Influence mechanism of fatty acid unsaturation on the intensification of low-rank coal flotation
-
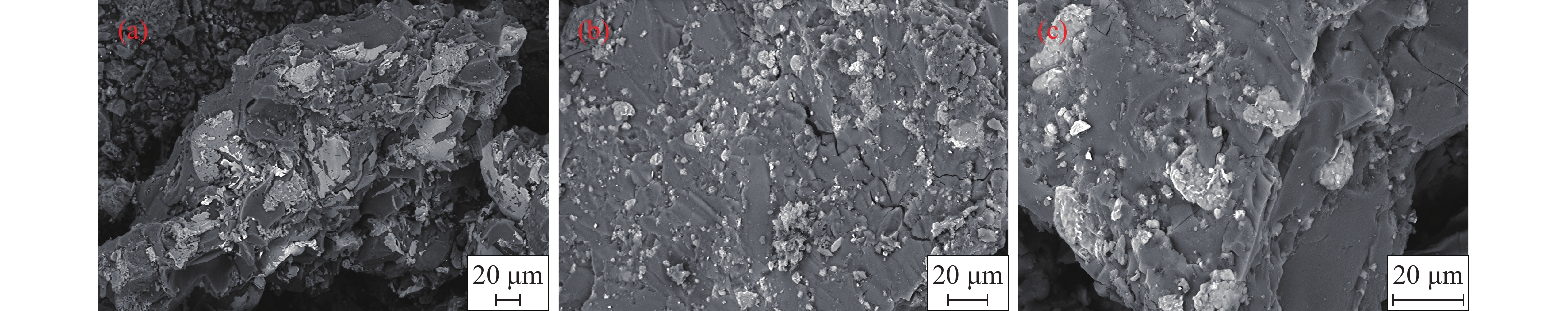
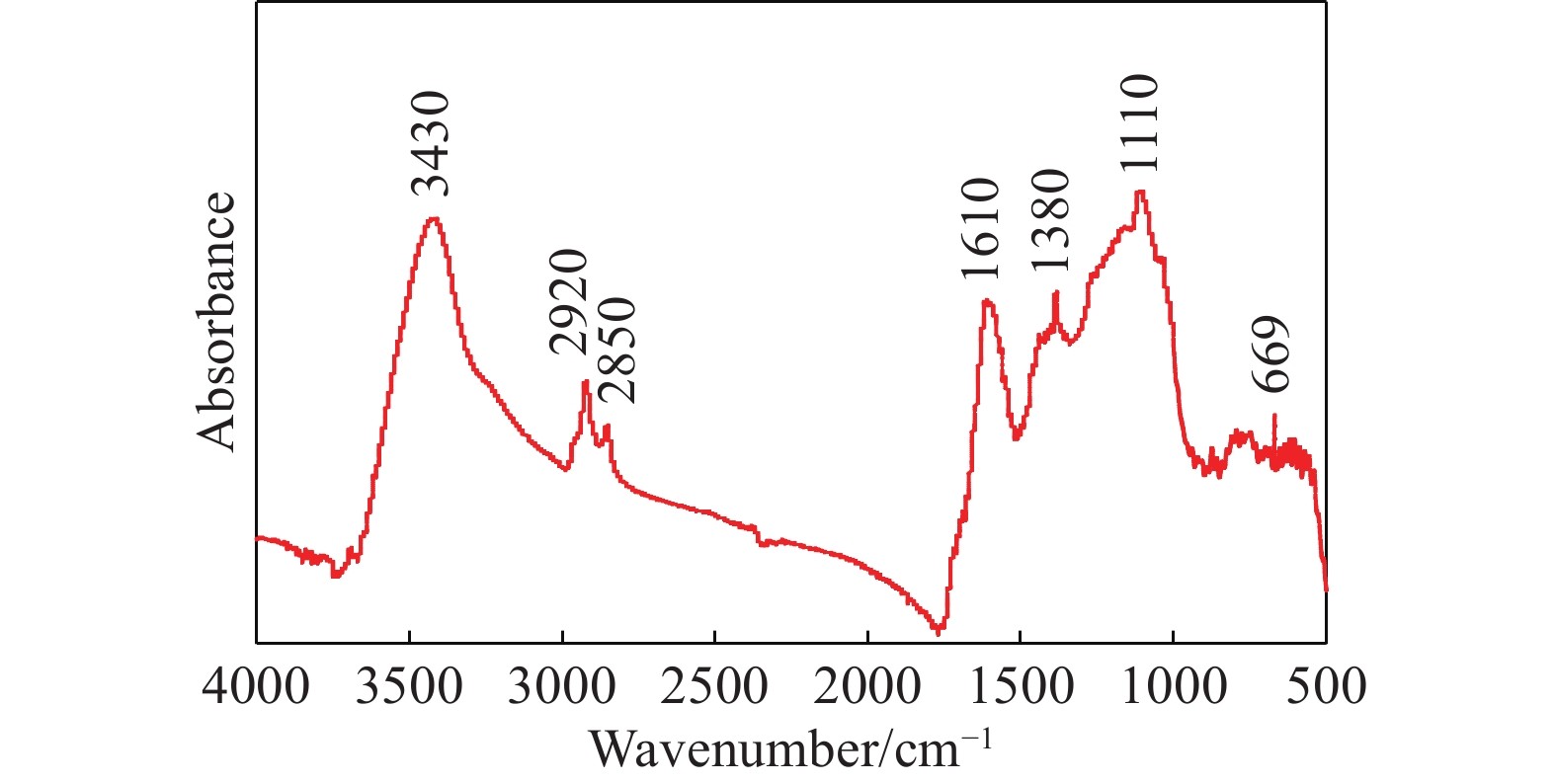
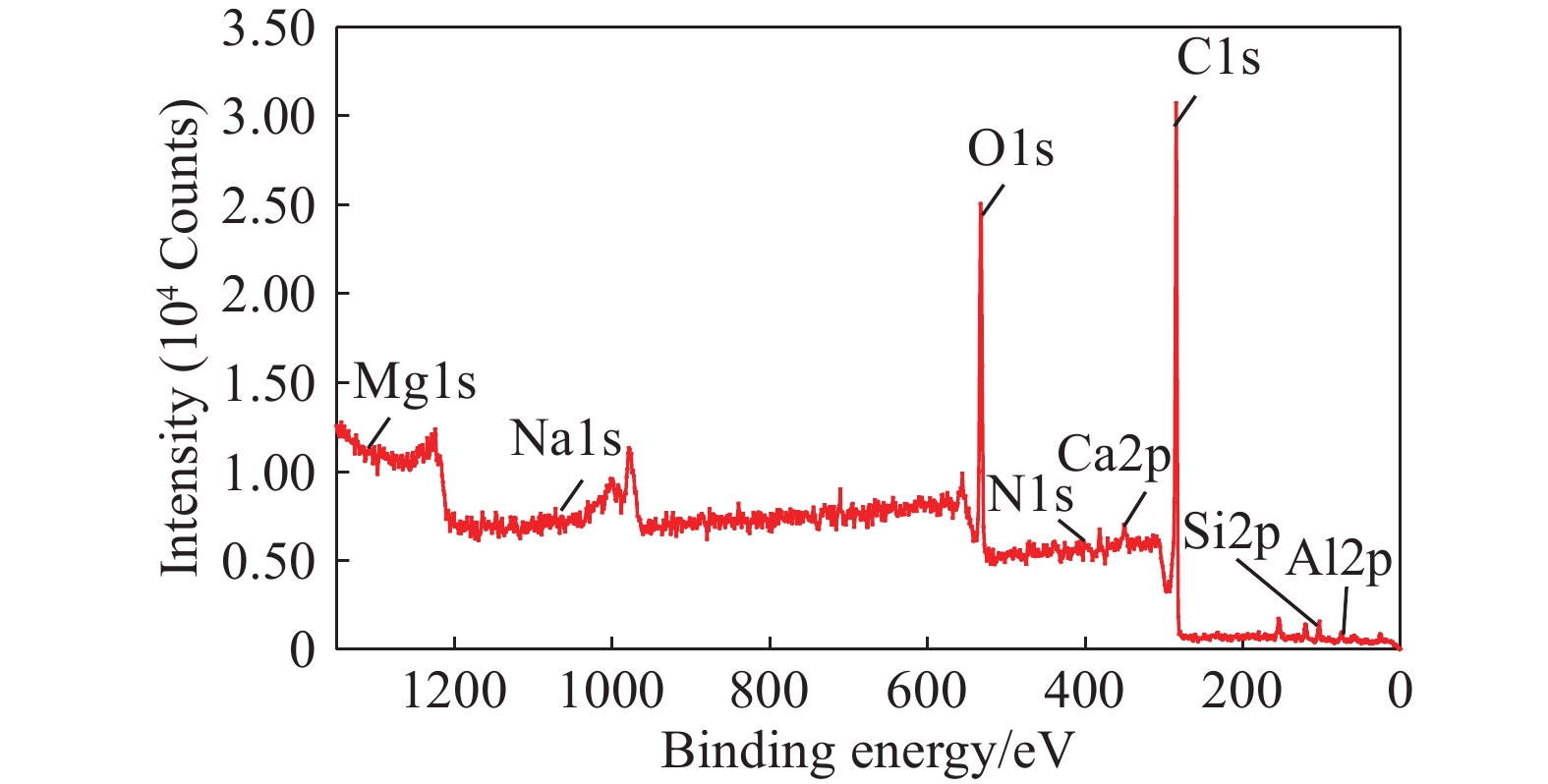
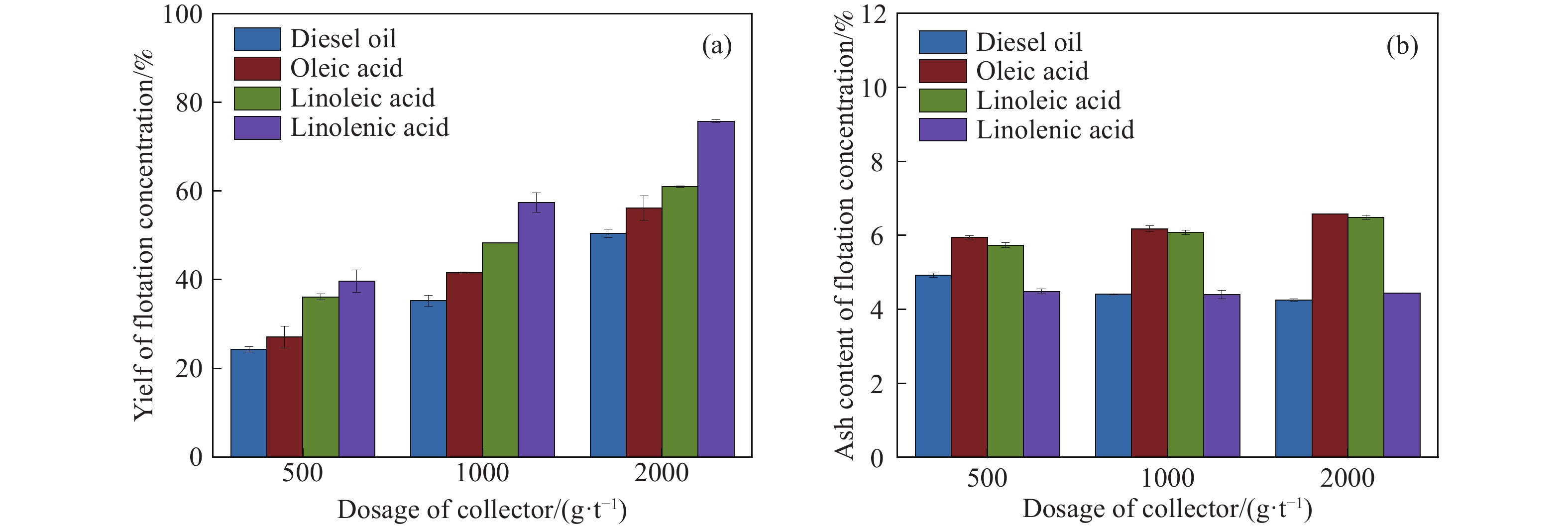
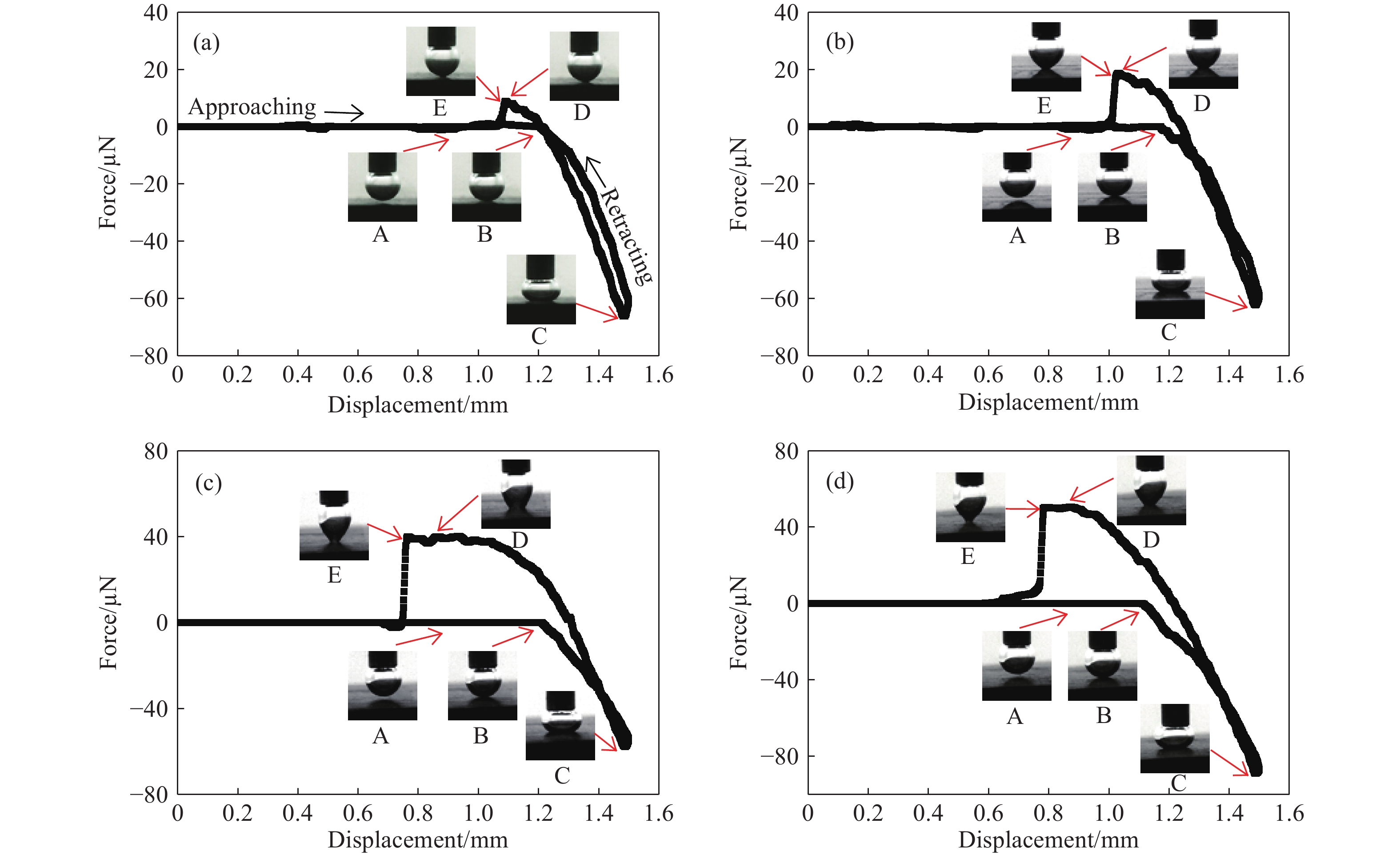
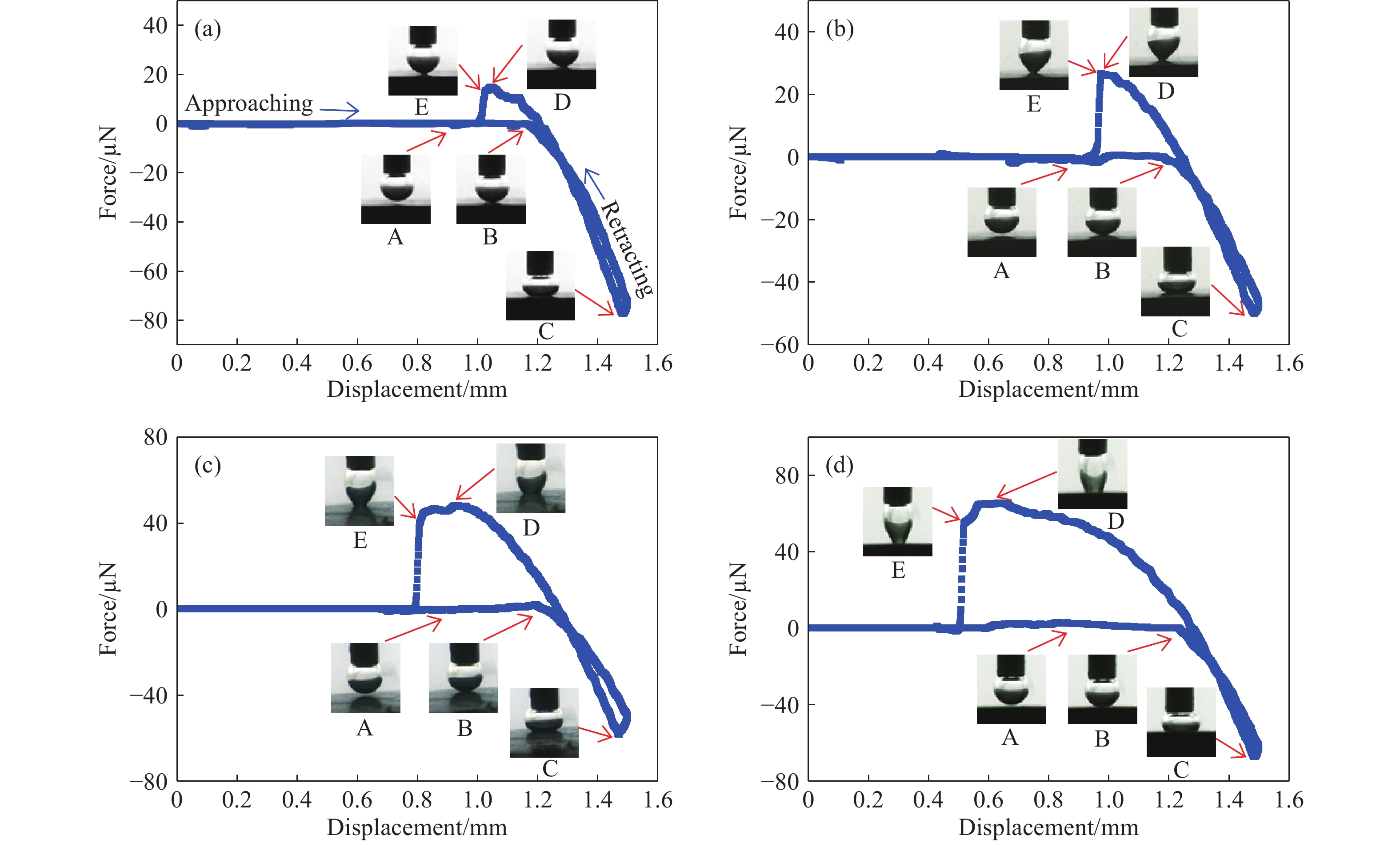
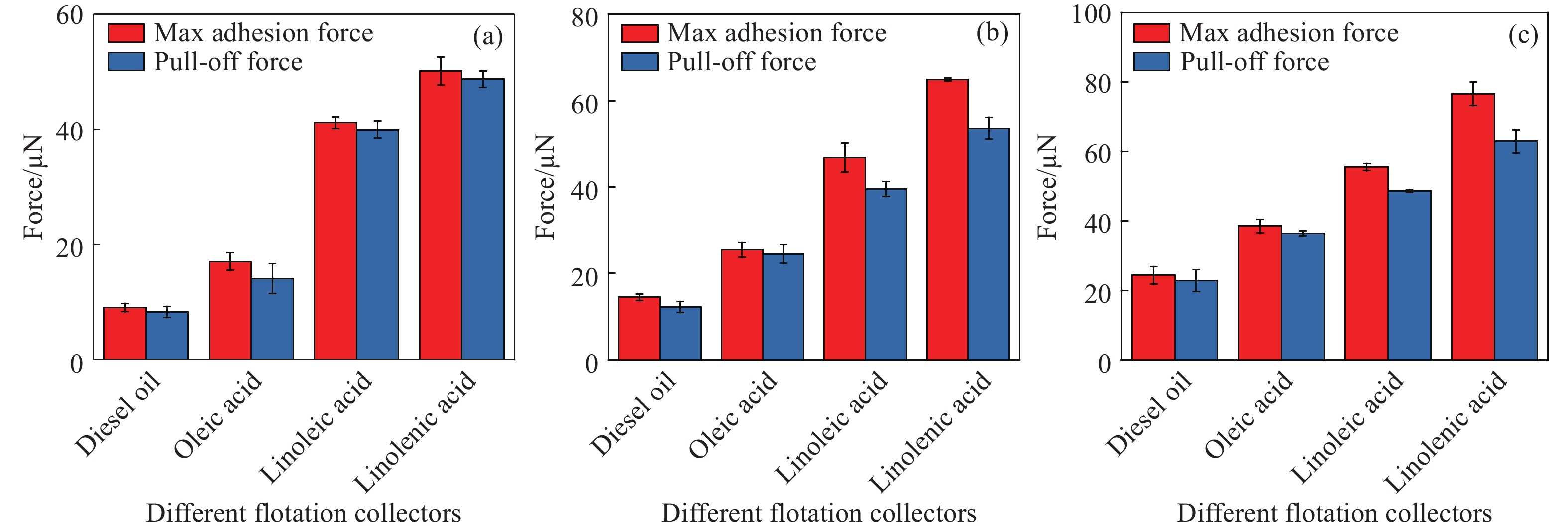
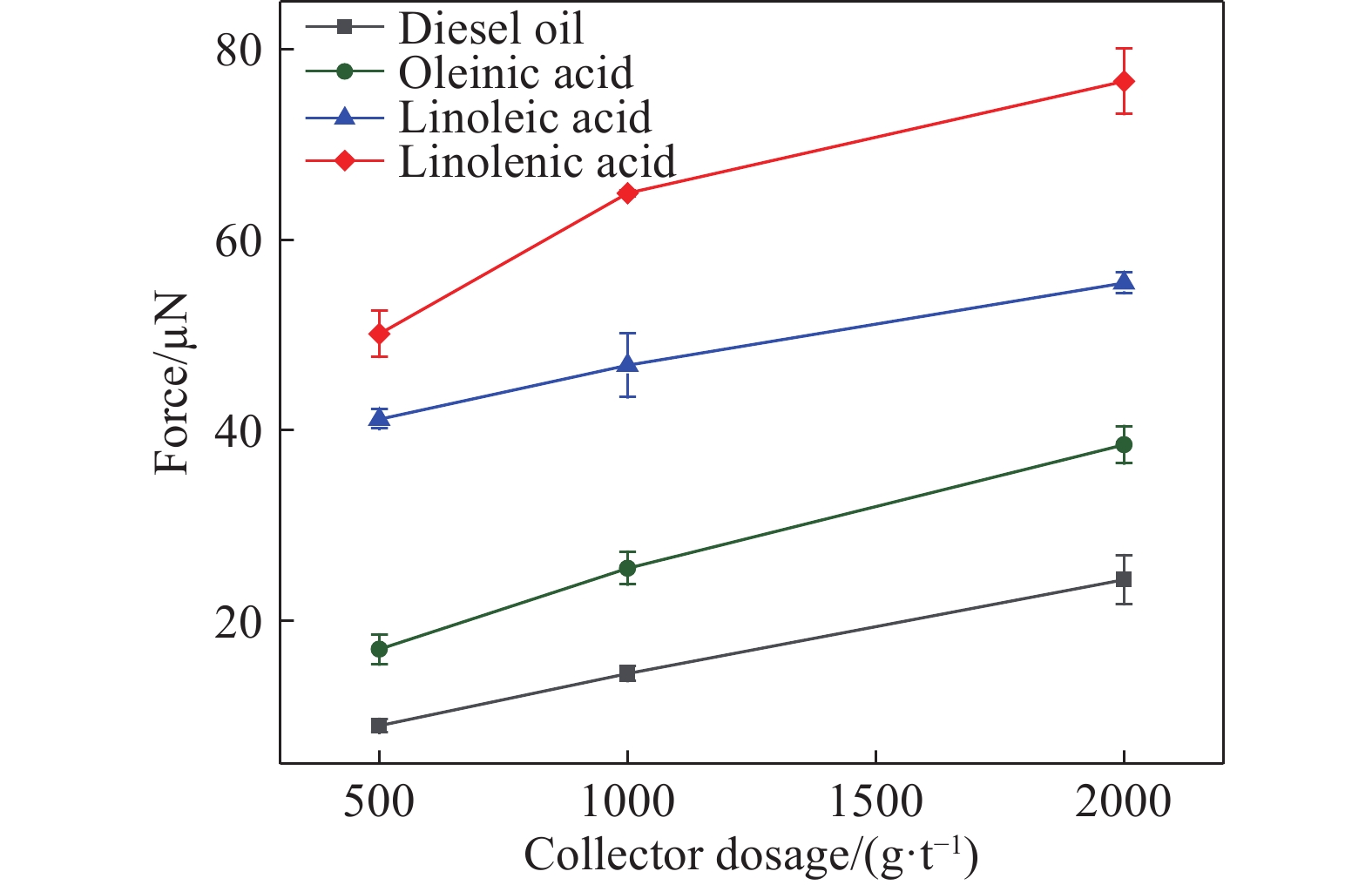
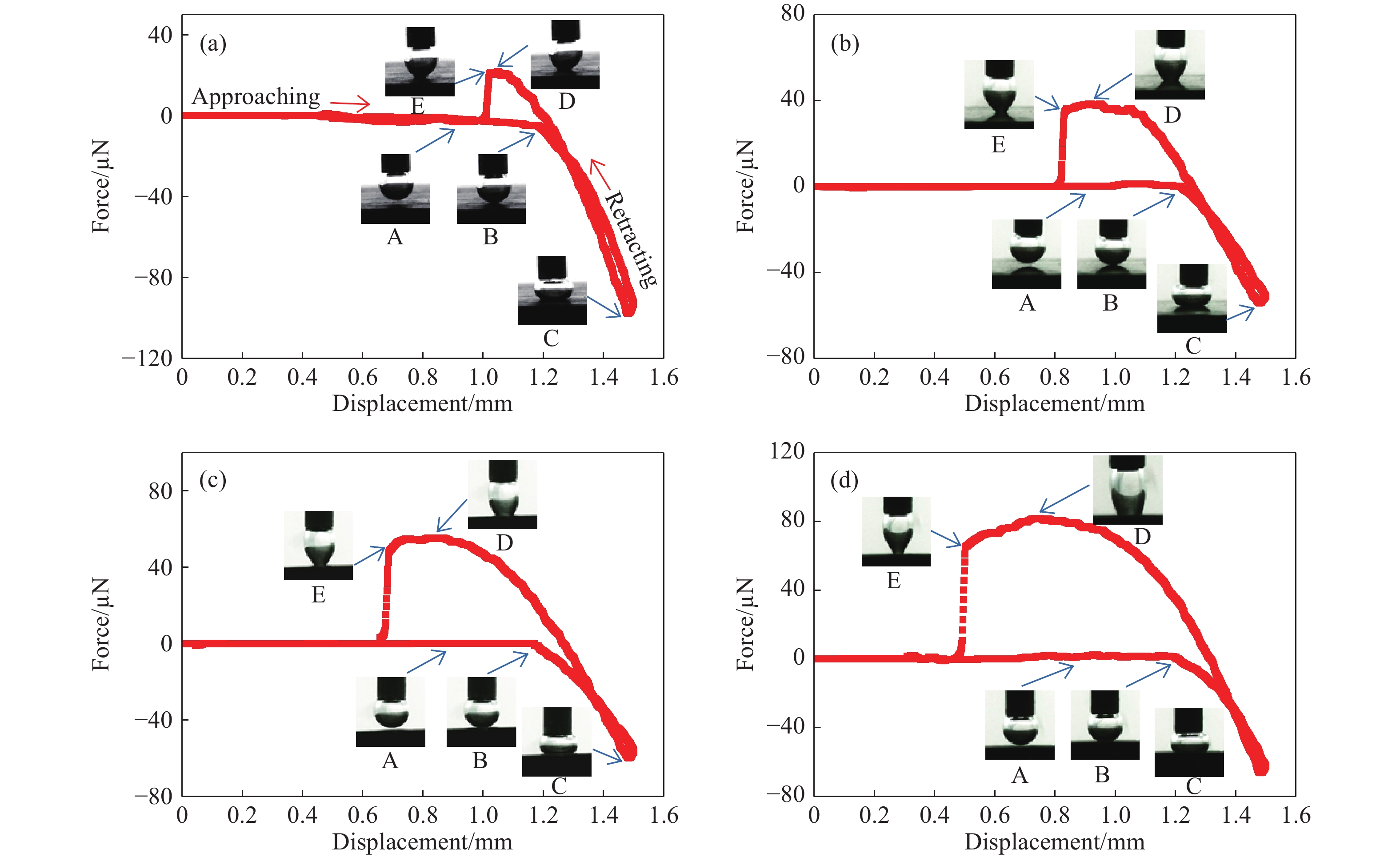
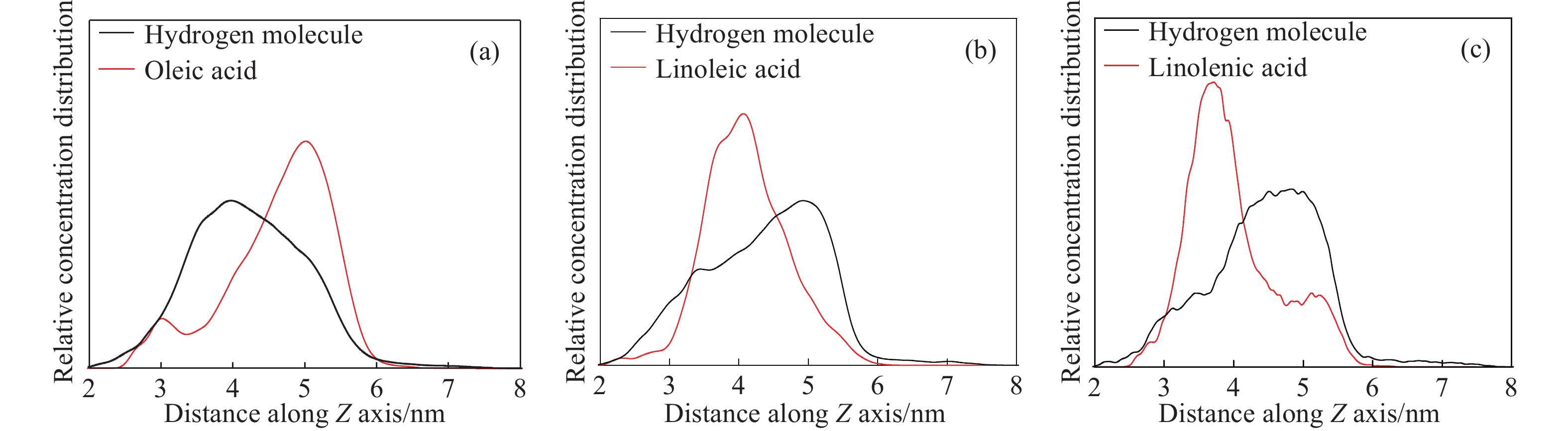
摘要: 為研究脂肪酸不飽和度對低階煤浮選的影響,選擇碳原子個數相同但雙鍵個數依次增加的油酸、亞油酸和亞麻酸作為浮選捕收劑對低階煤進行浮選,并與非極性捕收劑柴油進行對比,通過顆粒–氣泡間粘附力測試和藥劑吸附的分子動力學模擬,揭示了不飽和脂肪酸強化低階煤浮選的作用機制。結果表明,不飽和脂肪酸的浮選性能優于柴油,低階煤浮選產率隨脂肪酸不飽和度增加而增加。采用掃描電鏡(SEM)、傅里葉變換紅外光譜(FTIR)和X射線光電子能譜(XPS)對低階煤表面形貌和官能團進行分析。SEM結果表明,低階煤表面疏松,含有大量孔隙與裂隙,不利于藥劑在煤表面的鋪展。FTIR和XPS結果表明低階煤表面含有大量含氧官能團,表面疏水性較差,導致浮選回收率較低。對不同捕收劑條件下氣泡與煤表面粘附力進行測定,發現氣泡與煤表面間最大粘附力隨捕收劑不飽和程度增加而增加,這說明顆粒可浮性增加。進一步對不飽和脂肪酸吸附的分子動力學模擬進行分析,可知不飽和脂肪酸通過其極性基團與煤表面極性基團間形成氫鍵,從而在煤表面鋪展。雙鍵個數增加使得不飽和脂肪酸極性增加,在煤表面的鋪展程度逐漸增加,導致顆粒可浮性增加,這是低階煤浮選回收率隨脂肪酸不飽和程度增加而增加的主要原因。Abstract: To study the effect of fatty acid unsaturation on low-rank coal flotation, oleic acid, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid with the same number of carbon atoms but an increasing number of double bonds were selected as flotation collectors and compared with conventional nonpolar collector diesel oil. Adhesion force measurements between particles and bubbles and molecular dynamics simulation of reagent adsorption were used to reveal the mechanism of unsaturated fatty acids enhancing low-rank coal flotation. The flotation results show that unsaturated fatty acid collectors surpass nonpolar diesel oil in flotation performance, and the flotation yield of low-rank coal increases with fatty acid unsaturation. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to analyze the surface morphology and surface functional groups of low-rank coal. SEM results show that the surface of low-rank coal is loose and contains many pores and cracks, which is not conducive to the spreading of chemicals on coal surfaces and the mineralization of bubbles and particles. The results of FTIR and XPS show that the surface of low-rank coal contains several oxygen-containing functional groups and has poor hydrophobicity, resulting in low flotation recovery. The adhesion force between bubbles and coal surfaces was measured in different collector solutions. The maximum adhesion between bubbles and coal surfaces increased with collector unsaturation in diesel oil, oleic acid, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid systems, indicating an increase in the floatability of coal particles with collector unsaturation. Furthermore, the molecular dynamics simulation of unsaturated fatty acid adsorption showed that unsaturated fatty acids spread on coal surfaces through hydrogen bonding between the polar groups of these molecules and surfaces. With an increasing number of double bonds, unsaturated fatty acids become more polar, and the spread of unsaturated fatty acids on coal surfaces gradually becomes more extensive, which leads to increasing particle floatability. This is the main reason for the increase in flotation recovery of low-rank coal with unsaturated fatty acids.
-
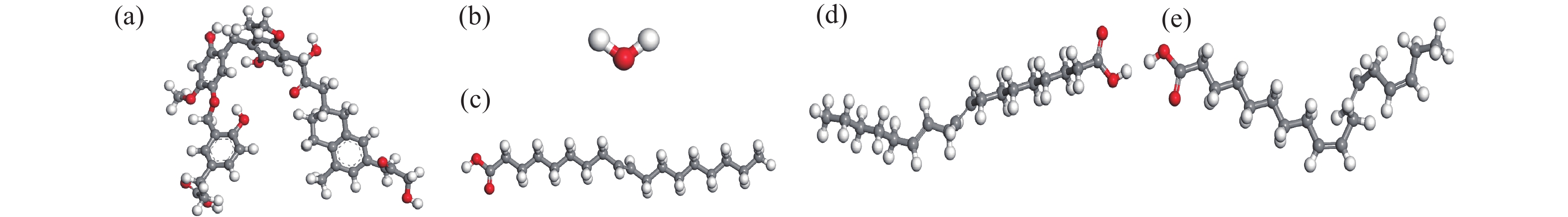
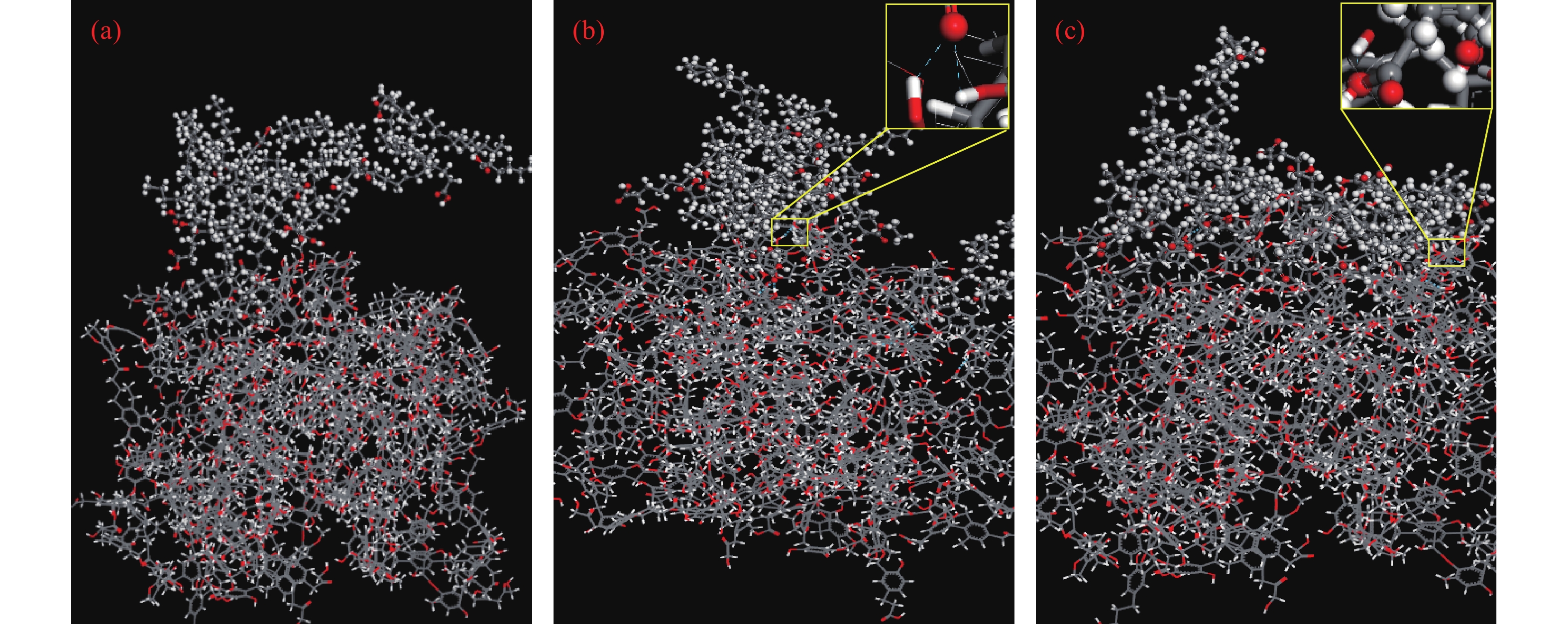
圖 2 分子結構。(a)Wender模型[21];(b)水分子;(c)油酸分子;(d)亞油酸分子;(e)亞麻酸分子 (紅色:氧原子;白色:氫原子;灰色:碳原子)
Figure 2. Molecular structures of (a) Wender model[21]; (b) hydrone; (c) oleic acid molecule; (d) linoleic acid molecule; (e) linolenic acid molecule (The colors are shown as follows: red, oxygen atoms; white, hydrogen atoms; gray, carbon atoms)
表 1 煤樣工業分析(質量分數)
Table 1. Proximate analysis of the coal sample
% Mad Aad Vdaf FCdaf 11.16 9.10 32.81 61.08 Note: ad—air dried basis;daf—dry ash free basis. 表 2 低階煤粒度組成分析
Table 2. Particle size and ash content distributions of low-rank coal
Size / mm Yield / % Ash / % Positive cumulative Yield / % Ash / % >0.500 0.33 11.88 0.33 11.88 0.500~0.250 39.91 7.86 40.24 7.89 0.250~0.125 25.15 7.64 65.39 7.79 0.125~0.074 8.31 7.31 73.69 7.74 0.074~0.045 9.23 8.13 82.92 7.78 <0.045 17.08 12.02 100.00 8.51 Total 100.00 8.51 — — 表 3 低階煤密度組成分析
Table 3. Density analysis of low-rank coal
Density grades /
(g·cm–3)Yield /
%Ash /
%Cumulative floate Cumulative sink Yield / % Ash / % Yield / % Ash / % <1.3 3.35 1.54 3.35 1.54 100.00 8.02 1.3–1.4 56.95 3.58 60.30 3.47 96.65 8.24 1.4–1.5 31.95 7.20 92.26 4.76 39.70 14.93 1.5–1.6 3.83 24.48 96.09 5.55 7.75 46.79 1.6–1.8 0.84 55.76 96.93 5.98 3.92 68.58 >1.8 3.08 72.08 100.00 8.02 3.08 72.08 Total 100.00 8.02 — — — — 表 4 低階煤表面元素組成及相對含量(質量分數)
Table 4. Surface element composition and relative contents of low-rank coal
% C O N Mg Ca Si Al Na 72.17 19.74 0.97 0.09 0.92 3.41 2.55 0.16 表 5 低階煤表面官能團組成及相對含量(質量分數)
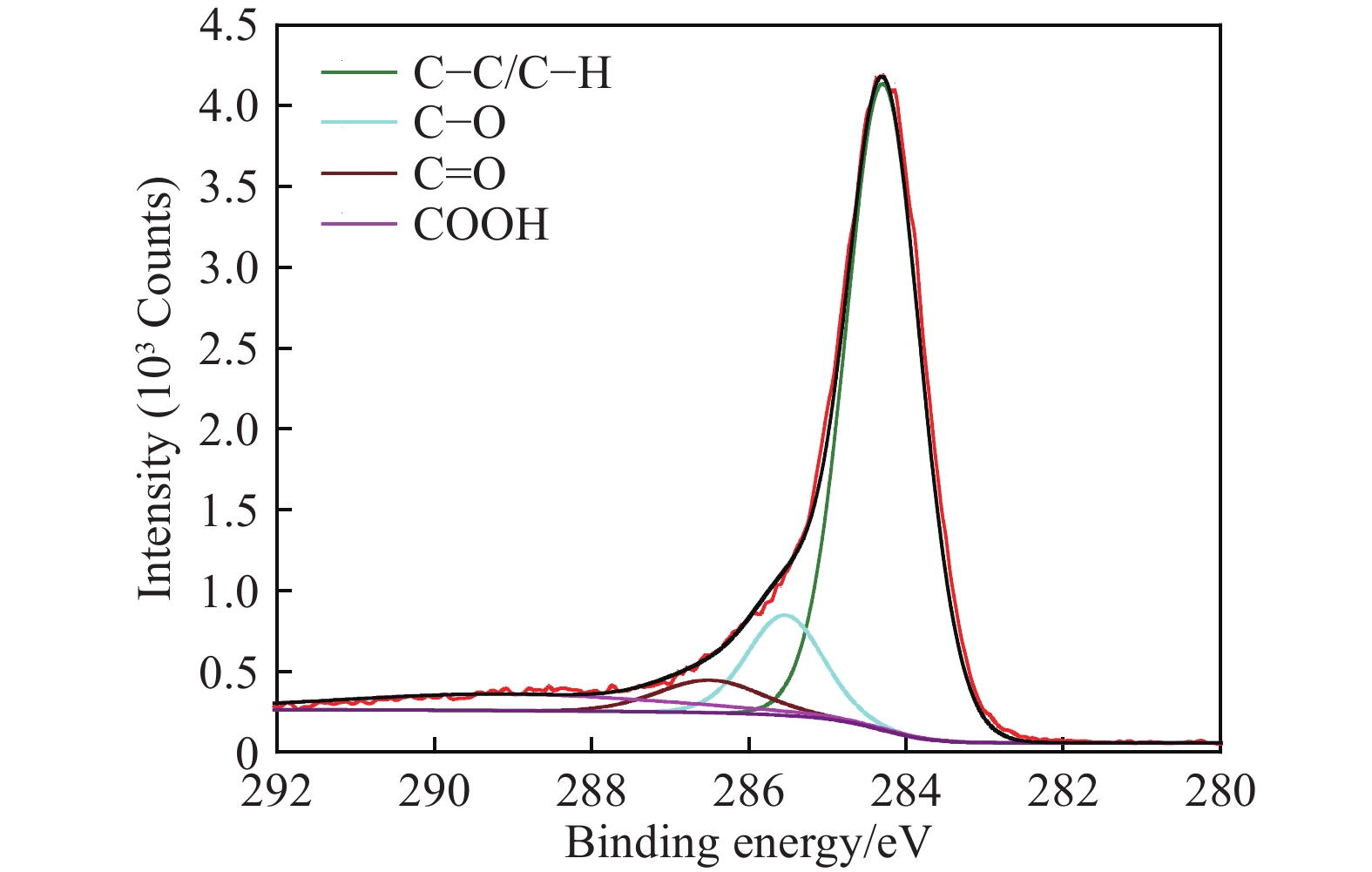
Table 5. Relative contents of functional groups on surface of low-rank coal
% C–C/C–H C–O C=O O=C–O 63.53 25.01 7.54 3.92 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Xie H P, Wu L X, Zheng D Z. Prediction on the energy consumption and coal demand of China in 2025. J China Coal Soc, 2019, 44(7): 1949 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0585謝和平, 吳立新, 鄭德志. 2025年中國能源消費及煤炭需求預測. 煤炭學報, 2019, 44(7):1949 doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0585 [2] Weng F. Characteristics of China's energy structure and its development prospect. Econ Vis, 2012(1): 90翁非. 中國能源結構特征及發展前瞻. 經濟視角(下), 2012(1):90 [3] Cai M F, Wu Y Q, Li P, et al. Present situation and ideas of green development of coal resources in Ningxia. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(1): 1蔡美峰, 吳允權, 李鵬, 等. 寧夏地區煤炭資源綠色開發現狀與思路. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(1):1 [4] Gao S L, Liu J T. Primary search on making low rank coal to super pure coal by surface modification. Coal Technol, 2004, 23(9): 68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8725.2004.09.049高淑玲, 劉炯天. 低階煤表面改性制備超凈煤初探. 煤炭技術, 2004, 23(9):68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8725.2004.09.049 [5] Qu J Z. Research on Reactive Oily Bubble Flotation Behavior of Low Rank Coal and its Flotation Technique [Dissertation]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2015屈進州. 低階煤活性油泡浮選行為與浮選工藝研究[學位論文]. 徐州: 中國礦業大學, 2015 [6] Chen S J. Surface/interface Characteristics of Shendong Long-flame Coal and its Attachment Mechanism with Reactive Oily Bubbles [Dissertation]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020陳松降. 神東長焰煤的表/界面特征及與活性油泡粘附的作用機制[學位論文]. 徐州: 中國礦業大學, 2020 [7] Gui X H. Two-stage Separation and Process Intensification of Fine Coal [Dissertation]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2012桂夏輝. 煤泥分選過程強化及兩段式分選研究[學位論文]. 徐州: 中國礦業大學, 2012 [8] Liu J T. Reflection on low-carbon development of coal energy in China. J China Univ Min &Technol (Soc Sci) , 2011, 13(1): 5劉炯天. 關于我國煤炭能源低碳發展的思考. 中國礦業大學學報(社會科學版), 2011, 13(1):5 [9] Xing Y W, Gui X H, Cao Y J, et al. Effect of compound collector and blending frother on froth stability and flotation performance of oxidized coal. Powder Technol, 2017, 305: 166 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.10.003 [10] Sen R, Srivastava S K, Singh M M. Aerial oxidation of coal-analytical methods, instrumental techniques and test methods: A survey. Indian J Chem Technol, 2009, 16(2): 103 [11] Chen S J, Yang Z, Chen L, et al. Wetting thermodynamics of low rank coal and attachment in flotation. Fuel, 2017, 207: 214 [12] Jia R H, Harris G H, Fuerstenau D W. An improved class of universal collectors for the flotation of oxidized and/or low-rank coal. Int J Miner Process, 2000, 58(1-4): 99 doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(99)00024-1 [13] Wen B F, Xia W C, Sokolovic J M. Recent advances in effective collectors for enhancing the flotation of low rank/oxidized coals. Powder Technol, 2017, 319: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.030 [14] Jin W. Study on Vegetable Oil Collector Enhanced Low-rank Coal Flotation [Dissertation]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019晉偉. 植物油捕收劑強化低階煤浮選試驗研究[學位論文]. 徐州: 中國礦業大學, 2019 [15] Dey S. Enhancement in hydrophobicity of low rank coal by surfactants–a critical overview. Fuel Process Technol, 2012, 94(1): 151 doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.10.021 [16] Gui X H, Xing Y W, Wang T X, et al. Intensification mechanism of oxidized coal flotation by using oxygen-containing collector α-furanacrylic acid. Powder Technol, 2017, 305: 109 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.09.058 [17] Miao Z Y, Xing Y W, Gui X H, et al. Anthracite coal flotation using dodecane and nonyl benzene. Int J Coal Prep Util, 2017, 38(8): 393 [18] Liang J D. Auto-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acid as well as its reaction products and action mechanism. Min Metall Eng, 1986, 6(3): 28梁經冬. 不飽和脂肪酸的自氧化現象及其反應產物的浮選性能與作用機理. 礦冶工程, 1986, 6(3):28 [19] Jin L Z, Zhao J D, Wang H, et al. Characteristic modification of coal-based activated carbon and its methane adsorption capacity. Chin J Eng, 2022, 44(4): 526金龍哲, 趙金丹, 王輝, 等. 煤基活性炭改性及其甲烷吸附能力. 工程科學學報, 2022, 44(4):526 [20] Zhu C Y, Li G S, Xing Y W, et al. Adhesion forces for water/oil droplet and bubble on coking coal surfaces with different roughness. Int J Min Sci Technol, 2021, 31(4): 681 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.03.002 [21] Wender I. Catalytic synthesis of chemicals from coal. Catal Rev, 1976, 14(1): 97 doi: 10.1080/03602457608073408 [22] Xu M D, Xing Y W, Cao Y J, et al. Waste colza oil used as renewable collector for low rank coal flotation. Powder Technol, 2019, 344: 611 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.12.058 [23] Xing Y W, Gui X H, Cao Y J, et al. Clean low-rank-coal purification technique combining cyclonic-static microbubble flotation column with collector emulsification. J Clean Prod, 2017, 153: 657 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.057 [24] Xu M D, Guo F Y, Zhang Y F, et al. Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on surface physicochemical properties of lignite and its flotation response. Powder Technol, 2021, 386: 81 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.03.024 [25] Yang Z L, Guo F Y, Xia Y C, et al. Improved floatability of low-rank coal through surface modification by hydrothermal pretreatment. J Clean Prod, 2020, 246: 119025 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119025 [26] Yang H C, Xing Y W, Sun L J, et al. Kinetics of bubble-particle attachment and detachment at a single-bubble scale. Powder Technol, 2020, 370: 251 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.05.064 [27] Sherman H, Nguyen A V, Bruckard W. An analysis of bubble deformation by a sphere relevant to the measurements of bubble-particle contact interaction and detachment forces. Langmuir, 2016, 32(46): 12022 doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02985 [28] Zhang L, Guo J Y, Xie Z X, et al. Micro-mechanism of improving low-rank coal flotation by using carboxylic acid collector: A DFT calculation and MD simulation study. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2021, 622: 126696 doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126696 [29] Xia Y C, Zhang R, Xing Y W, et al. Improving the adsorption of oily collector on the surface of low-rank coal during flotation using a cationic surfactant: An experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Fuel, 2019, 235: 687 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.059 [30] He M, Zhang W, Cao X Q, et al. Adsorption behavior of surfactant on lignite surface: A comparative experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(2): 437 doi: 10.3390/ijms19020437 -




 下載:
下載: