Research on the low-carbon development technology route of iron and steel enterprises under the “double carbon” target
-
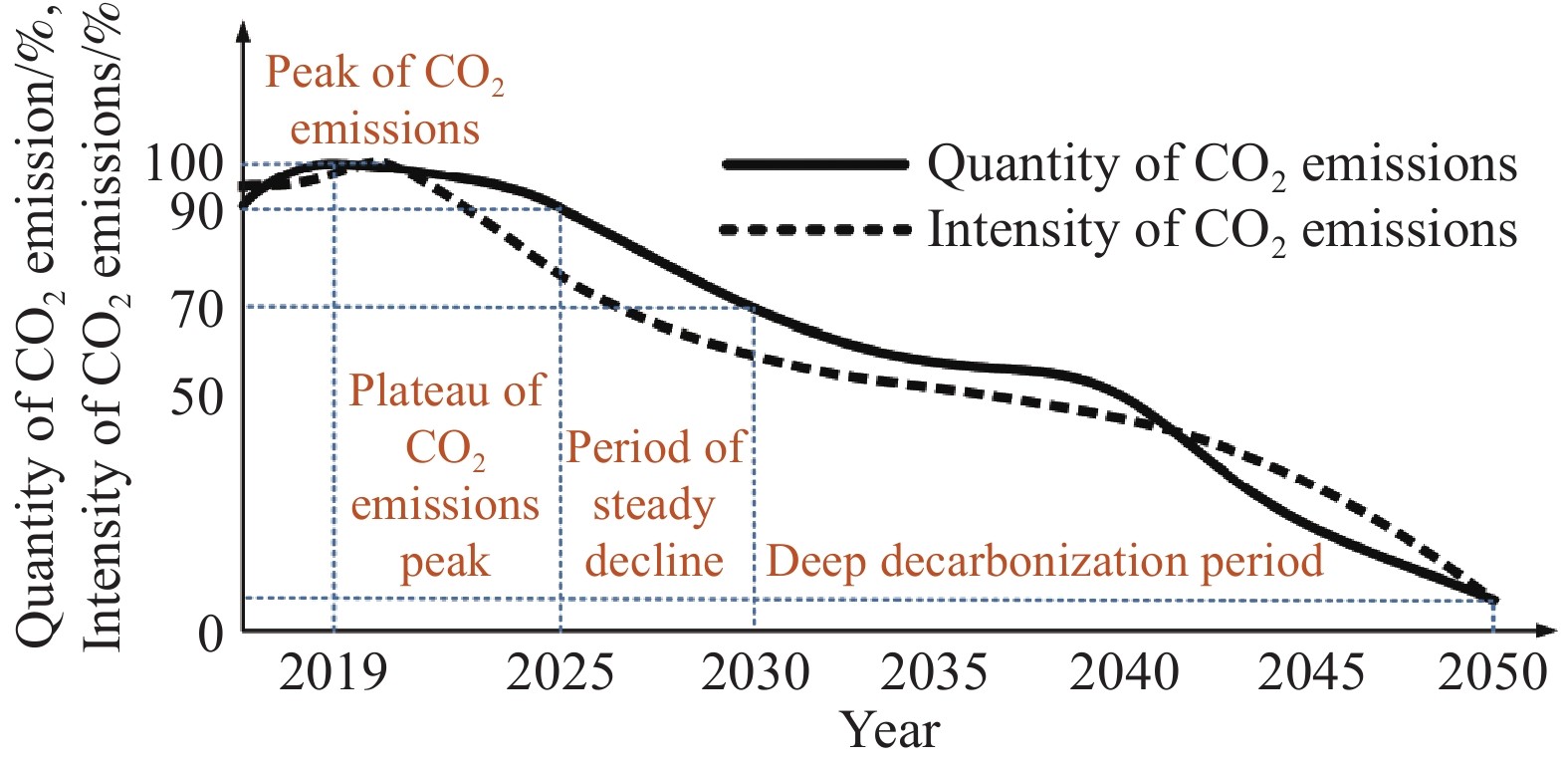
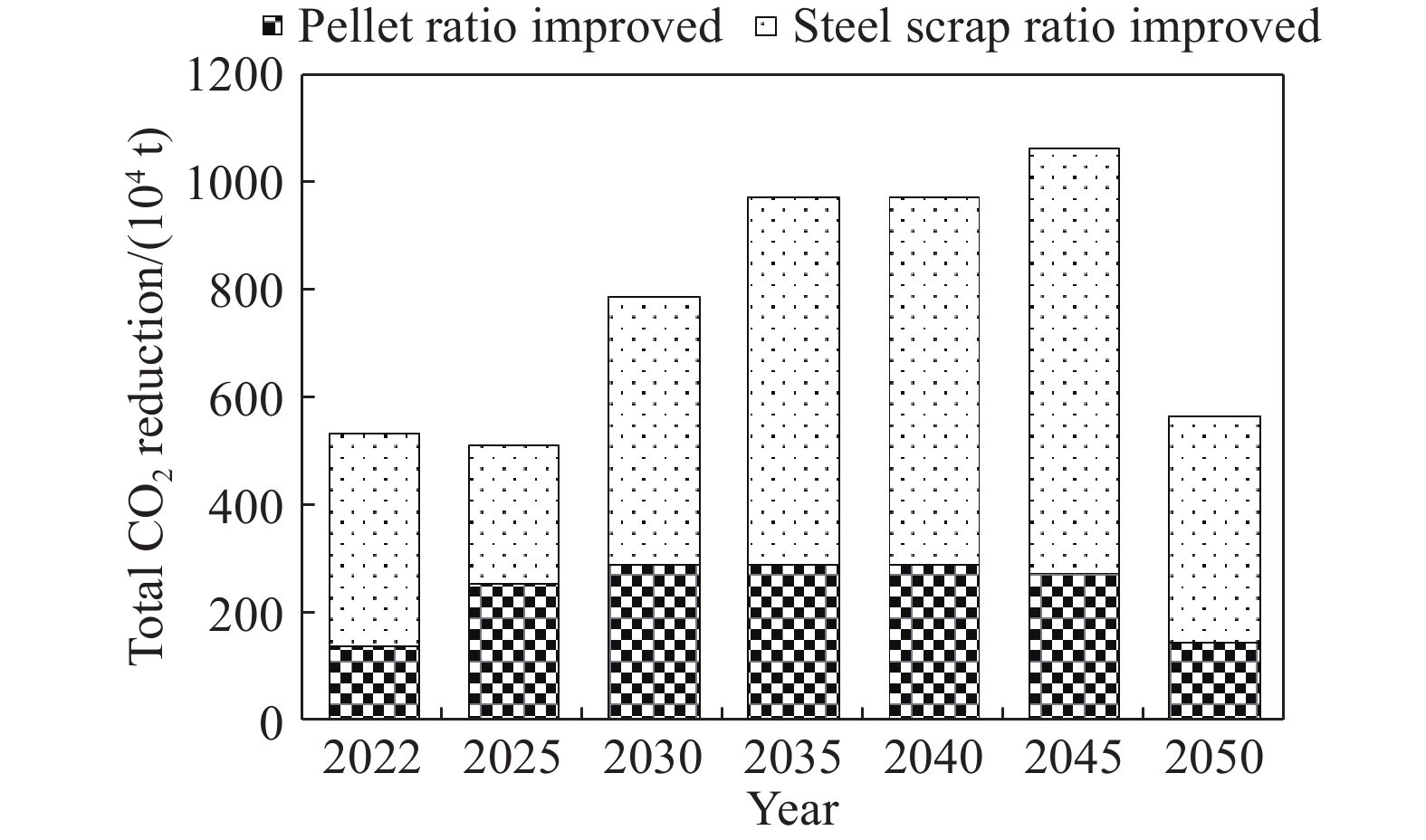
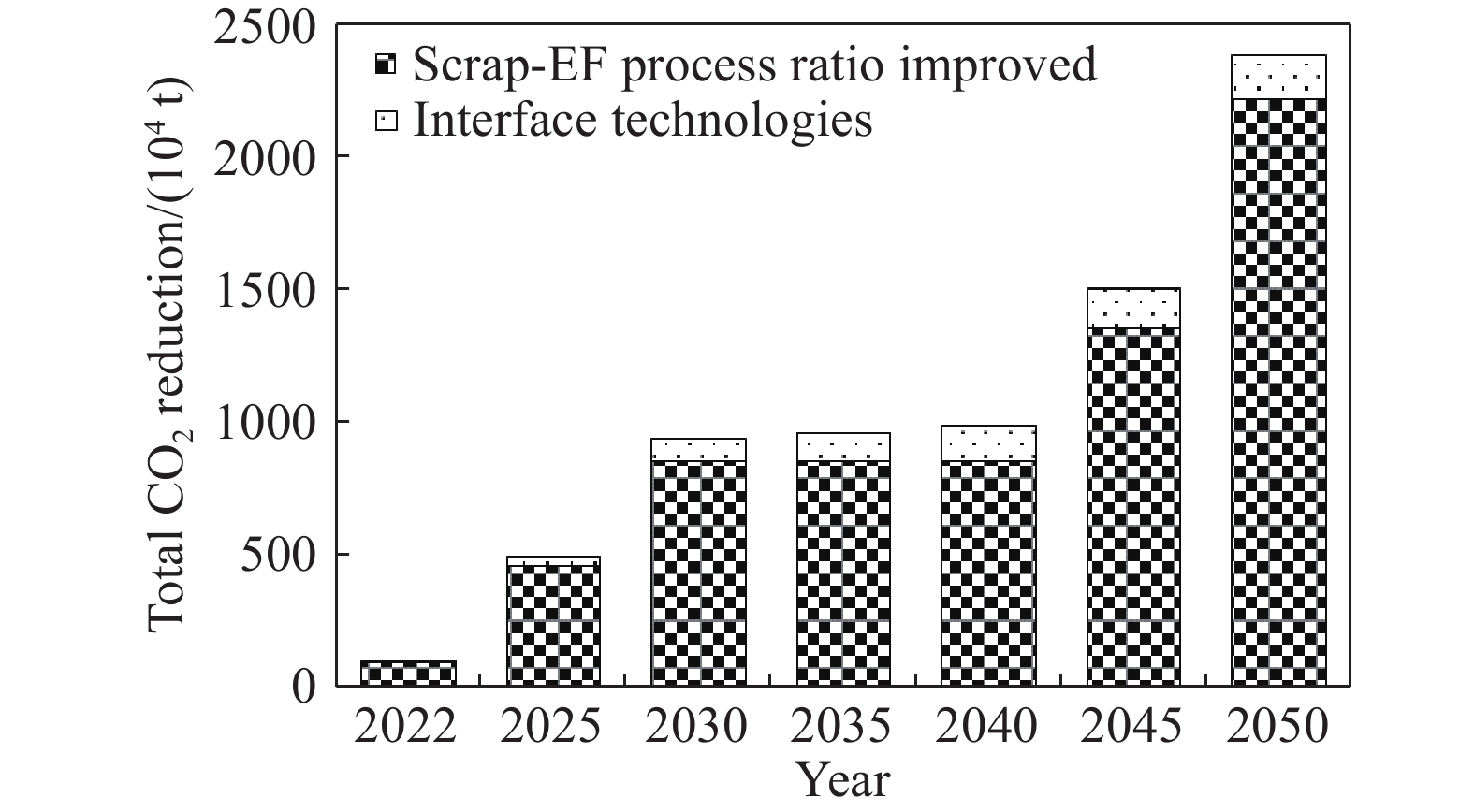
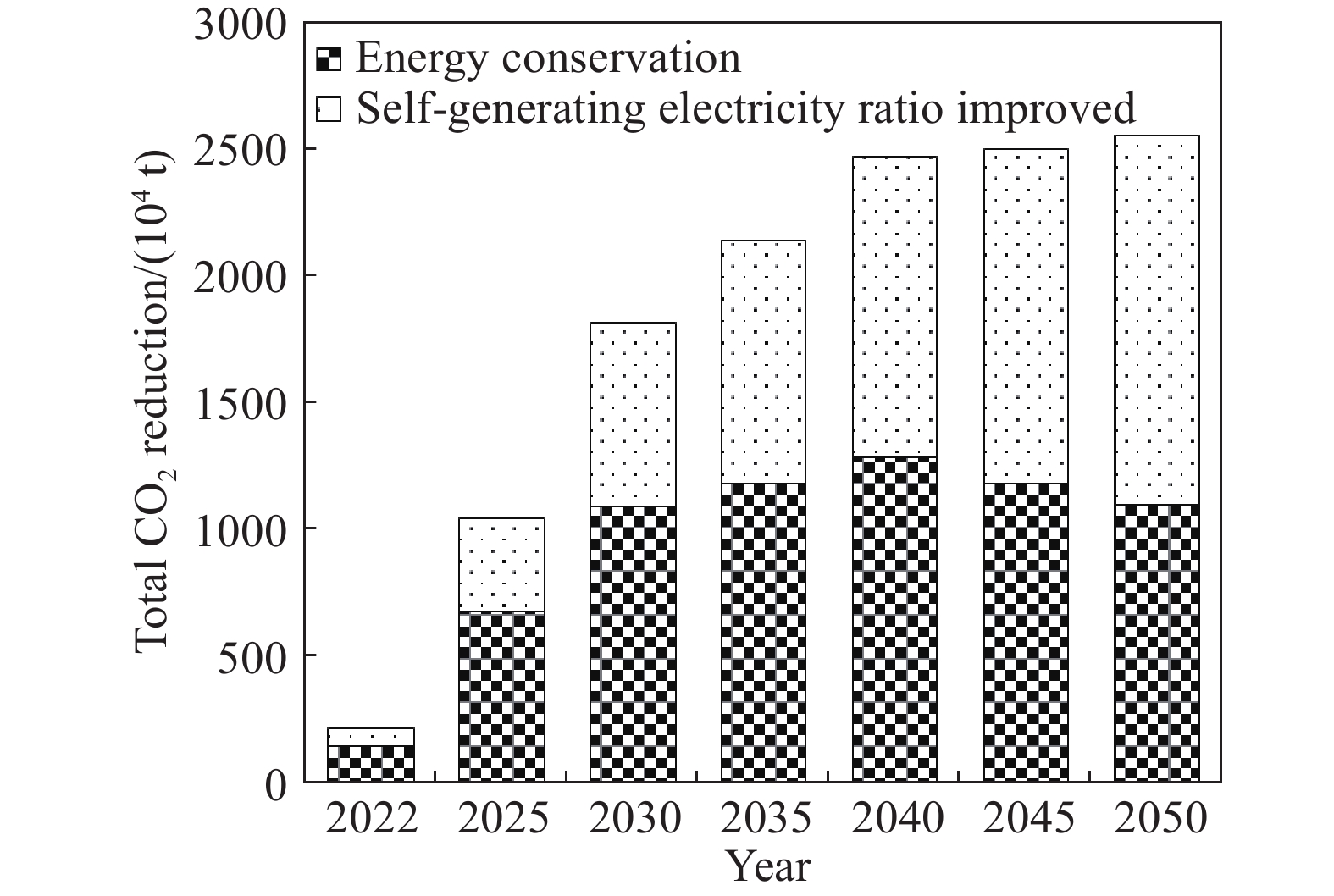
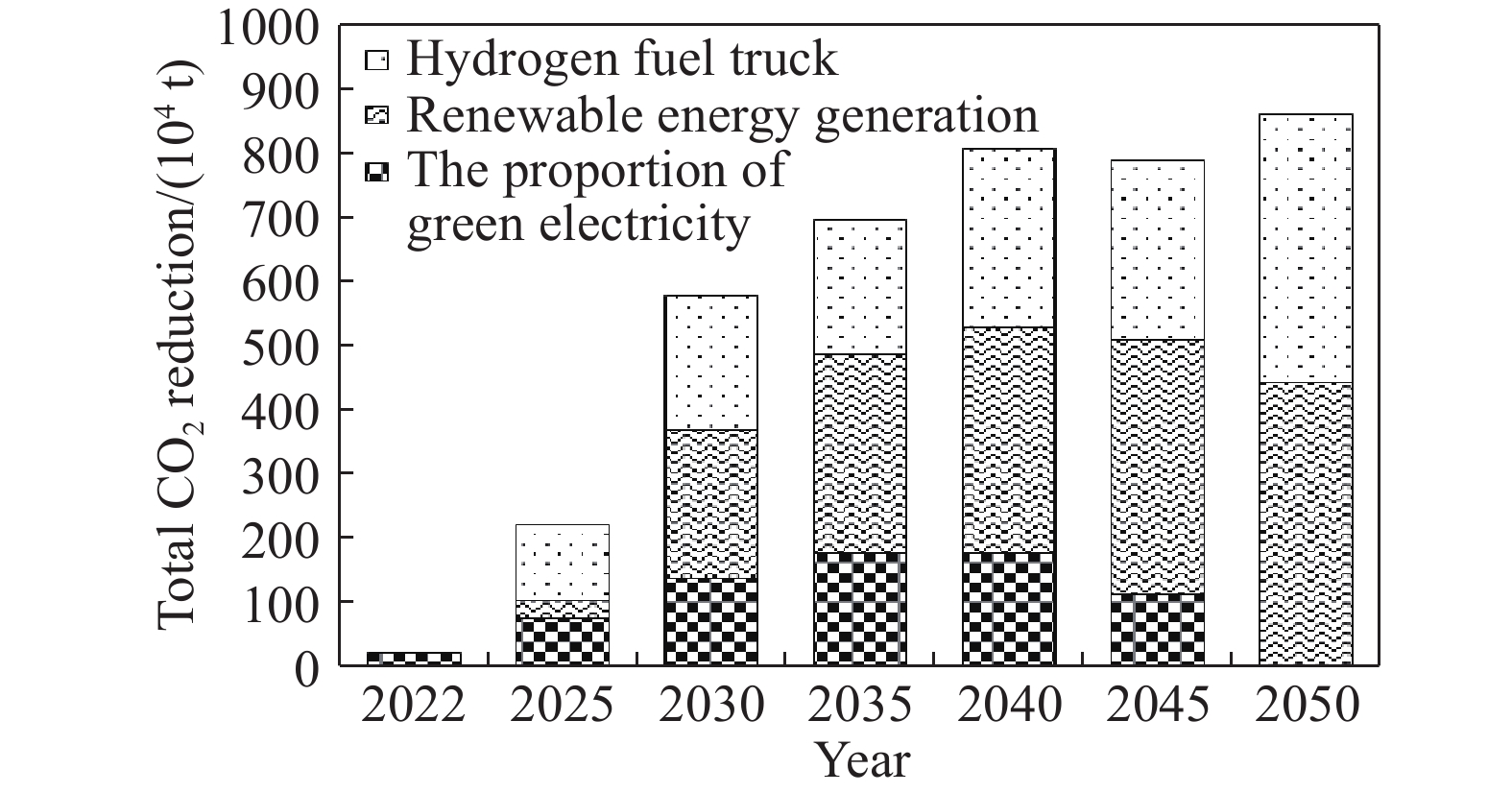
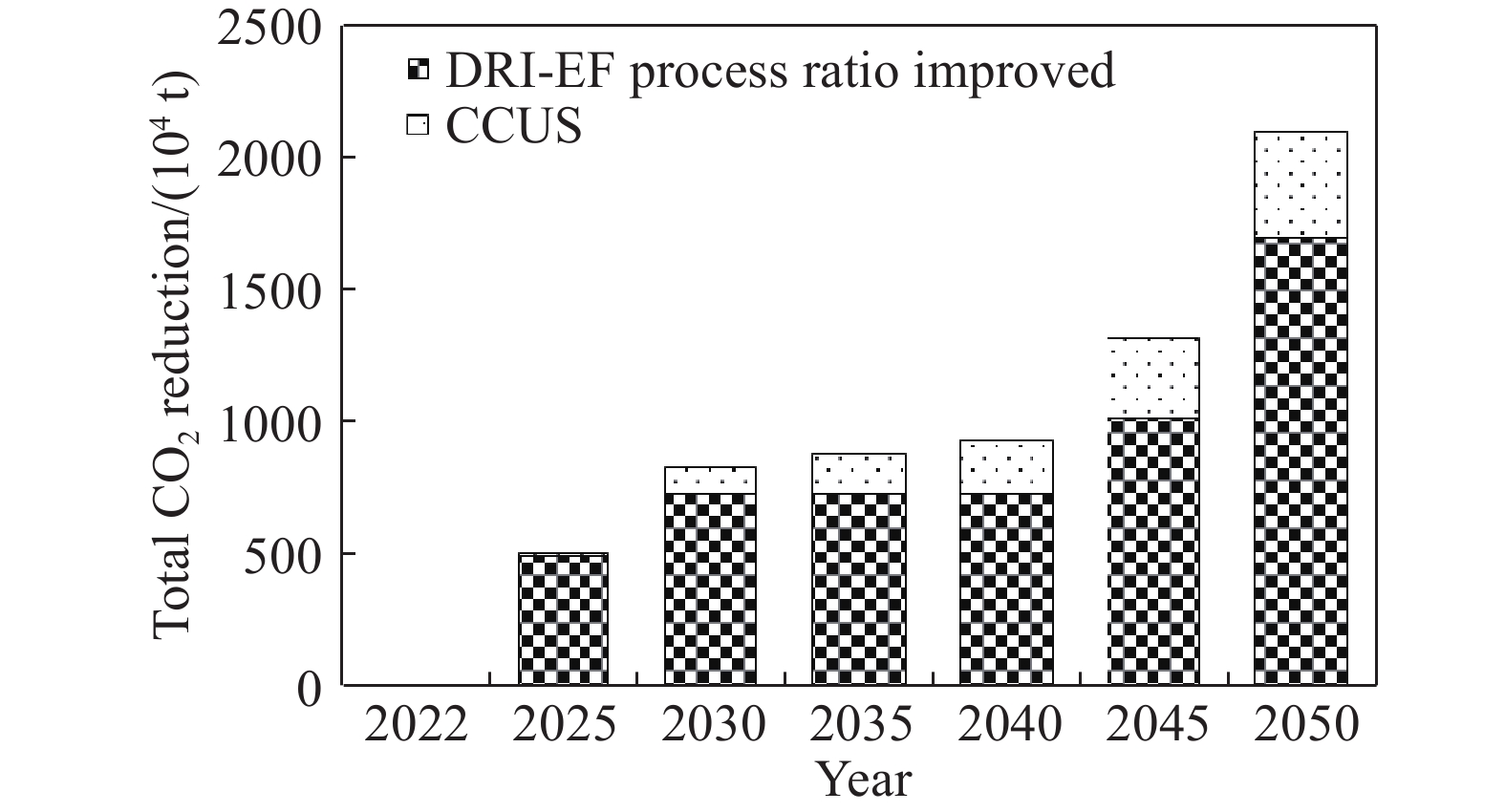
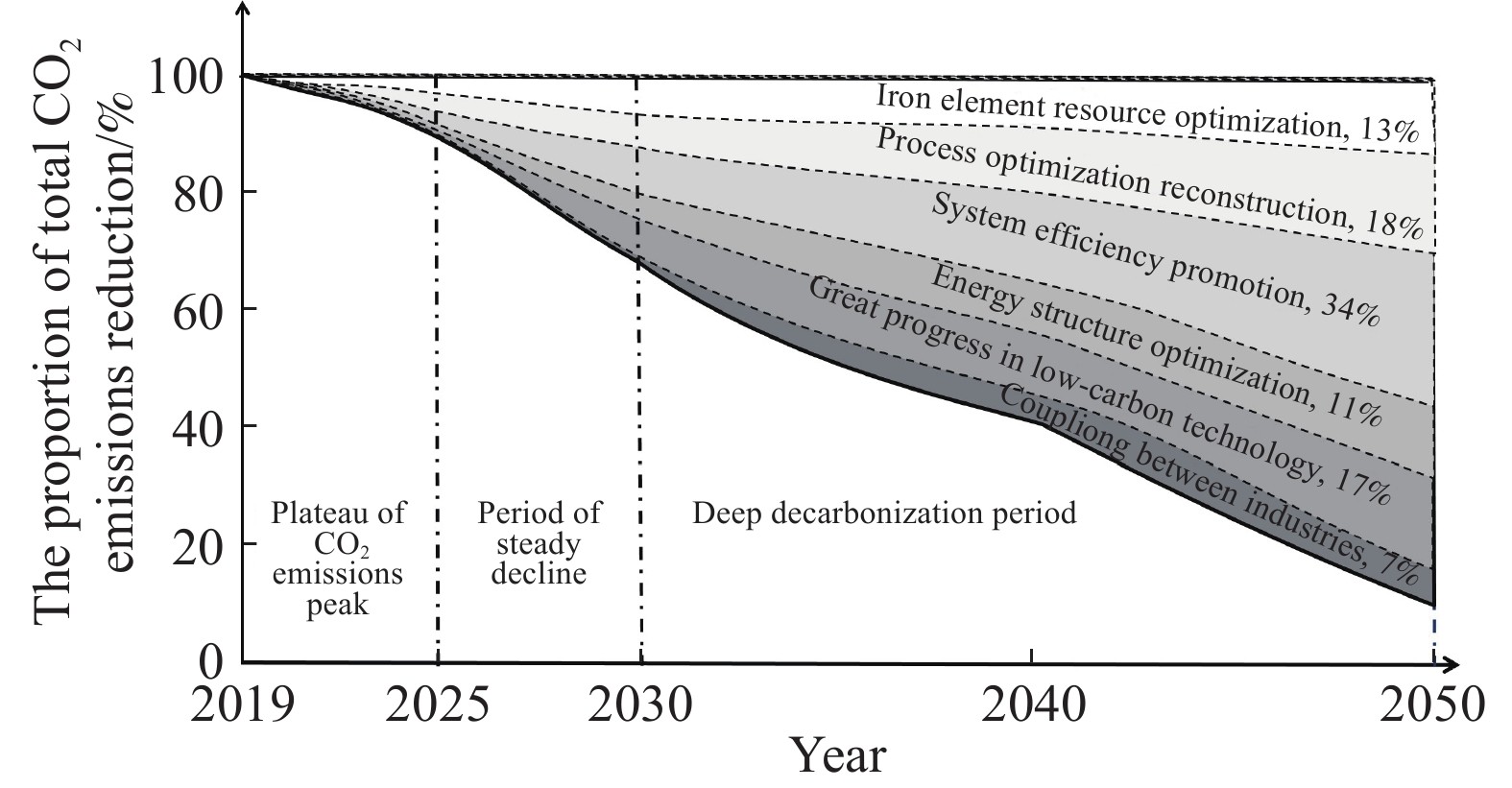
摘要: 為落實國家“碳達峰、碳中和”發展目標,解決鋼鐵行業低碳發展過程中面臨的瓶頸和難題,展開了一系列政策、技術和行動方案的研究。對比國內外鋼鐵企業碳排放強度的現狀及變化趨勢,分析了引起碳排放強度差異性的原因,并給出我國鋼鐵工業“碳達峰、碳中和”發展的總體方向。解析了中國鋼鐵工業及國內大型鋼鐵企業的“碳達峰、碳中和”目標及實施方案,并重點基于某大型鋼鐵企業當前生產、裝備、工藝流程、碳排放實際情況,在充分考慮了未來產能裝備、工藝變革、技術創新、能源轉型等方面規劃的基礎之上,制定了具體的低碳發展技術路線圖,為我國鋼鐵企業落實國家“碳達峰、碳中和”目標提供了示范和引領。路線圖指出,該企業低碳發展將經歷“碳達峰平臺期、穩步下降期及深度脫碳期”三個階段,通過實施鐵素資源優化、流程優化重構、系統能效提升、用能結構優化、低碳技術變革、產業耦合降碳六大技術路徑,建設碳排放數據管理體系及鋼鐵產品全生命周期(LCA)碳足跡兩大平臺,實現2025年碳排放總量較峰值降低10%,2030年碳排放總量較峰值降低30%,最終在2050年實現碳中和,并詳細闡明了該企業對各技術路徑的規劃目標,測算了各減碳技術路徑實施后帶來的碳減排量期望值,比較了不同技術路徑在不同發展階段所帶來的減碳效果。最后,結合該企業低碳發展技術路線圖的制定和實施過程,提出我國鋼鐵企業低碳發展的建議。Abstract: To implement the national development goal of “carbon peak, carbon neutral” and address the bottlenecks and challenges encountered by the steel industry in the process of moving toward low-carbon development, a series of studies on policies, technologies, and action plans has been conducted. Given the current situation and changing trend of carbon dioxide emission intensity of domestic and foreign iron and steel enterprises, the reasons for the different intensities of carbon dioxide emissions were analyzed. Further, general directions for carbon dioxide emission peak and carbon dioxide neutralization development in the Chinese iron and steel industry were provided. This study also analyzed the “carbon peak, carbon neutral” targets and implementation plans of the Chinese iron and steel industry and large domestic steel enterprises. The study mainly assessed the current production, current equipment used, technological process, and actual case of carbon dioxide emissions of a large iron and steel enterprise. Future changes in production equipment, production process evolution, technological innovation, and energy transformation based on planning aspects were fully considered in this analysis. A concrete technology roadmap of low-carbon development was made for Chinese iron and steel enterprises as a guide in implementing the national goal of “carbon peak, carbon neutralization.” This roadmap emphasizes that the enterprise will encounter three stages: carbon peak stage platform, steadily declining period, and depth of decarburization. It suggests the consideration of the following: implementing six technical development path that iron element resource optimization, process optimization reconstruction, system efficiency promotion, energy structure optimization, great progress in low-carbon technology, coupling between industries, and constructing a data management system for carbon dioxide emissions, and constructing carbon footprint platforms for the full life-cycle assessment (LCA) of steel products. The analysis found that the total carbon dioxide emissions in 2025 and 2030 will be reduced by 10% and 30%, respectively, and carbon dioxide neutrality will be achieved in 2050. Additionally, the plans of enterprises for their technological paths are clarified. The expected reduction in carbon emissions owing to the implementation of each technological path toward carbon dioxide reduction is calculated. The carbon reduction effects of different technological paths are compared in various development stages. Finally, combined with the establishment and execution process of the low-carbon development technology roadmap of enterprises, some suggestions on the low-carbon development of Chinese iron and steel enterprises are provided.
-
Key words:
- steel industry /
- carbon up to peak /
- carbon neutral /
- technology roadmap /
- implementation plan
-
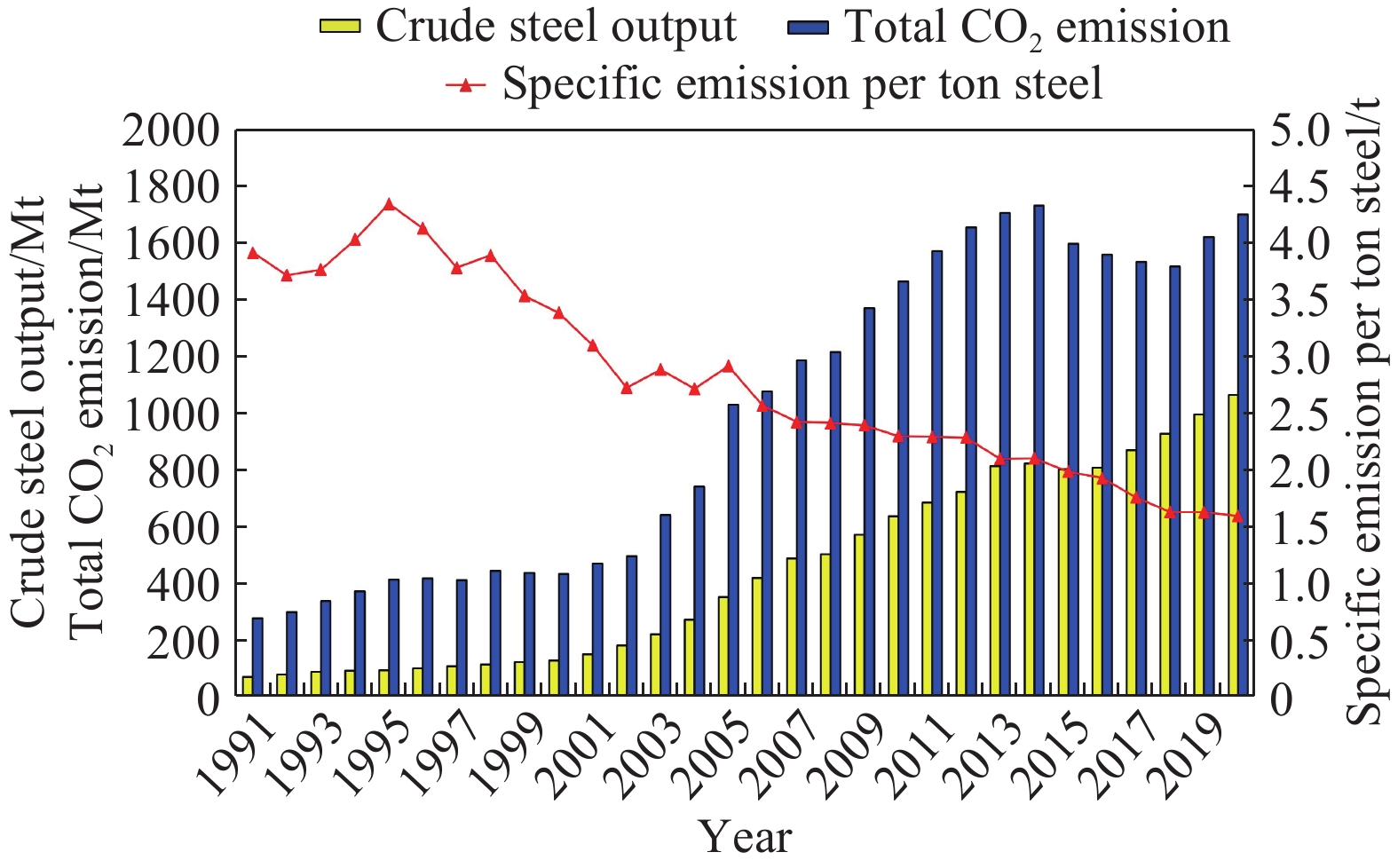
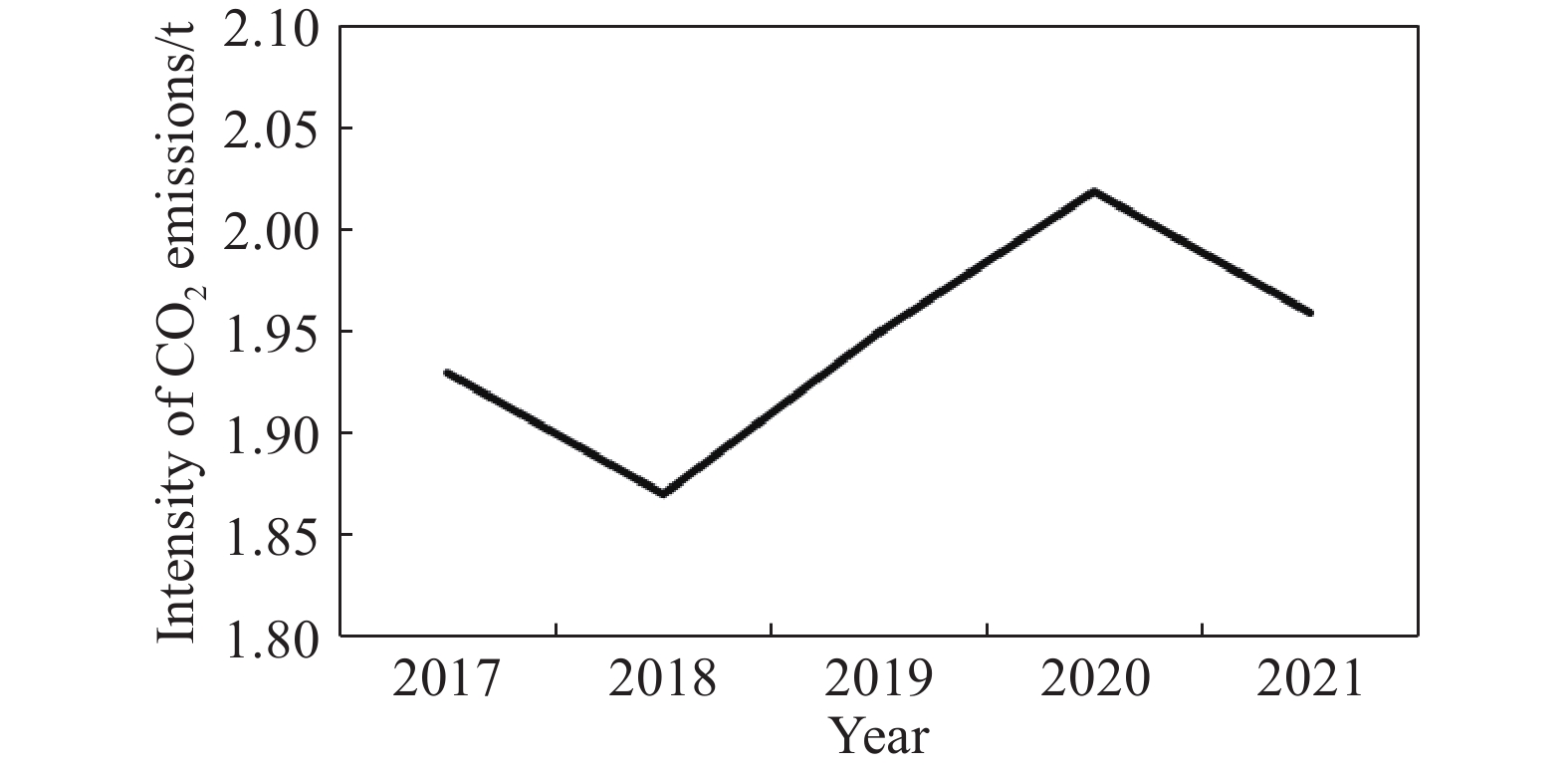
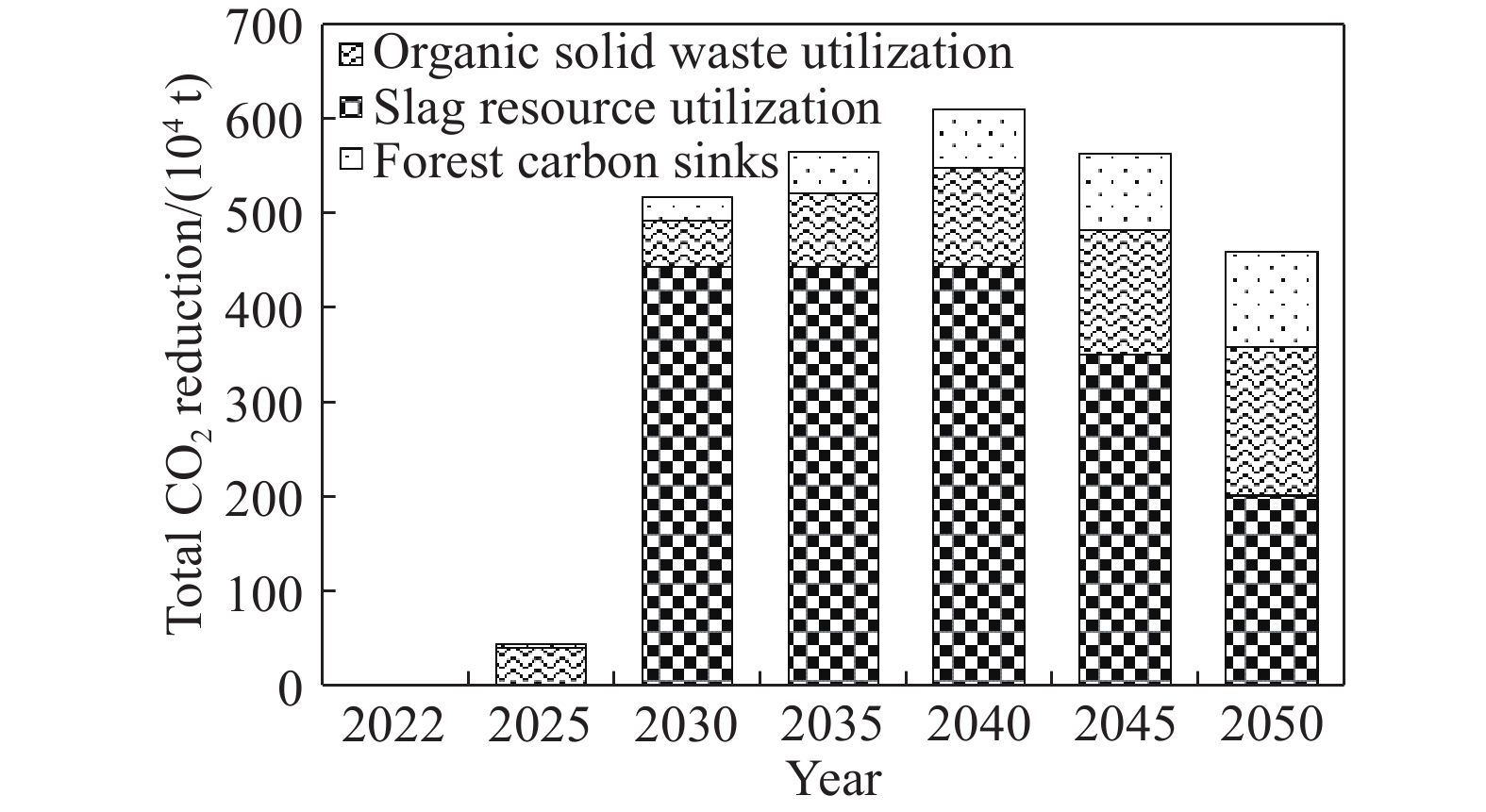
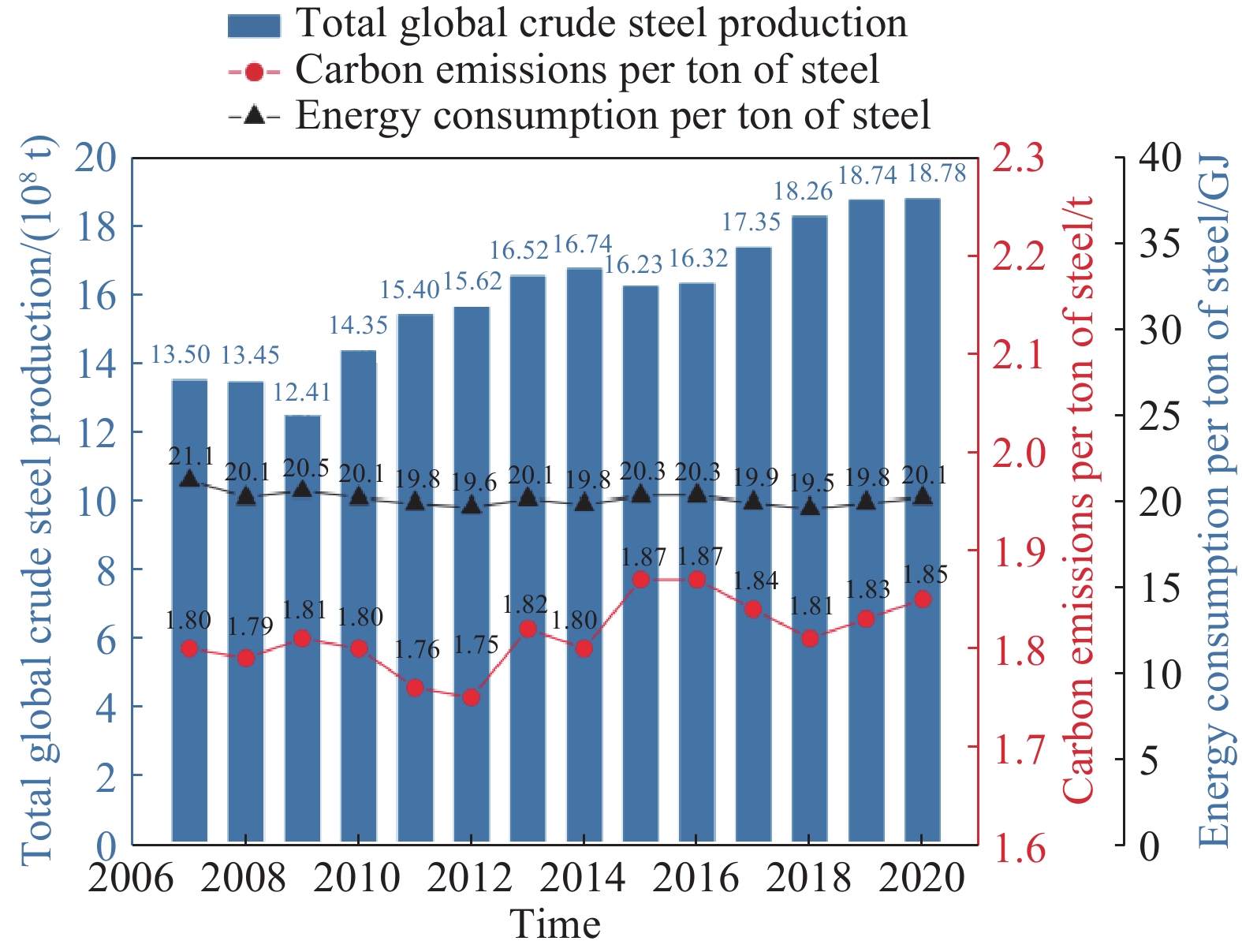
圖 1 全球鋼鐵企業粗鋼產量、噸鋼碳排放及噸鋼能耗情況[5]
Figure 1. Crude steel output, carbon emission, and energy consumption per ton of steel in global steel enterprises
www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] World Steel Association. Climate change and the production of iron and steel [R/OL]. Website Online (2021-05-17) [2022-09-22]. https://worldsteel.org/publications/policy-papers/climate-change-and-the-production-of-iron-and-steel/ [2] ArcelorMittal. Climate Action Reports (2019) [R/OL]. Website Online (2019-05-20) [2022-09-22]. https://corporate.arcelormittal.com/sustainability/climate-action-reports [3] Nippon Steel Corporation. Nippon Steel Sustainability Report 2020 [R/OL]. Website Online (2020-10-09) [2022-09-22]. https://www.nipponsteel.com/common/secure/en/csr/report/nsc/pdf/report2020.pdf [4] POSCO. POSCO’s dialogue for climate action—Building a better future together with sustainable steel [R/OL]. Website Online (2020-12-11) [2022-09-22]. http://corporatecitizenship.posco.com/citizen/resources/file/report/eng/2020_POSCO_CLIMATE_ACTION_REPORT.pdf [5] Cui Z F, Xu A J, Shangguan F Q. Low-carbon development strategy analysis of the domestic and foreign steel industry. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(9): 1496崔志峰, 徐安軍, 上官方欽. 國內外鋼鐵行業低碳發展策略分析. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(9):1496 [6] Shangguan F Q, Li X P, Zhou J C, et al. Strategic research on development of steels crap resources in China. Iron Steel, 2020, 55(6): 8 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190427上官方欽, 酈秀萍, 周繼程, 等. 中國廢鋼資源發展戰略研究. 鋼鐵, 2020, 55(6):8 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190427 [7] Shangguan F Q, Yin R Y, Li Y, et al. Dissussion on strategic significance of developing full scrap EAF process in China. Iron Steel, 2021, 56(8): 86 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200401上官方欽, 殷瑞鈺, 李煜等. 論中國發展全廢鋼電爐流程的戰略意義. 鋼鐵, 2021, 56(8):86 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200401 [8] Yao T L, Wu W, Yang Y, et al. Analysis on low-carbon development of China's steel industry under “dual-carbon” goal. J Iron Steel Res, 2022, 34(6): 505 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20210399姚同路, 吳偉, 楊勇, 等. “雙碳”目標下中國鋼鐵工業的低碳發展分析. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2022, 34(6):505 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20210399 [9] Shangguan F Q, Liu Z D, Yin R Y. Study on implementation path of “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality” in steel industry in China. China Metall, 2021, 31(9): 15 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210393上官方欽, 劉正東, 殷瑞鈺. 鋼鐵行業“碳達峰”“碳中和”實施路徑研究. 中國冶金, 2021, 31(9):15 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210393 [10] Xing Y, Cui Y K, Tian J L, et al. Application status and prospect of low carbon technology in iron and steel industry. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(4): 801 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204030邢奕, 崔永康, 田京雷, 等. 鋼鐵行業低碳技術應用現狀與展望. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(4):801 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204030 [11] Wang X D, Hu Q C, Zhang X D. Developing the full potential of preironmaking system to catch up with the advanced level of the industry. Hebei Metall, 2022(7): 1王新東, 胡啟晨, 張曉冬. 發揮鐵前系統潛力 趕超行業先進水平. 河北冶金, 2022(7):1 [12] Wang X D, Tian J L, Song C Y. Innovative practice technology and outlook in large iron and steel enterprise green manufacturing. Iron Steel, 2018, 53(2): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20170533王新東, 田京雷, 宋程遠. 大型鋼鐵企業綠色制造創新實踐與展望. 鋼鐵, 2018, 53(2):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20170533 [13] Wang X D, Li J X, Hu Q C. Application practice of source and process sulfur-nitrate reduction technology based on optimization of blast furnace charge structure. Iron Steel, 2019, 54(12): 104 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190287王新東, 李建新, 胡啟晨. 基于高爐爐料結構優化的源頭減排技術及應用. 鋼鐵, 2019, 54(12):104 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190287 [14] Wang X D, Jin Y L. Strategy analysis and testing study of high ratio of pellet utilized in blast furnace. Iron Steel, 2021, 56(5): 7 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210081王新東, 金永龍. 高爐使用高比例球團的戰略思考與球團生產的試驗研究. 鋼鐵, 2021, 56(5):7 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210081 [15] Zhou J C, Shangguan F Q, Ding Y, et al. Discuss on interface technology and energy loss of main Interface in steel manufacturing process. Iron Steel, 2020, 55(12): 99 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200091周繼程, 上官方欽, 丁毅, 等. 鋼鐵制造流程“界面”技術與界面能量損失分析. 鋼鐵, 2020, 55(12):99 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200091 [16] Yang J P, Zhang J S, Liu Q. Research progress on three kinds of classic process interface technologies in steelmaking?continuous casting section. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(12): 1542楊建平, 張江山, 劉青. 煉鋼?連鑄區段3種典型工序界面技術研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(12):1542 [17] He K, Wang L. Development and status of production energy consumption of China’s iron and steel industry. China Metall, 2021, 31(9): 26 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210303何坤, 王立. 中國鋼鐵工業生產能耗的發展與現狀. 中國冶金, 2021, 31(9):26 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210303 [18] Zhang Q, Cai J J. Systemic energy saving and energy efficiency improving of iron and steel making process. Iron Steel, 2021, 56(8): 32 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210222張琦, 蔡九菊. 鋼鐵制造流程系統節能與能效提升. 鋼鐵, 2021, 56(8):32 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20210222 [19] Xue Y L, Zhang J, Liu Y, et al. Roadmap of coal control and carbon reduction in the steel industry under the carbon peak and neutralization target. Environ Sci, 2022, 43(10): 4392 doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201081薛英嵐, 張靜, 劉宇, 等. “雙碳”目標下鋼鐵行業控煤降碳路線圖. 環境科學, 2022, 43(10):4392 doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201081 [20] Lu J, Fan J. Improve the comprehensive utilization level of metallurgical slag and promote cross industry collaborative carbon reduction [N]. China Enterprise New (2022-03-08) [2022-09-22]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCNDLAST2022&filename=CQYB202203080040&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=DF8C08wGV6naTjKjMf7YIzLsu4jYC1DdTlb-TWH_qdqBBI-taGN7CLUISW8gT3TRh2LrOqS8m3Q%3d鹿娟, 范捷. 提升冶金渣綜合利用水平, 促進跨行業協同減碳[N]. 中國企業報 (2022-03-08) [2022-09-22]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&dbname=CCNDLAST2022&filename=CQYB202203080040&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=DF8C08wGV6naTjKjMf7YIzLsu4jYC1DdTlb-TWH_qdqBBI-taGN7CLUISW8gT3TRh2LrOqS8m3Q%3d [21] Wang X D, Zhang C, Sun Y J, et al. Application practice of green manufacturing technology in tangsteel new district of HBIS group. Environ Eng, 2022, 40(7): 179 doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202207026王新東, 張弛, 孫宇佳, 等. 河鋼唐鋼新區綠色制造技術應用實踐. 環境工程, 2022, 40(7):179 doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202207026 [22] Wang X D. Paths and measures of technology upgrading in the new development stage of HBIS. Hebei Metall, 2022(1): 1 doi: 10.13630/j.cnki.13-1172.2022.0101王新東. 河鋼新發展階段技術升級的路徑與措施. 河北冶金, 2022(1):1 doi: 10.13630/j.cnki.13-1172.2022.0101 [23] Li X C, Li B. Low carbon transition path of China’s iron and steel industry under global temperature-control target. Iron Steel, 2019, 54(8): 224 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190178李新創, 李冰. 全球溫控目標下中國鋼鐵工業低碳轉型路徑. 鋼鐵, 2019, 54(8):224 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190178 [24] Wang X Y, Li B, Lu C, et al. China’s iron and steel industry carbon emissions peak pathways. Res Environ Sci, 2022, 35(2): 339 doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.11.11汪旭穎, 李冰, 呂晨, 等. 中國鋼鐵行業二氧化碳排放達峰路徑研究. 環境科學研究, 2022, 35(2):339 doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.11.11 [25] Shao Y J, Xu L, Liu X P. Discussion on solution of “carbon neutrality” in China’s steel production. China Metall, 2022, 32(4): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210664邵遠敬, 徐蕾, 劉校平, 等. 中國鋼鐵生產“碳中和”解決方案探討. 中國冶金, 2022, 32(4):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20210664 [26] Cheng M L. Analysis and prospect of carbon dioxide emission reduction path of iron and steel enterprises. Metall Econ Manage, 2022(4): 18程茉莉. 鋼鐵企業二氧化碳減排路徑分析及展望. 冶金經濟與管理, 2022(4):18 -




 下載:
下載: