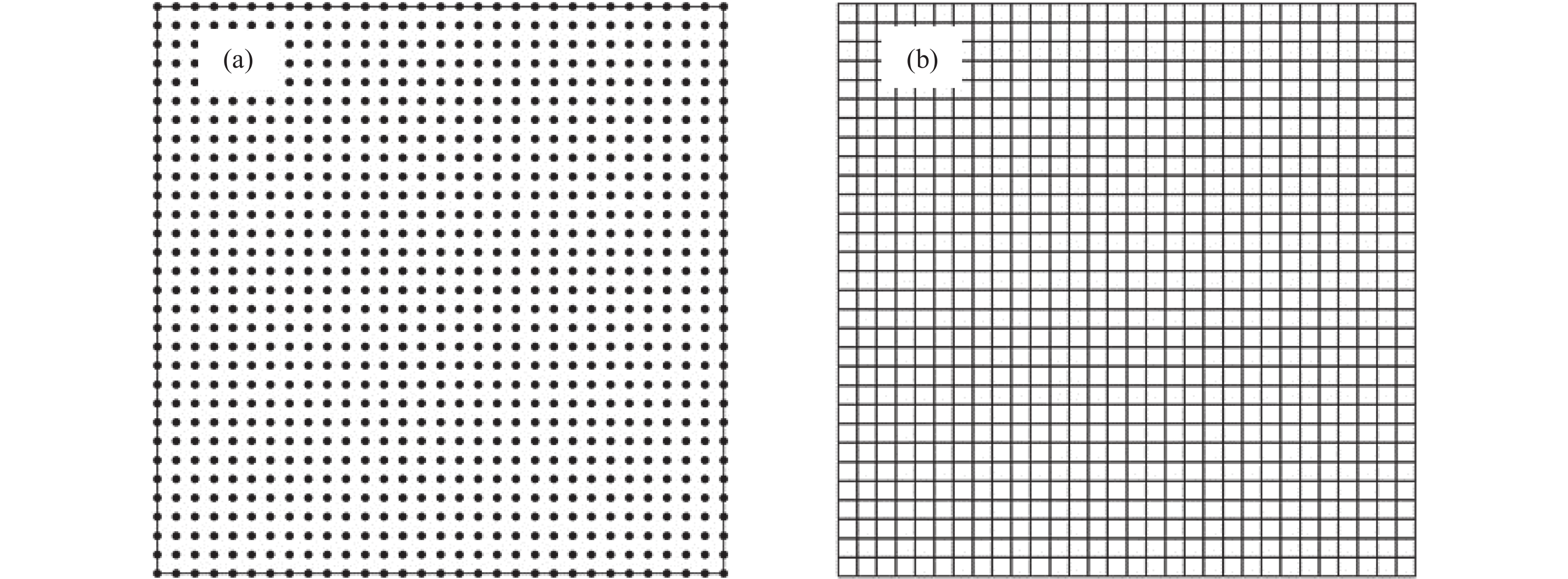
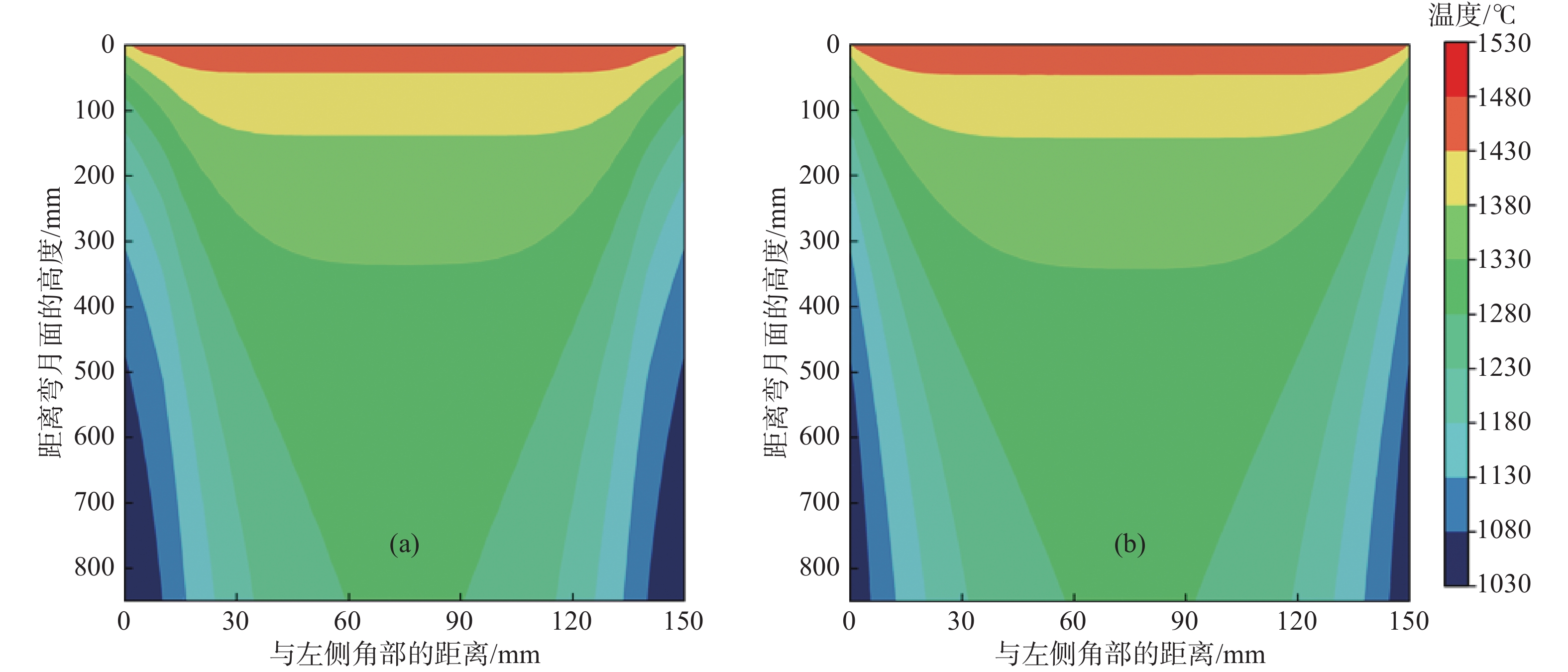
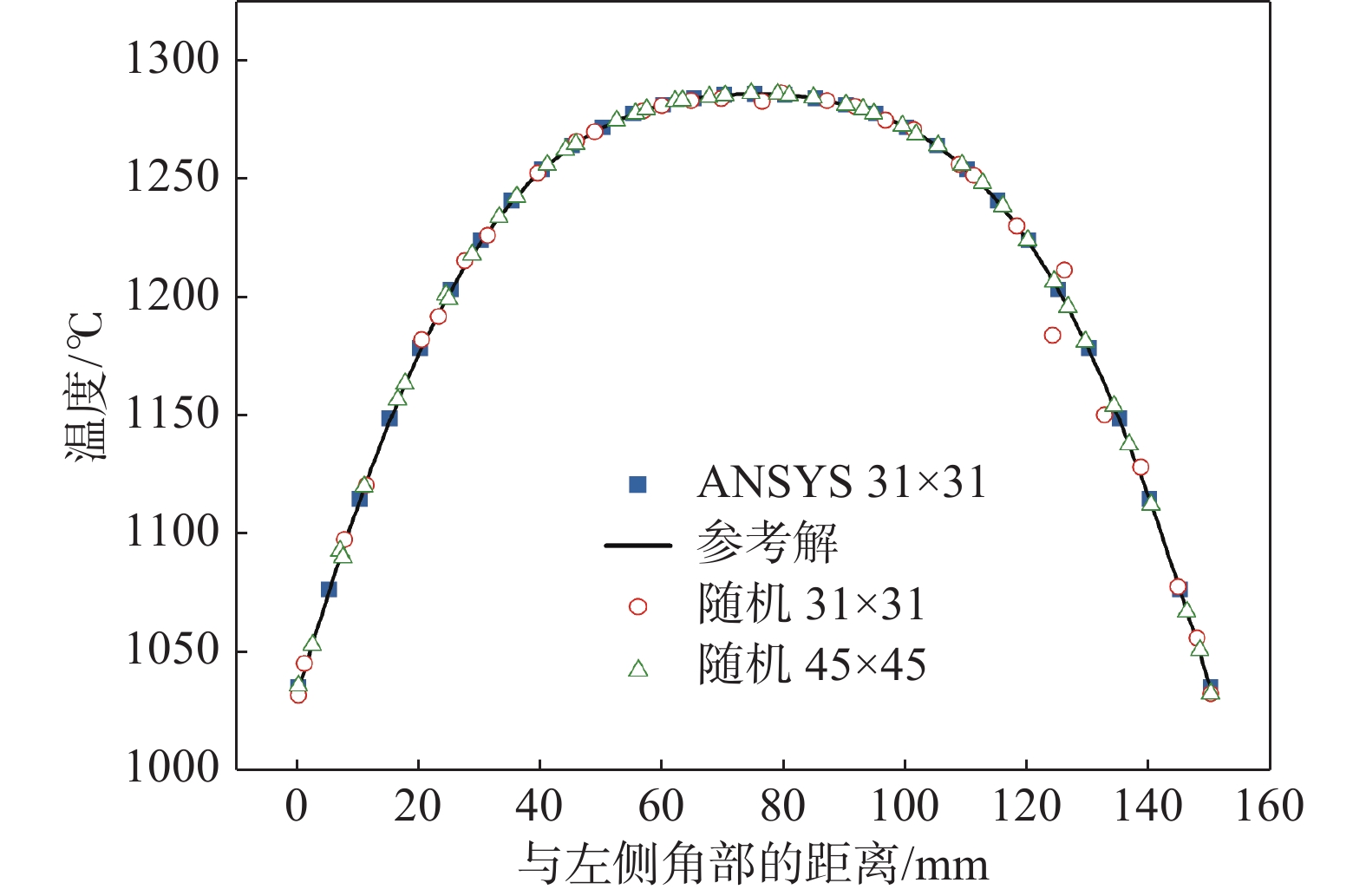
摘要: 為考察無網格方法求解鑄坯凝固過程的可行性,本文依據移動最小二乘和變分原理,推導并建立了基于無網格伽遼金法的結晶器內鑄坯凝固過程二維非穩態傳熱/凝固數學模型。以小方坯凝固過程為對象,分別采用節點均勻布置、加密布置、隨機布置方式,模擬分析了小方坯凝固過程的溫度場變化,并將計算結果與參考解、有限元法數值解進行了對比,結果證實無網格伽遼金法在計算精度、自適應性、網格依賴性等方面均優于有限元法。研究結果為無網格方法應用于連鑄過程的傳熱、凝固以及應力/應變行為的數值計算提供參考。Abstract: The mold is the core component of a continuous caster, and the complex metallurgical behavior in the mold is the primary factor determining the quality of continuous casting slabs. The numerical simulation method based on meshing, such as the finite element method, has become an important method to study the complex heat transfer and mechanical behavior in the mold. With in-depth research, the meshing-based numerical simulation method has been found incapable of accurately reconstructing the solidified shell shape of slabs and tracing the liquid-solid phases coexisting region, and addressing some complex problems such as large deformation and crack propagation is difficult. To investigate the feasibility of the meshless method for solving the solidification process of continuous casting billet, according to the moving least square method and variational principle, a two-dimensional unsteady transient heat transfer mathematical model of billet solidification process in mold was established based on element-free Galerkin method. In this work, an arrangement of the uniform, increased density, and randomly distributed nodes was used to calculate the change of temperature field during the billet solidification process. The calculation results of the element-free Galerkin method were compared with the reference solution and the numerical solution of the finite element method. The results show that the element-free Galerkin method outperforms the finite element method in terms of accuracy, adaptability, and mesh-dependence. The study results provide references for applying the meshless method to the numerical calculation of heat transfer, solidification, and stress/strain behaviors in the continuous casting process.
-
表 1 工藝參數和鑄坯熱物性參數
Table 1. Casting conditions and thermophysical properties of slab
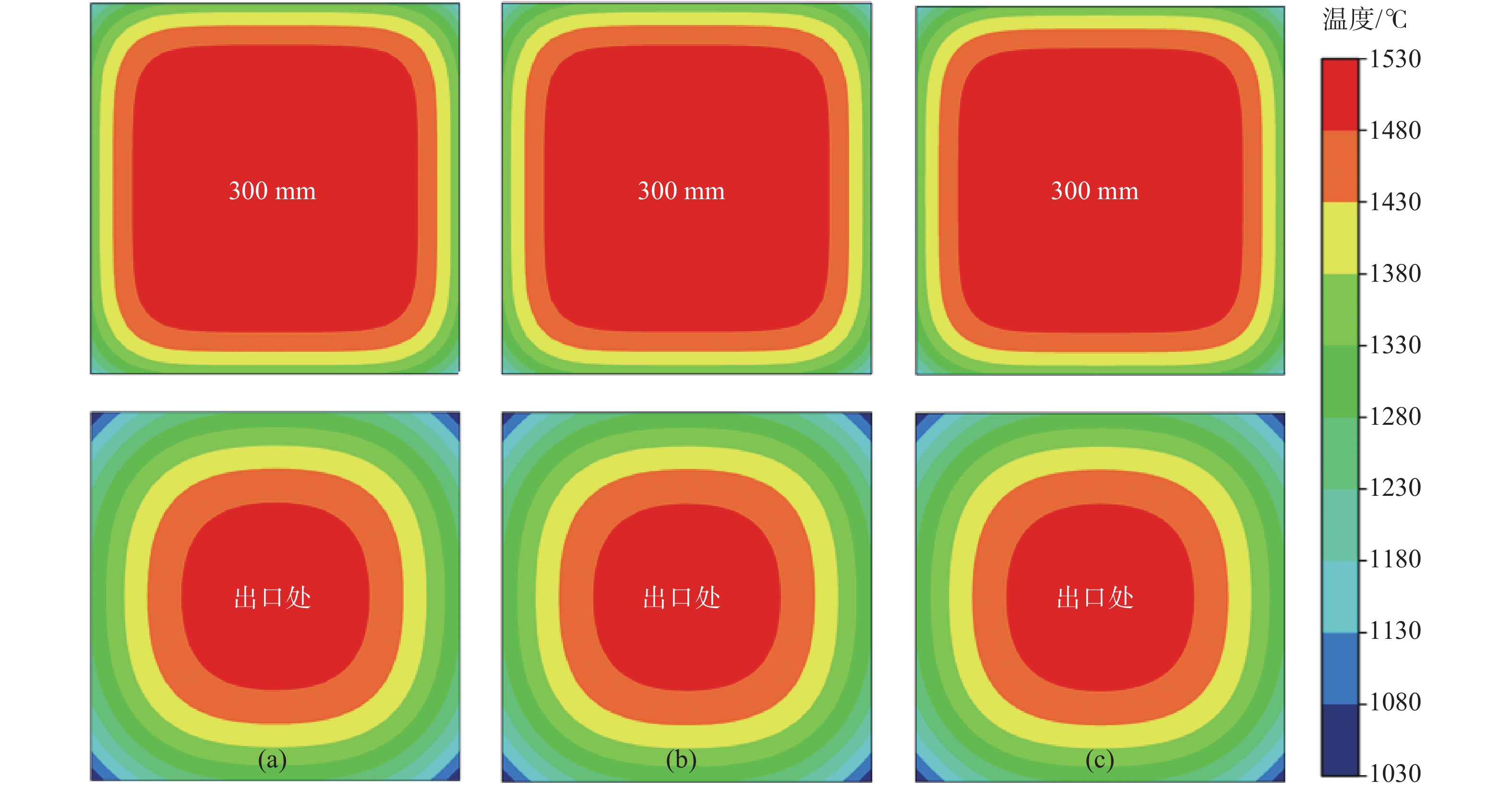
參數 數值 拉速/(m·min?1) 2.2 澆鑄溫度/℃ 1530.0 結晶器高度/m 1.0 液位高度/m 0.85 結晶器水量/(m3·h?1) 119.8 結晶器水流速/(m·s?1) 12.7 固/液相線溫度/℃ 1440.0/1505.0 密度/(kg·m?3) 7500-1.2(T?Tliq) 導熱系數/(W·m?1·K?1) Kc(13.86 + 0.01113T) 比熱容/(J·kg?1·K?1) 666 + 0.17T 潛熱/(J·kg?1) 272000 表 2 兩種方法數值解的對比
Table 2. Comparison of the numerical results of two methods
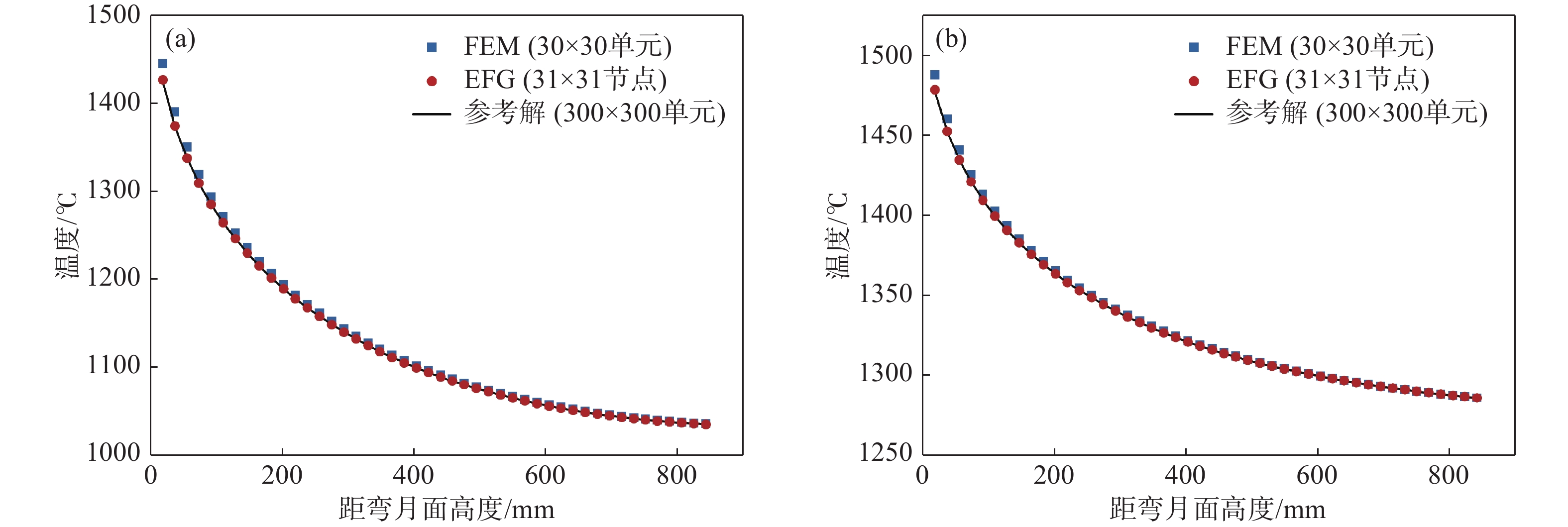
位置 至彎月面距離 EFG加密 (31×31節點) 有限元加密 (2056單元) 溫度/℃ 差值/℃ 溫度/℃ 差值/℃ 鑄坯角部 300 mm 1140.24 ?0.23 1141.10 ?1.09 600 mm 1058.85 ?0.27 1059.42 ?0.84 結晶器出口 1035.12 ?0.01 1035.69 ?0.58 表面中心 300 mm 1339.80 0.39 1341.04 ?0.85 600 mm 1300.80 0.06 1301.43 ?0.57 結晶器出口 1286.01 ?0.07 1286.25 ?0.31 表 3 EFG 45×45隨機布點與有限元法數值解的對比
Table 3. Comparison of EFG 45×45 random nodes and FEM numerical results
至彎月距離 EFG (45×45節點) 有限元 (31×31節點) 有限元加密 (2056單元) 溫度/℃ 差值/℃ 溫度/℃ 差值/℃ 溫度/℃ 差值/℃ 300 mm 1139.51 0.50 1143.27 ?3.26 1141.10 ?1.09 600 mm 1058.61 ?0.03 1059.97 ?1.39 1059.42 ?0.84 結晶器出口 1035.17 ?0.06 1035.62 ?0.51 1035.69 ?0.58 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Jing D J, Cai K K. Numerical simulation of the coupling phenomenon between thermal and mechanical fields of billet in continuous casting mold. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2000, 22(5): 417 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2000.05.007荊德君, 蔡開科. 連鑄結晶器內鑄坯溫度場和應力場耦合過程數值模擬. 北京科技大學學報, 2000, 22(5):417 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2000.05.007 [2] Dalrymple R A, Rogers B D. Numerical modeling of water waves with the SPH method. Coastal Eng, 2006, 53(2-3): 141 doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2005.10.004 [3] Cingoski V, Miyamoto N, Yamashita H. Element-free Galerkin method for electromagnetic field computations. IEEE Trans Magn, 1998, 34(5): 3236 doi: 10.1109/20.717759 [4] Adams B, Wicke M. Meshless approximation methods and applications in physics based modeling and animation // EUROGRAPHICS 2009. Munich, 2009: 213 [5] Liu M B, Liu G R, Zong Z, et al. Computer simulation of high explosive explosion using smoothed particle hydrodynamics methodology. Comput Fluids, 2003, 32(3): 305 doi: 10.1016/S0045-7930(01)00105-0 [6] Zhang L, Shen H F, Rong Y M, et al. Numerical simulation on solidification and thermal stress of continuous casting billet in mold based on meshless methods. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 466(1-2): 71 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.103 [7] Vertnik R, ?arler B. Solution of a continuous casting of steel benchmark test by a meshless method. Eng Anal Boundary Elem, 2014, 45: 45 doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2014.01.017 [8] Yamasaki N, Shima S, Tsunenari K, et al. Particle-based numerical analysis of spray water flow in secondary cooling of continuous casting machines. ISIJ Int, 2015, 55(5): 976 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.55.976 [9] Vaghefi R, Hematiyan M R, Nayebi A. Three-dimensional thermo-elastoplastic analysis of thick functionally graded plates using the meshless local Petrov - Galerkin method. Eng Anal Boundary Elem, 2016, 71: 34 doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2016.07.001 [10] Hostos J C á, Bencomo A D, Cabrera E S P. Simple iterative procedure for the thermal-mechanical analysis of continuous casting processes using the element-free Galerkin method. J Therm Stresses, 2018, 41(2): 160 doi: 10.1080/01495739.2017.1389325 [11] Hu P H, Wang X D, Wei J J, et al. Investigation of liquid/solid slag and air gap behavior inside the mold during continuous slab casting. ISIJ Int, 2018, 58(5): 892 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2017-393 [12] Fan Y H. A Study of Meshless Method in Numerical Heat Transfer[Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2005范悅宏. 無網格法在數值傳熱學中的應用研究[學位論文]. 南京: 南京理工大學, 2005 [13] Savage J, Pritchard W H. The problem of rupture of the billet in the continuous casting of steel. J Iron Steel Inst, 1954, 178(3): 269 [14] Li D H, Gao Y B, Xin Q B, et al. The processing method and application study for latent heat releases in alloy castings. Foundry, 2004, 53(12): 1005 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4977.2004.12.013李東輝, 高云寶, 辛啟斌, 等. 鑄件凝固潛熱的處理方法與應用研究. 鑄造, 2004, 53(12):1005 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4977.2004.12.013 [15] Liu X. Meshless Method. Beijing: Science Press, 2011劉欣. 無網格方法. 北京: 科學出版社, 2011 [16] Belytschko T, Lu Y Y, Gu L. Element-free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng, 1994, 37(2): 229 doi: 10.1002/nme.1620370205 [17] Liu G R, Gu Y T. An Introduction to Meshfree Methods and Their Programming. Dordrecht: Springer, 2005 [18] Wu S C, Liu G R, Cui X Y, et al. An edge-based smoothed point interpolation method (ES-PIM) for heat transfer analysis of rapid manufacturing system. Int J Heat Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(9-10): 1938 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.12.062 -




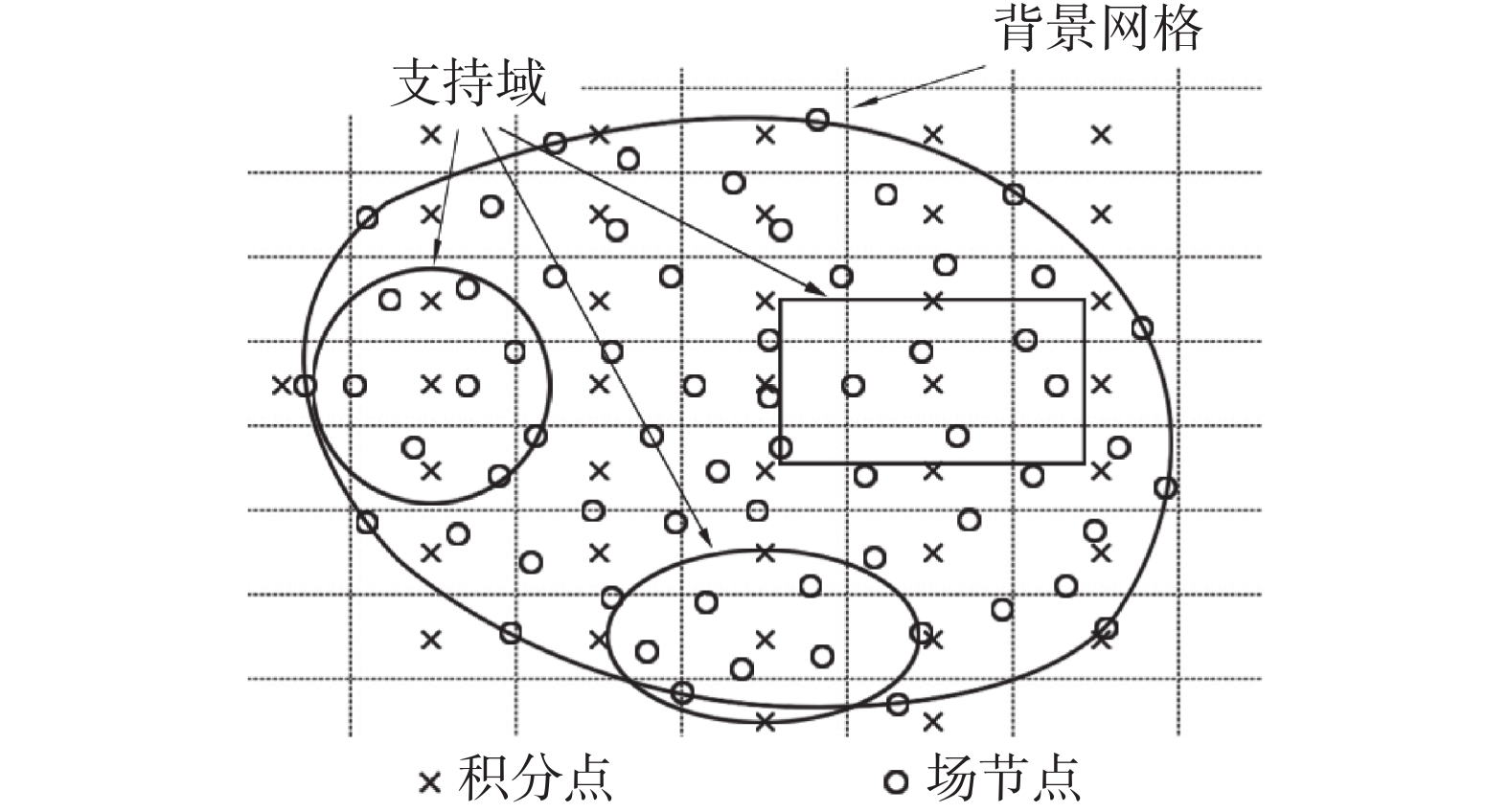
 下載:
下載: