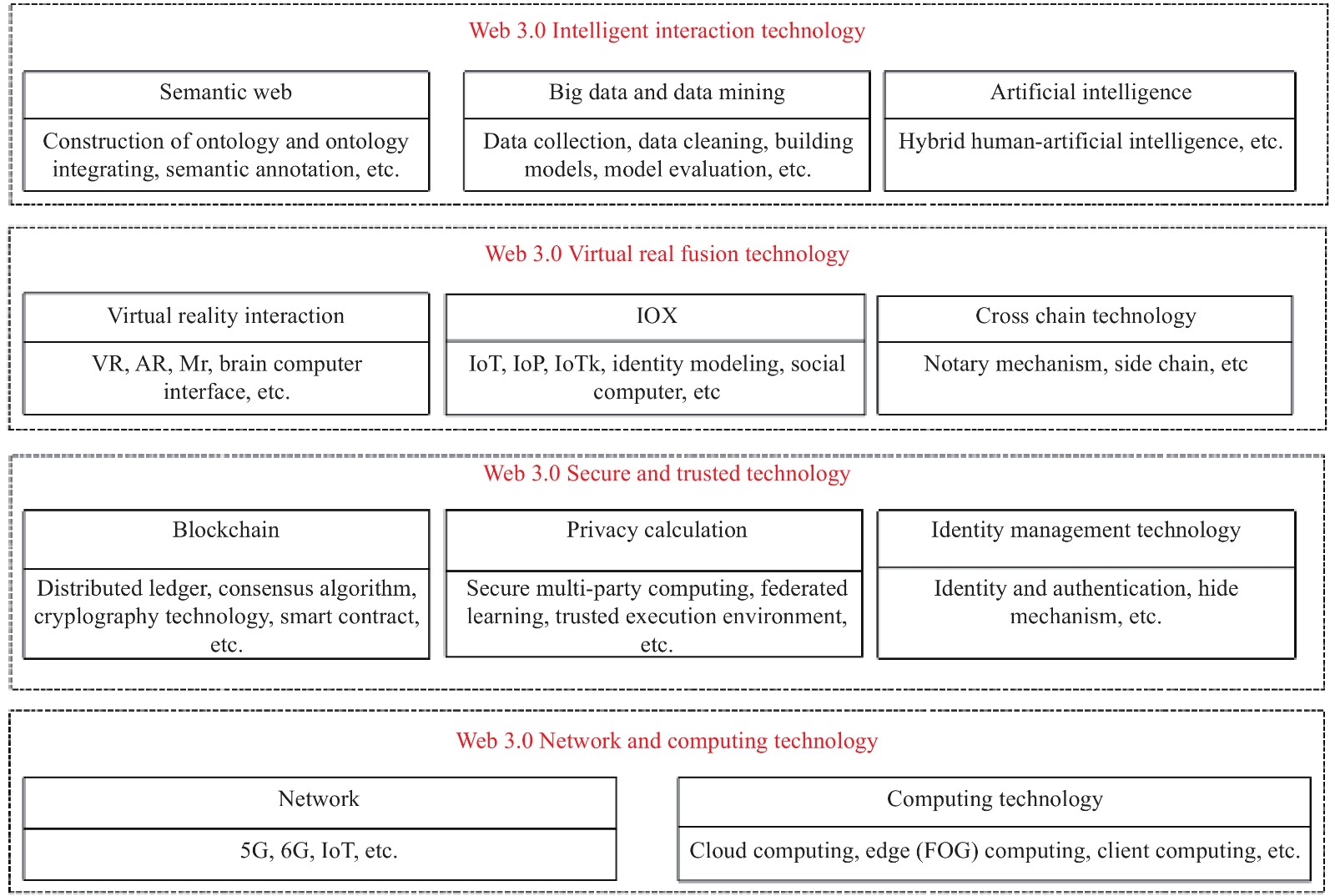
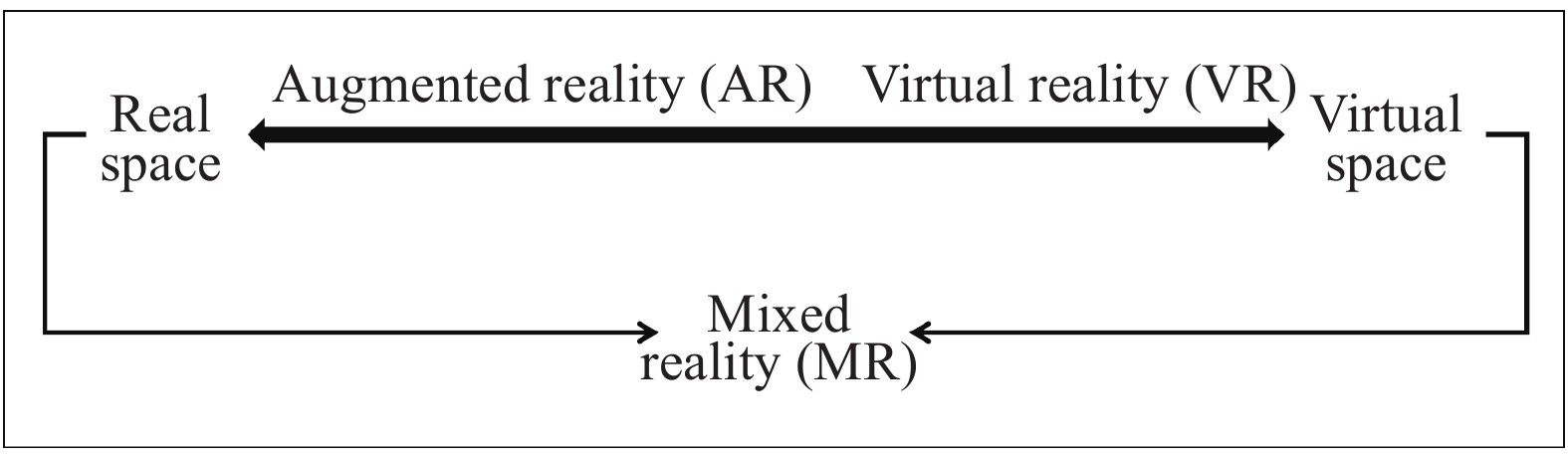
-
摘要: Web 3.0作為人類所期待的下一代互聯網受到了學術界、產業界等廣泛關注,本文從不同國家(包括政策、公司和產品)、國際組織(ITU、IEEE、IET、W3C)和數據庫(Scopus、CNKI)出版物數量角度分析了Web 3.0的發展歷程以及發展現狀,得出Web 3.0中的基礎技術仍然是制約其發展的瓶頸.本文對Web 3.0中的基礎技術深入剖析,從網絡與計算技術(5G、6G、物聯網、云計算、邊緣計算及端計算),安全可信技術(區塊鏈技術、隱私計算、身份管理技術),虛實融合技術(虛實交互技術、IoX、跨鏈技術),智能交互技術(語義網、大數據與數據挖掘、人工智能)四個維度進行闡述.最后對未來Web 3.0在經濟、社會、文化方面引起的變革進行了總結.目前無論基于是信息技術升級的需求,還是走出疫情困擾持續低迷的全球經濟需求,都需要Web 3.0為經濟、科技、文化、社會的變革注入新動能.Abstract: Web 3.0 has widely piqued the interest of academia and industry as the next-generation internet. Therefore, this study analyzes the development process and status of Web 3.0 from the perspectives of countries (policies, companies, and products), international organizations (ITU, IEEE, IET, and W3C), and publications databases (Scopus, CNKI). It is concluded that the fundamental technology in Web 3.0 remains the bottleneck limiting its further development. This study performed an in-depth analysis of the fundamental technologies in Web 3.0 from four perspectives. The first is computing and networking. The ubiquitous “Internet of Things” architecture generates a large amount of real-time data, and it has become an inevitable trend to form a cloud, edge, and end multi-level computing collaboration mode. Furthermore, 5G and 6G network and computing technologies work collaboratively to lay a solid foundation for the best user experience. The second is a secure and reliable technology. In Web 3.0, data become users’ data assets. Blockchain technology, privacy-computing technology, and identity management technology are needed to build the technical foundation for value transmission when transferring digital assets and currency. The third technology is virtual-real fusion. Web 3.0 is a three-dimensional holographic, which means that not only will the virtual and real world be integrated, but the virtual world will also break the barriers between each virtual ecology. The technologies related to the fusion of the virtual and real world include virtual and real interaction technology, IoX and technologies related to the fusion of the virtual world include cross-chain technology. The fourth is intelligent interaction technology. The new generation of the internet will not only respond mechanically to the users’ search content but will also be able to read information like humans, providing users with more accurate, reliable, and personalized services. Intelligent interaction technology mainly includes: semantic web technology, big data, data mining technology, and artificial intelligence technology. Finally, it summarizes the future changes caused by Web 3.0 in the economy, society, culture, and Web 3.0 road with Chinese characteristics. Web 3.0 economic reform is mainly reflected in user-centered value creation. The social reform of Web 3.0 is mainly reflected in reshaping organizations, transforming from traditional and centralized to decentralized organizations. The cultural reform of Web 3.0 is mainly reflected in three fields. It protects the rights and interests of artists and artistic works, which greatly promotes the creation of art in Web 3.0; moreover, it promotes the preservation of cultural heritage and the development of tourism. It also establishes Game Finance (GameFi) to promote the improvement of language, writing, music, aesthetics, and other aspects of games. At present, we need Web 3.0 to impart new momentum to the economic, technological, cultural, and social changes, whether it is based on the demand for upgrading information technology or the need to get rid of the persistent downturn in the global economy caused by the epidemic.
-
表 1 Web 1.0到Web 3.0的特點對比分析表
Table 1. Comparison and analysis of features of Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
Stage Function Technology Information properties Profit model Representative platform Web 1.0 Display information, etc. HTML, XML, CSS, etc. Platforms create, platforms own, and platforms control Platforms gain profits Sohu, Sina, NetEase, etc. Web 2.0 Interactive, etc. Blog,TAG,SNS,RSS,Wiki,AJAX,REST,etc. Users create, platforms own, and platforms control Platforms distribute profits WeChat, Youtube, Google, etc. Web 3.0 Intelligent interaction and virtual reality integration
safe and reliable, etc.Semantic web, immersive technology, decentralized technology, etc. Users create, users own, and users control Users distribute profits Opensea,Genopets,Berty Technologies, etc. 表 2 部分專家及研究者對Web 3.0的見解
Table 2. Opinions of experts and researchers on Web 3.0
Author Time Essay Description Cui-hong Hu 2012 Research on Web 3.0 application in the resources integration portal Web 3.0 will intelligently integrate Internet information and build personalized Internet for users[3]. Yu-heng Sun 2014 Visualization analysis of domestic Web 3.0 research progress Web 3.0 is characterized by personalization, precision, intelligence, and diversification[4]. Keshab Nath 2014 Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 - Evolution of the Web and
its Various ChallengesWeb 3.0 can be defined as a semantic network and personalized network[5]. Abdul Ghaffar Khan 2019 A journey of WEB and Blockchain towards Industry 4.0: An Overview Web 3.0 usually refers to the semantic web[6]. Blair MacIntyre 2018 Thoughts on the Future of WebXR and the Immersive Web Build the future immersive network through WebXR technology[7]. Faten Adel Alabdulwahhab 2018 Web 3.0: The Decentralized Web Blockchain networks and
Protocol InnovationThe direction of the future network is a decentralized network[8]. Massimo Ragnedda 2020 Social, Economic, and Technological
ChallengesWeb 3.0 has no control center and a unique profit center based on decentralized implementation[9]. Zhuo-tao Liu 2021 Make Web 3.0 Connected Web 3.0 contains three key factors: blockchains, federated or centralized platforms, and interoperability platforms[10]. Xiao-zhun Peng 2022 Web 3.0, Metauniverse, and the Development of Financial Technology Based on decentralized and interactive internet[11]. Yan Liu 2022 Three-tier technical architecture supports Web 3.0 Web 3.0 returns the ownership of digital content and the corresponding value distribution right to the creators[12]. 表 3 中國和美國在消費互聯網中的Web 3.0相關產品
Table 3. Web 3.0 related products in the consumer internet in China and the United States
Country Market Company Products/services Blockchain Blockchain type Features Open source China Tencent Magic Nucleus Zhi Xin Chain Alliance chain NFT platform. Yes Alibaba Jingtan AntChain Alliance chain NFT platform. No JD Lingxi JD Chain Alliance chain NFT platform. Yes USA Ardrive Ardrive Arweave Public chain Decentralized cloud disk platform. Yes Uniswap Labs Uniswap Ethereum Public chain Decentralized exchange platform. Yes Berty Technologies Berty IPFS Public chain Instant messaging software platform. Yes OpenSea OpenSea Ethereum, Polygon Public chain NFT trading platform. Yes ConsenSys Metamask Ethereum Public chain Decentralized Wallet platform. Yes Genopets Genopets Solana Public chain “Sports Earn Coins” NFT game platform. Brave Software Brave Solana Public chain Decentralized browser platform. Yes Livepeer, Inc. Livepeer Ethereum Public chain Decentralized video transcoding platform. Yes Sound.xyz Sound.xyz Arweave Public chain Decentralized music platform. Yes 表 4 中國和美國在工業互聯網中的Web 3.0相關產品
Table 4. Web 3.0 related products in the industrial internet in China and the United States
Country Market Company Products/services Blockchain Blockchain type Application scenario Open source China Haier Haier Internet of Clothing Hichain Alliance chain Clothing management No Inspur Inspur Quality Code Inspur Quality Chain Alliance chain Supply chain No Tianhecloud Tianhe Chain Control Tianhe Chain Alliance chain Managing industry, object tracking No USA IBM IBM Waston Hyperledger Alliance chain Food safety, healthcare, supply chain, and object tracking[16] Yes Trace Labs Oringintrail Multiple Blockchains Public chain Data provenance, drug safety, and food safety[16] Yes Servntire Netobjex Multiple Blockchains Public chain Smart cities, manufacturing industry, automotive industry, etc.[16] Yes 表 5 Web 3.0的發展階段
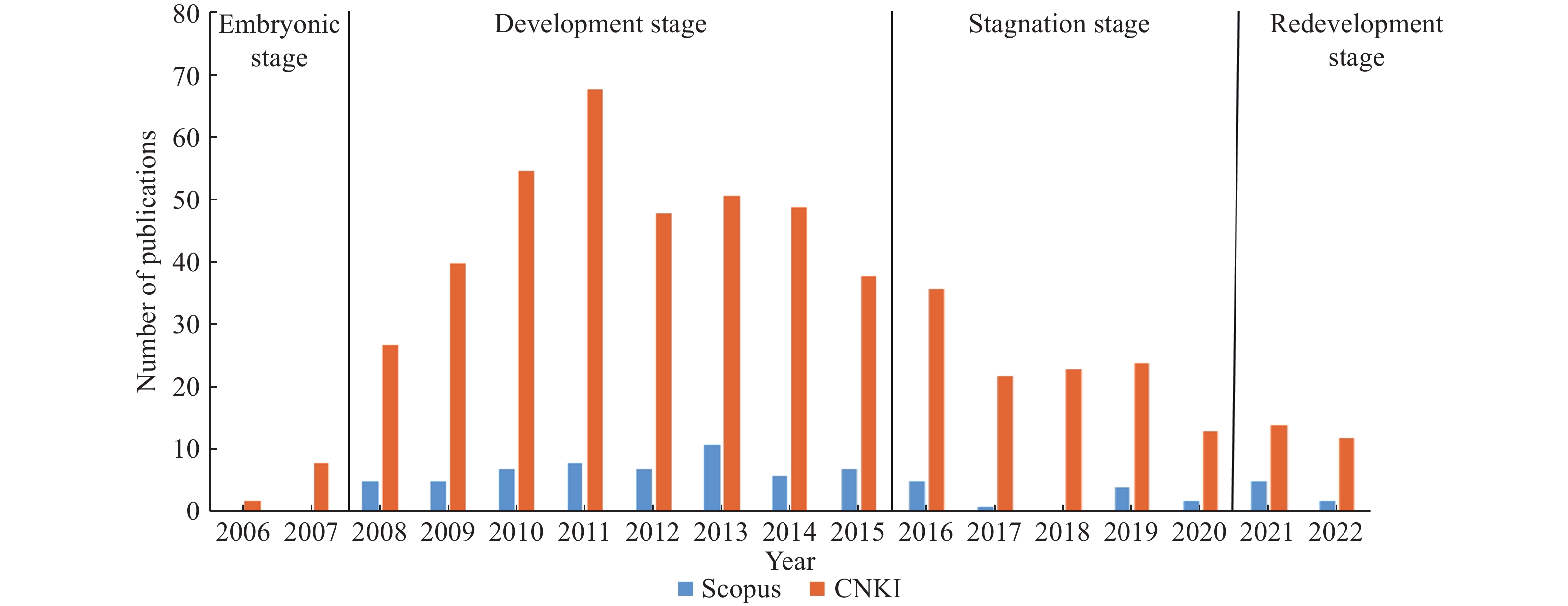
Table 5. Development stage division of Web 3.0
Period Stage Description Total number of publications Annual average number of publications Scopus CNKI Scopus CNKI 2006–2007 Embryonic Stage People have positive ideas about Web 3.0. 0 10 0 5 2008–2016 Development Stage Mainly based on smart applications. 61 412 6.78 45.78 2017–2020 Stagnation stage Restricted by many issues. 7 82 1.75 20.5 2021–2022 Redevelopment stage Integrate multi-technology to achieve
product transformation.7 26 3.5 13 表 6 隱私計算
Table 6. Privacy calculations
Method Secure multi-party computation Federated learning Trusted computing environment Core concept Data-oriented. The original data flow between nodes after a series of operations. Model-oriented. The original data is only trained locally, and the computation results are exchanged between nodes. Data-oriented. The original data is encrypted and performed in a secure computing environment provided by special hardware. Application direction Focus on the need for multi-party data for joint computational analysis. Focus on the need for multi-party data for distributed machine learning model training. Focus on the need for multi-party data for joint computational analysis. Original data flow direction Original data is encrypted and exchanged. Original data is not exchanged. Original data is encrypted and exchanged. Hardware requirements Common hardware. Common hardware. Specified hardware. www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Litan R E, Rivlin A M. Projecting the economic impact of the Internet. Am Econ Rev, 2001, 91(2): 313 doi: 10.1257/aer.91.2.313 [2] China Institute of Communications. One article to understand the development of industrial Internet platform in China. [EB/ OL]. Science Education (2019-04-15) [2022-09-14].https://www.china-cic.cn/detail/15/46/1741中國通訊學會. 一文讀懂工業互聯網平臺在中國的發展歷程[EB/OL]. 科普教育(2019-04-15) [2022-09-14].https://www.china-cic.cn/Detail/15/46/1741 [3] Hu C H. Research on Web 3.0 application in the resources integration portal // 2012 Second International Conference on Business Computing and Global Informatization. Shanghai, 2012: 728 [4] Sun Y S, Xiong Y, Chen W. Visual analysis of research development on Web 3.0 in China. J Inf Resour Manag, 2014, 4(3): 18孫雨生, 熊英, 陳衛. 國內Web 3. 0研究進展可視化分析. 信息資源管理學報, 2014, 4(3):18 [5] Nath K, Dhar S, Basishtha S. Web 1.0 to Web 3.0-Evolution of the Web and its various challenges // 2014 International Conference on Reliability Optimization and Information Technology (ICROIT). Faridabad, 2014: 86 [6] Khan A G, Zahid A H, Hussain M, et al. A journey of WEB and blockchain towards the industry 4.0: An overview // 2019 International Conference on Innovative Computing (ICIC). Lahore, 2019: 1 [7] Maclntyre B, Smith T F. Thoughts on the future of WebXR and the immersive web // 2018 IEEE international symposium on mixed and augmented reality adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct). Munich, 2018: 338 [8] Alabdulwahhab F A. Web 3.0: the decentralized web blockchain networks and protocol innovation // 2018 1st International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS). Riyadh, 2018: 1 [9] Ragnedda M, Destefanis G. Blockchain and Web 3.0. London: Routledge, 2019 [10] Liu Z T, Xiang Y X, Shi J, et al. Make Web 3.0 connected. IEEE Trans Dependable Secure Comput, 2022, 19(5): 2965 doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2021.3079315 [11] Peng X Z, Dong C C. Web 3.0, metauniverse and the development of financial technology. FinTech Time, 2022, 30(8): 18彭小準, 董晨晨. Web3.0, 元宇宙與金融科技的發展. 金融科技時代, 2022, 30(8):18 [12] Liu Y. Three tier technical architecture supports Web 3.0. Science and Technology Daily, 2022-07-11劉艷. 三層技術架構撐起Web 3.0. 科技日報, 2022-07-11 [13] Li J Q, Yu F R, Deng G Q, et al. Industrial Internet: A survey on the enabling technologies, applications, and challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1504 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2691349 [14] Li K K, Li Z H. The liveliness and calmness of Web 3.0. Large scale applications still need time to test [N]. China Business News, 2022-07-18 (C02)李昆昆, 李正豪. Web 3.0的熱鬧與冷靜大規模應用仍需時間檢驗. 中國經營報, 2022-07-18(C02) [15] Gyro Research Institute. Blockchain+Industrial Internet Industry Research Report [EB/OL]. Tencent (2021-01-13) [2022-09-14].https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20210125A0AVAP00陀螺研究院. 區塊鏈+工業互聯網行業研究報告[EB/OL]. 騰訊網(2021-01-13) [2022-09-14].https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20210125A0AVAP00 [16] Latif S, Idrees Z, e Huma Z, et al. Blockchain technology for the industrial Internet of Things: A comprehensive survey on security challenges, architectures, applications, and future research directions. Trans Emerging Tel Tech, 2021, [17] Ning H S, Wang Z O. Future internet of things architecture: Like mankind neural system or social organization framework? IEEE Commun Lett, 2011, 15(4): 461 [18] Vega M T, Liaskos C, Abadal S, et al. Immersive interconnected virtual and augmented reality: A 5G and IoT perspective. J Netw Syst Manage, 2020, 28(4): 796 doi: 10.1007/s10922-020-09545-w [19] Zhou P, Shen K, Kumar N, et al. Communication-efficient offloading for mobile-edge computing in 5G heterogeneous networks. IEEE Internet Things J, 2021, 8(13): 10237 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3029166 [20] Qiao X Q, Huang Y K, Dustdar S, et al. 6G vision: An AI-driven decentralized network and service architecture. IEEE Internet Comput, 2020, 24(4): 33 doi: 10.1109/MIC.2020.2987738 [21] Hu P F, Chen W. Software-defined edge computing (SDEC): Principles, open system architecture and challenges // 2019 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced & Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Cloud & Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation. Leicester, 2019: 8 [22] Liu H, Ning H S, Xiong Q X, et al. Shared authority based privacy-preserving authentication protocol in cloud computing. IEEE T Parall Distr, 2014, 26(1): 241 [23] Ning H S, Liu H. Cyber-physical-social-thinking space based science and technology framework for the Internet of Things. Sci China Inf Sci, 2015, 58(3): 1 [24] Ning H S, Liu H. Cyber-physical-social based security architecture for future Internet of Things. Adv Internet Things, 2012, 2(1): 1 doi: 10.4236/ait.2012.21001 [25] Yao X X, Farha F, Li R Y, et al. Security and privacy issues of physical objects in the IoT: Challenges and opportunities. Digit Commun Netw, 2021(3): 373 [26] Yao Q. Review of research progress of distributed ledger technology. Wuhan Finance, 2018(3): 4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3540.2018.03.002姚前. 分布式賬本技術研究進展綜述. 武漢金融, 2018(3):4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3540.2018.03.002 [27] Zhou J P, Feng Y X, Wang Z Y, et al. Using secure multi-party computation to protect privacy on a permissioned blockchain. Sensors (Basel) , 2021, 21(4): 1540 doi: 10.3390/s21041540 [28] Ohata S. Recent advances in practical secure multi-party computation. IEICE Trans Fundament Electron,Commun Com Sci, 2020, 103(10): 1134 [29] Melis L, Song C, De Cristofaro E, et al. Exploiting unintended feature leakage in collaborative learning // 2019 IEEE symposium on security and privacy (SP). San Francisco, 2019: 691 [30] Wei K, Li J, Ding M, et al. Federated learning with differential privacy: Algorithms and performance analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur, 2020, 15: 3454 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2988575 [31] Peng T, Guan K J, Liu J R. A privacy-preserving mobile crowdsensing scheme based on blockchain and trusted execution environment. IEICE Trans Inf Syst, 2022, E105.D(2): 215 doi: 10.1587/transinf.2021BCP0001 [32] Yao Q, Zhang D W. Survey on identity management in blockchain. J Softw, 2021, 32(7): 2260 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006309姚前, 張大偉. 區塊鏈系統中身份管理技術研究綜述. 軟件學報, 2021, 32(7):2260 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006309 [33] Nameless. Brain-computer interface: From science fiction to reality. Today Sci &Technol, 2021(2): 43佚名. 腦機接口: 從科幻走向現實. 今日科技, 2021(2):43 [34] Ning H S, Shi F F, Cui S, et al. From IoT to future cyber-enabled Internet of X and its fundamental issues. IEEE Internet Things J, 2021, 8(7): 6077 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3033547 [35] Guo Z, Guo S Y, Zhang S L, et al. Analysis of cross-chain technology of blockchain. Chin J Internet Things, 2020, 4(2): 35 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00162郭朝, 郭帥印, 張勝利, 等. 區塊鏈跨鏈技術分析. 物聯網學報, 2020, 4(2):35 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00162 [36] Han X, Yuan Y, Wang F Y. Security problems on blockchain: The state of the art and future trends. Acta Autom Sin, 2019, 45(1): 206韓璇, 袁勇, 王飛躍. 區塊鏈安全問題: 研究現狀與展望. 自動化學報, 2019, 45(1):206 [37] Wei W H. Research on semantic web and its core technology. China Comput &Commun, 2021, 33(11): 6魏武華. 語義Web及其核心技術研究綜述. 信息與電腦(理論版), 2021, 33(11):6 [38] Shi F F, Li Q J, Zhu T, et al. A survey of data semantization in Internet of Things. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 313 doi: 10.3390/s18010313 [39] Zhang X, Li X, Wen Y Q, et al. Building virtual ontologies in semantic web. J Southeast Univ (Nat Sci Ed) , 2015, 45(4): 652張祥, 李星, 溫韻清, 等. 語義網虛擬本體構建. 東南大學學報(自然科學版), 2015, 45(4):652 [40] Nguyễn V B. Đề xuất hệ thống thông minh hỗ trợ tìm kiếm việc làm//Hội thảo Khoa học Quốc gia. Việt, 2013 [41] Kiyomoto S, Rahman M S, Basu A. On blockchain-based anonymized dataset distribution platform // 2017 IEEE 15th International Conference on Software Engineering Research, Management and Applications. London, 2017: 85 [42] Jung M Y, Jang J W. Data management and searching system and method to provide increased security for IoT platform // 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC). Jeju, 2017: 873 [43] Zhang F, Zhang Y H. A big data mining and blockchain-enabled security approach for agricultural based on Internet of Things. Wirel Commun Mob Comput, 2020, 2020: 6612972 [44] Zhang Z M, Shi F F, Wan Y L, et al. Application progress of artificial intelligence in military confrontation. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(9): 1106張智敏, 石飛飛, 萬月亮, 等. 人工智能在軍事對抗中的應用進展. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(9):1106 [45] Chen L M, Ning H S, Nugent C D, et al. Hybrid human-artificial intelligence. Computer, 2020, 53(8): 14 doi: 10.1109/MC.2020.2997573 [46] Ning H S, Yin R, Ullah A, et al. A survey on hybrid human-artificial intelligence for autonomous driving. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst, 2022, 23(7): 6011 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3074695 [47] Gao Q N, Ning H S, Du B. A survey on the development of intelligent robots in speech emotion recognition // 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC). Harbin, 2021: 951 [48] Chohan U W. Web 3.0: The future architecture of the Internet? SSRN Journal,https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4037693 [49] Keizer N V, Yang F, Psaras I, et al. The case for AI based Web3 reputation Systems // 2021 IFIP Networking Conference (IFIP Networking). Espoo and Helsinki, 2021: 1 [50] Cunningham S, Flew T. A Research Agenda for Creative Industries. London: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2019 [51] Tr?ek D. Cultural heritage preservation by using blockchain technologies. Herit Sci, 2022, 10(1): 6 doi: 10.1186/s40494-021-00643-9 [52] Nameless. Use blockchain digital collections to tell a good story about China—the third session of the frontier workshop of “China’s impression of the cultural meta universe” was successfully held [EB/OL]. China’s Actual Condition Website (2022-09-26)[2022-09-26]. http://guoqing.china.com.cn/2022-09/26/content_78437960.htm佚名. 運用區塊鏈數字藏品講好中國故事—“文化元宇宙的中國印象”前沿工作坊第三期順利舉辦[EB/OL]. 中國國情網 (2022-09-26)[2022-09-26]. http://guoqing.china.com.cn/2022-09/26/content_78437960.htm [53] ‘Digital Collection’ brings traditional culture ‘alive’ [EB/OL]. Hangzhou CPPCC News Network. (2022-09-26)[2022-09-26]. https://www.hzzx.gov.cn/content/2021-12/13/content_8117464.htm“數字藏品”讓傳統文化“活起來”[EB/OL]. 杭州政協新聞 (2022-12-13)[2022-12-13]. https://www.hzzx.gov.cn/content/2021-12/13/content_8117464.htm -




 下載:
下載: