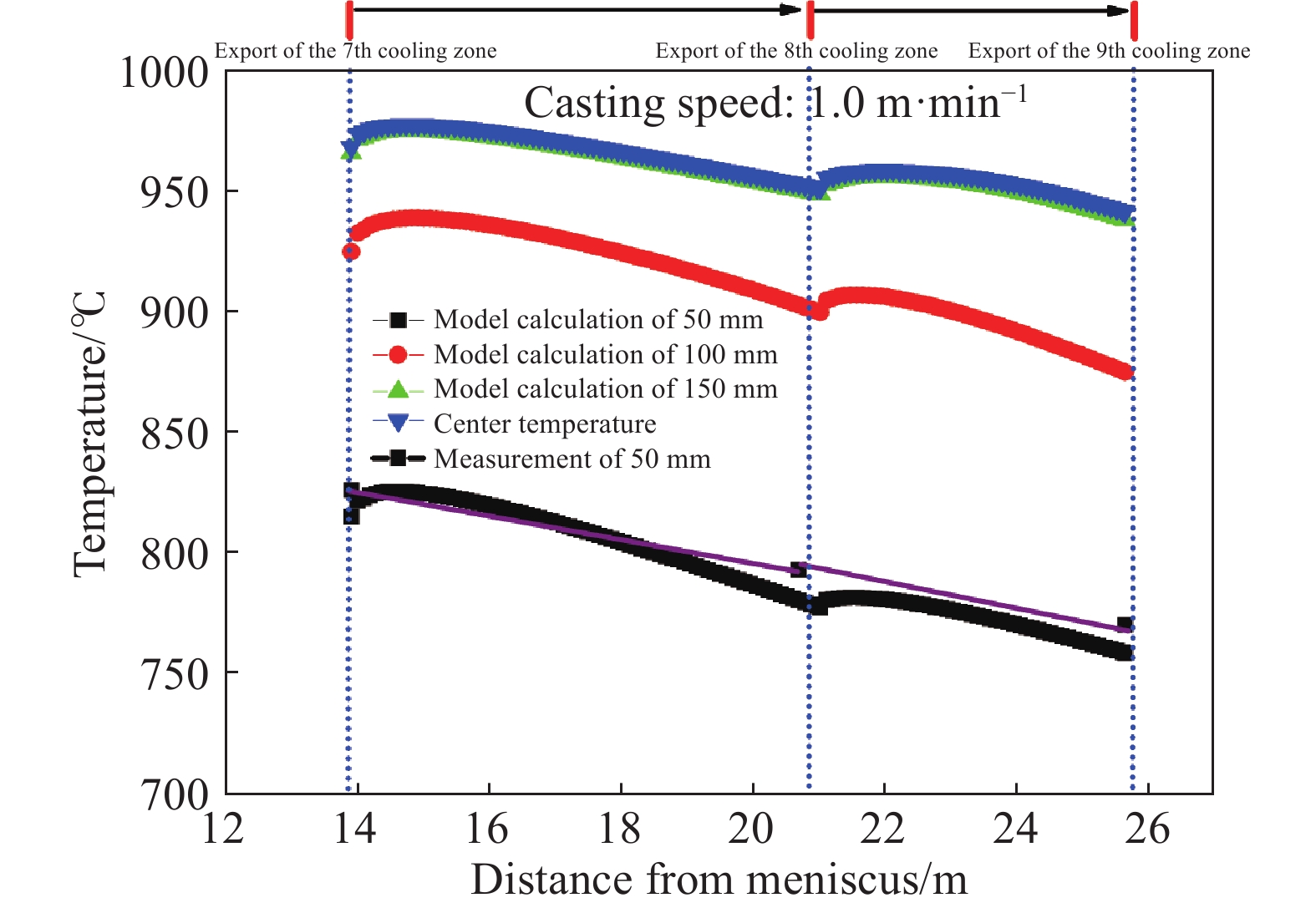
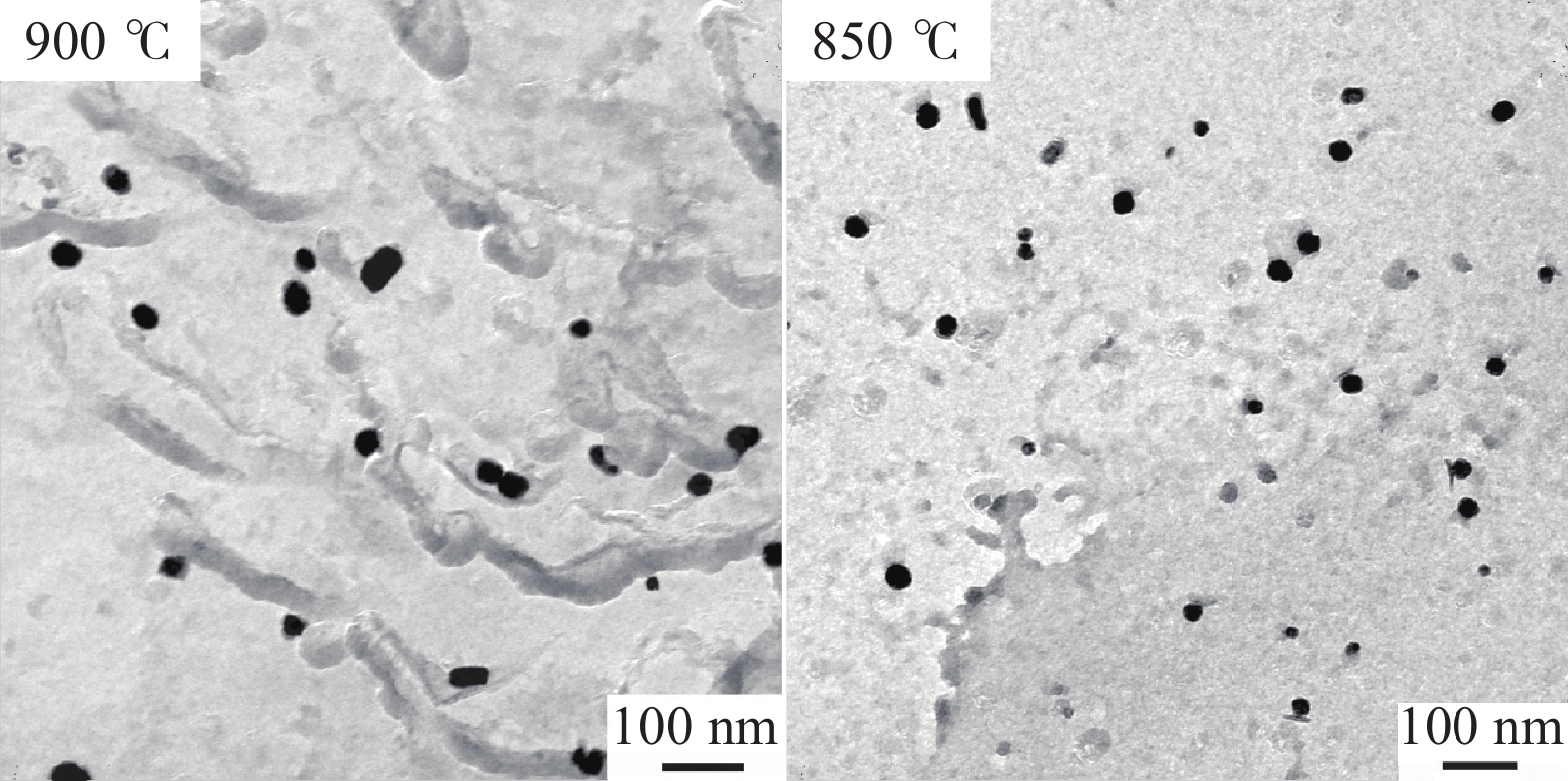
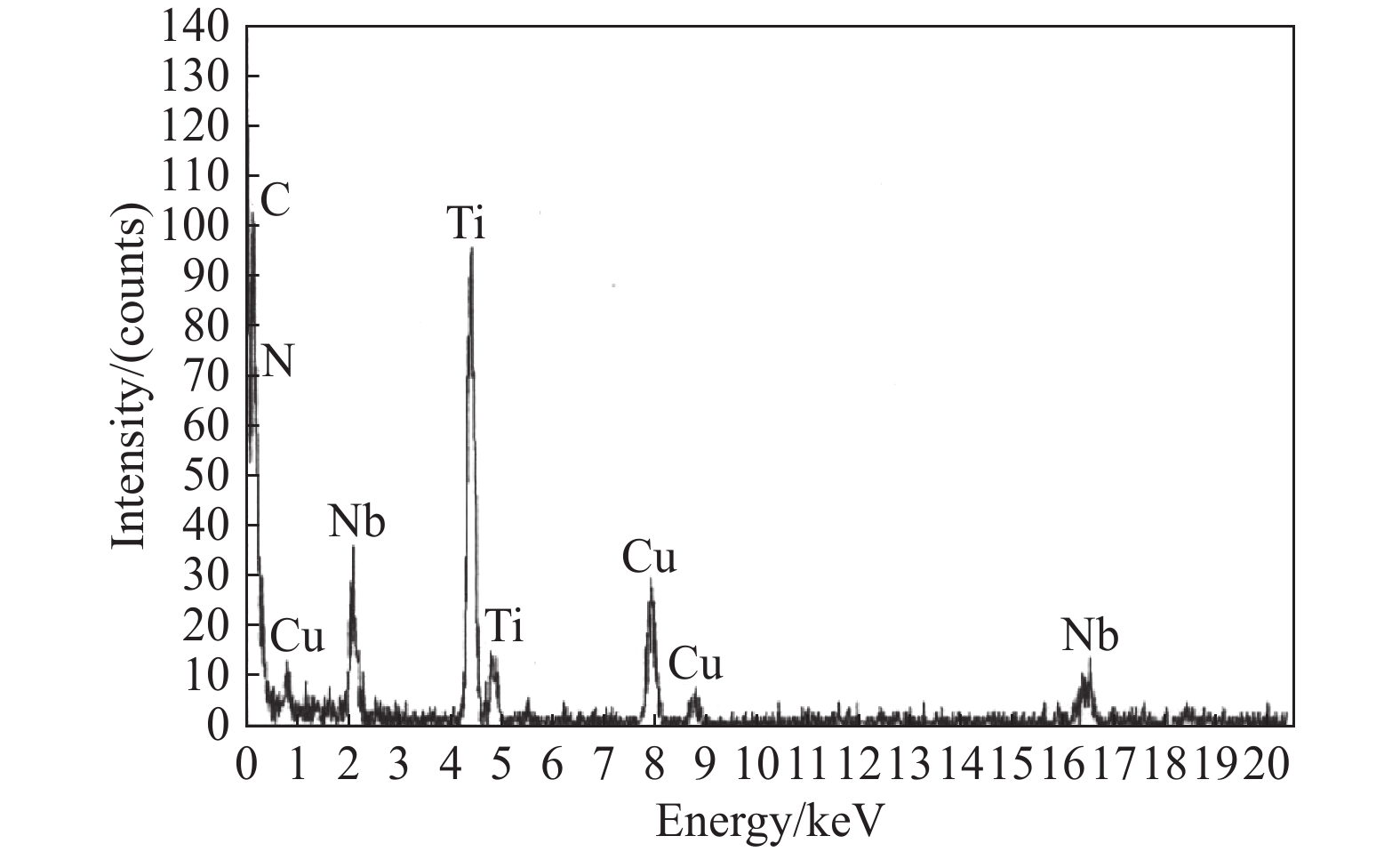
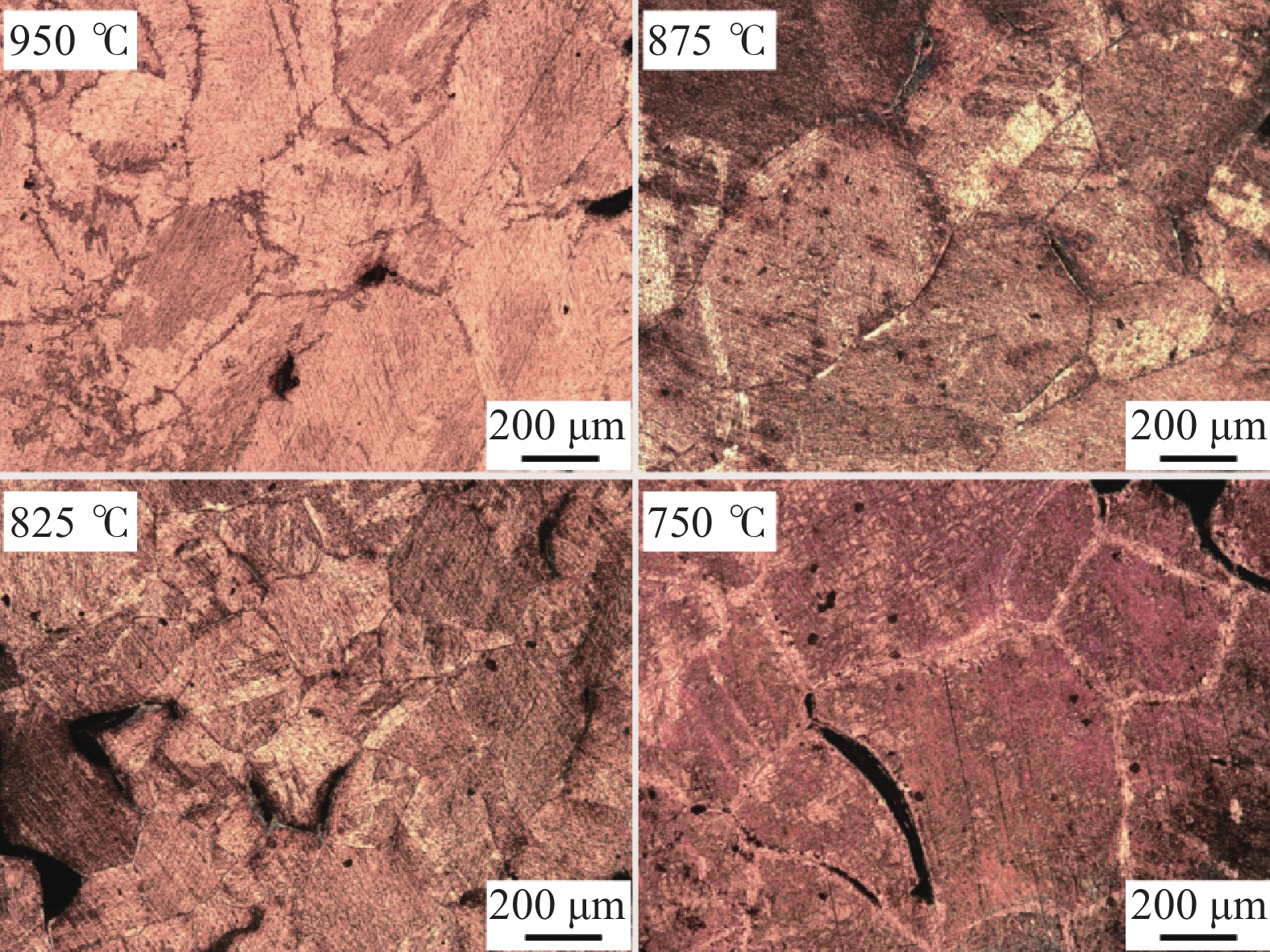
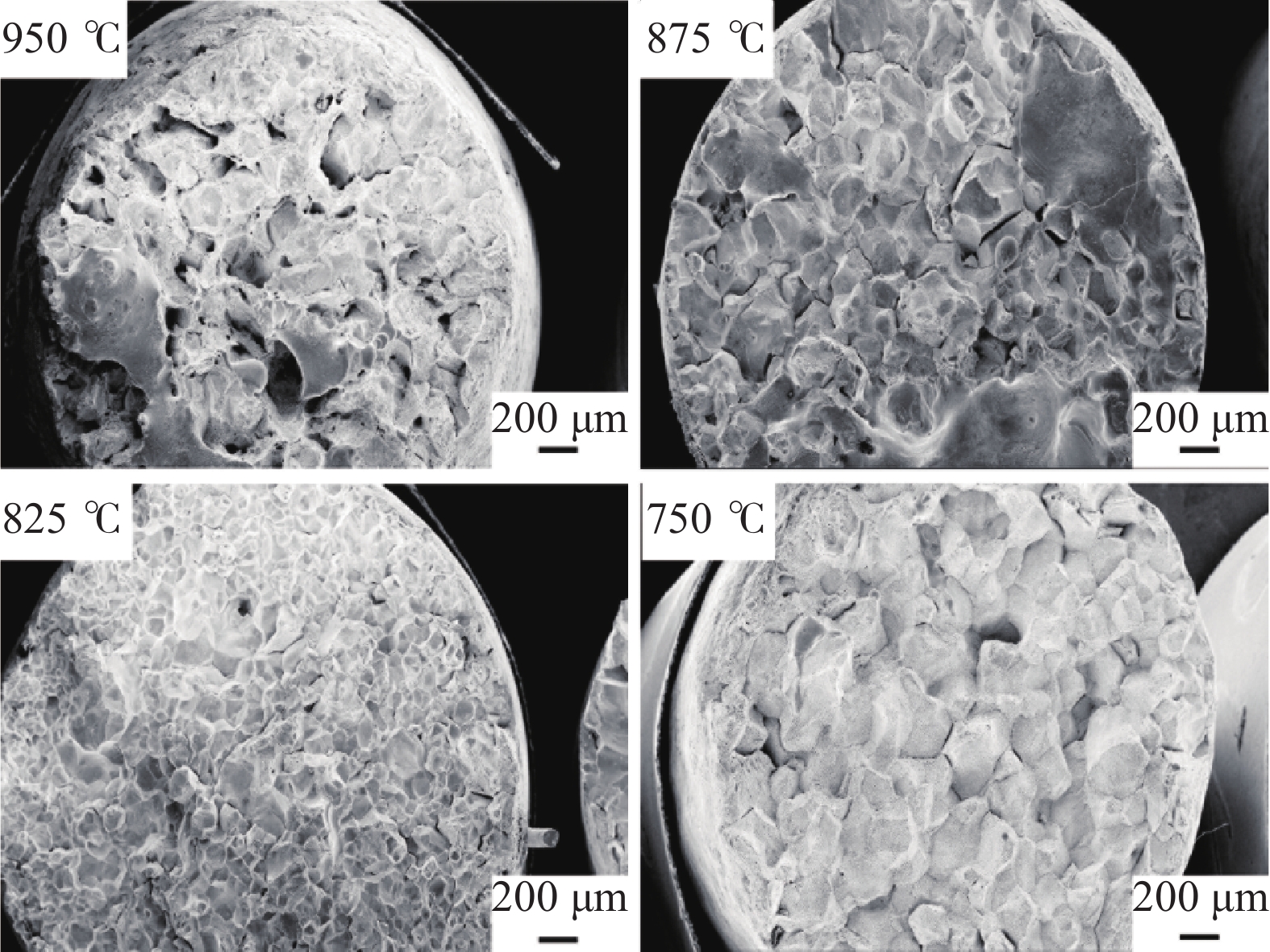
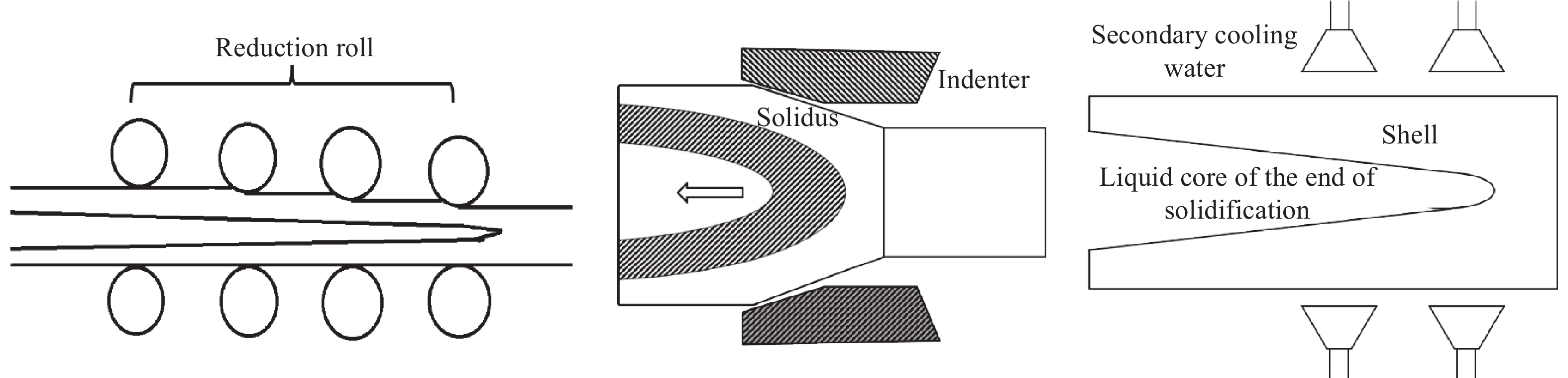
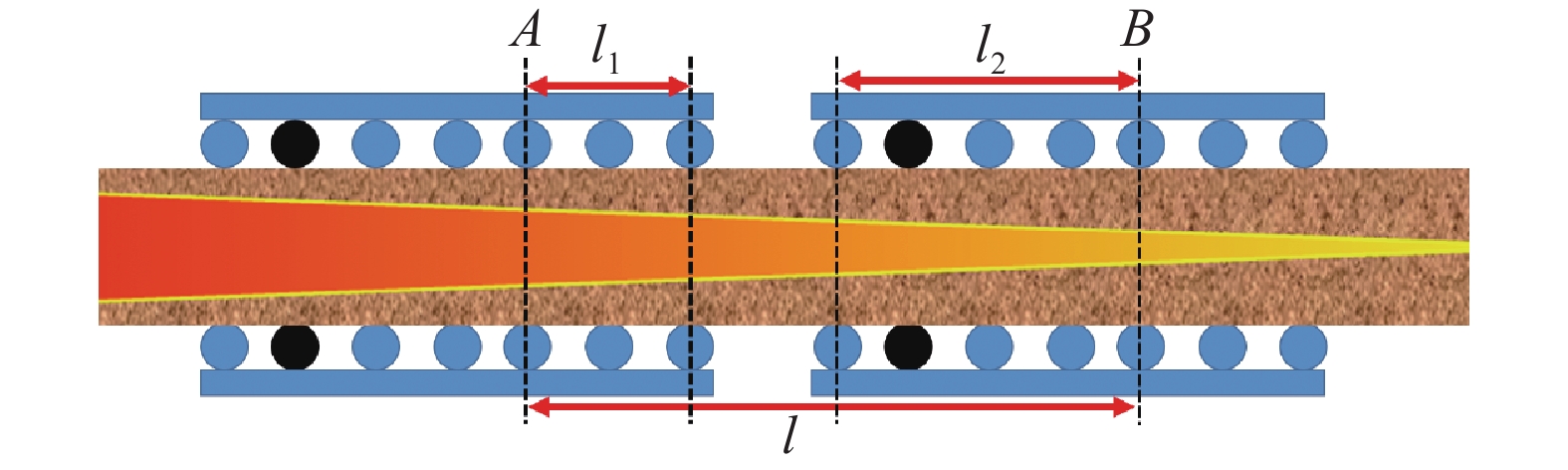
Research and application of three-dimensional dynamic secondary cooling and accurate soft reduction for continuous casting slab
-
摘要: 在現有工藝條件下,校驗和完善二冷區鑄坯凝固傳熱計算數學模型,開發三維二冷配水模型,解決目前設備狀況下冷卻水分布不均勻對鑄坯溫度的影響,從而控制鑄坯表面質量,特別是鑄坯的角部裂紋,同時對板坯連鑄二冷配水制度進行改進和優化,使之滿足高效連鑄生產條件和改善鑄坯質量的需要。提出壓下參數計算公式,結合所開發三維二冷配水模型,優化現有壓下工藝,提出并應用精準可控單段壓下、非穩態壓下控制,集中解決連鑄板坯中心偏析、中心疏松和縮孔等內部質量問題。同時優化模型數據庫,使之數據更加完備,模型計算更加準確,同時模型具備異鋼種混澆過程二冷及壓下控制功能,能夠進行凝固終點W形預測與控制,可進一步提高模型適用性和準確性。模型開發并成功在多家鋼廠現場應用,有效改善了鑄坯裂紋和偏析等鑄坯表面和內部的質量問題。Abstract: The surface and corner cracks of continuous casting billet form during the continuous casting process, especially in medium-carbon steel. Surface defects of such billets are directly related to the secondary cooling process of continuous casting, while the center deviation of the billet, center shrinkage, and center loosening in medium-carbon steel, medium-carbon alloy steel, and high-carbon steel are especially prominent. Such quality defects are related to the secondary cooling and press-down process of continuous casting. These two defects are the main factors restricting continuous casting production. The secondary cooling of the continuous casting process has an important influence on the surface and internal quality of the slab, especially the temperature of the slab corners, which directly affects the surface quality of the slab. Under the existing process conditions, the mathematical model for calculating the solidification heat transfer of the slab in the secondary cooling zone is calibrated and improved, and a three-dimensional secondary cooling model is developed to solve the influence of uneven cooling due to water distribution on the temperature of the slab. This controls the surface quality of the slab, especially the corner cracks of the slab, and improves and optimizes the slab continuous casting secondary cooling system to improve the slab quality. An equation for calculating the soft reduction parameters is proposed, and the existing soft reduction process is optimized by combining the developed three-dimensional secondary cooling model with the proposed and applied controllable single-stage soft reduction and unsteady soft reduction control to solve the internal quality problems, such as central segregation, central porosity, and shrinkage of the continuous casting slab. At the same time, the model database is optimized to make the data more complete and the model calculation more accurate. This model adds the technology of mixed casting of different grades of steel and the technology of predicting and controlling the W-shaped solidification to further improve the applicability and accuracy of the model. The model has been developed and successfully applied in several steel plants, and the result shows that the proposed model can improve the surface and internal quality of cast slabs effectively, such as cracks and segregation.
-
Key words:
- continuous casting slab /
- secondary cooling /
- accurat soft reduction /
- double-target temperature /
- crack /
- segregation
-
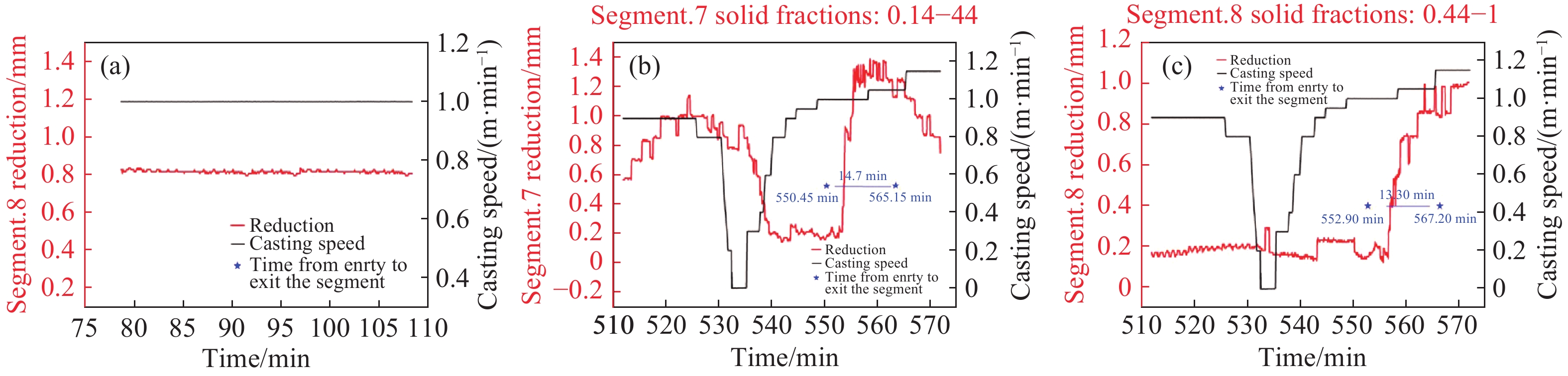
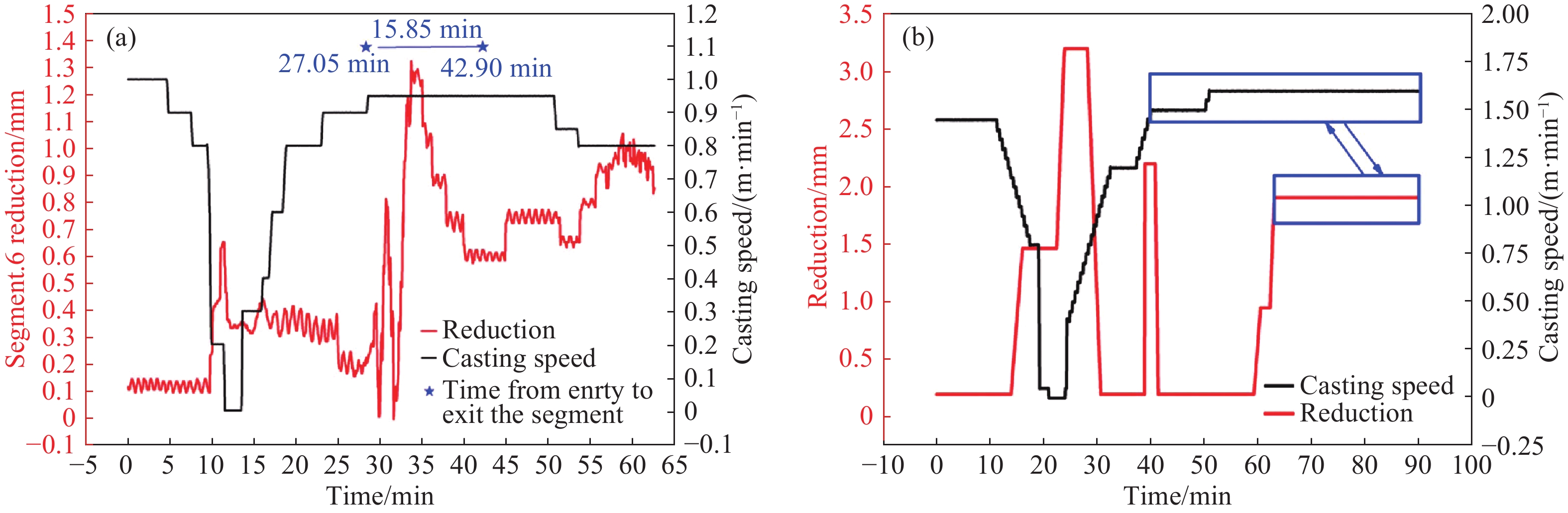
圖 11 穩態與非穩態過程典型扇形段壓下量的變化。(a)穩態時第8扇形段壓下量變化;(b)為非穩態時第7扇形段壓下量變化;(c)為非穩態時第8扇形段壓下量變化
Figure 11. Variation of the typical soft reduction at the steady state and nonsteady state: (a) variation of the reduction amount of seg.8 at the steady state;(b) variation of the reduction amount of segment.7 at the nonsteady state;(c) variation of the reduction amount of segment.8 at the nonsteady state
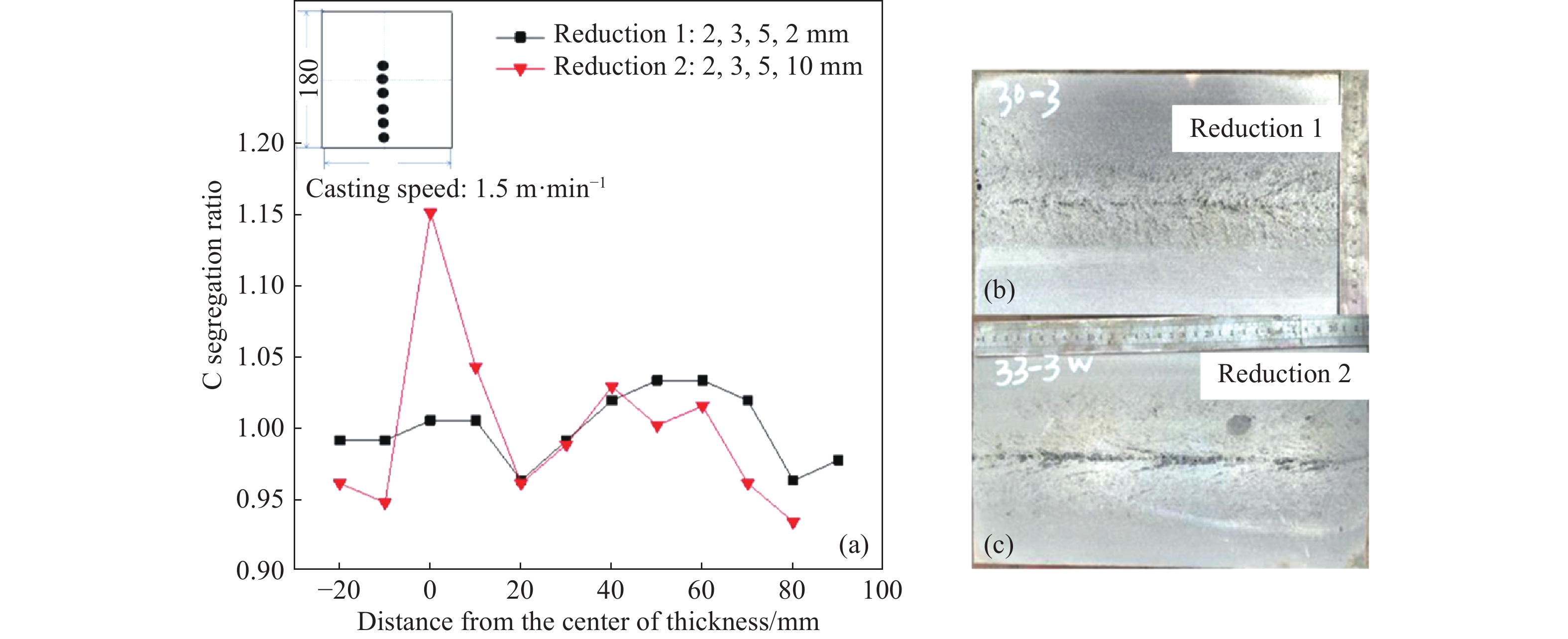
圖 15 不同末端壓下量鑄坯中心偏析情況。(a)兩種末端壓下量對應C偏析度結果;(b)末端壓下2 mm低倍結果;(c)末端壓下10 mm低倍結果
Figure 15. Center segregation of different reduction amount at the end of solidification:(a) result of C segregation ratio;(b) macrostructure of C segregation of 2 mm reduction amount;(c) macrostructure of C segregation of 10 mm reduction amount
表 1 實驗鋼種化學成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Chemical composition of experimental steel grades (mass fraction)
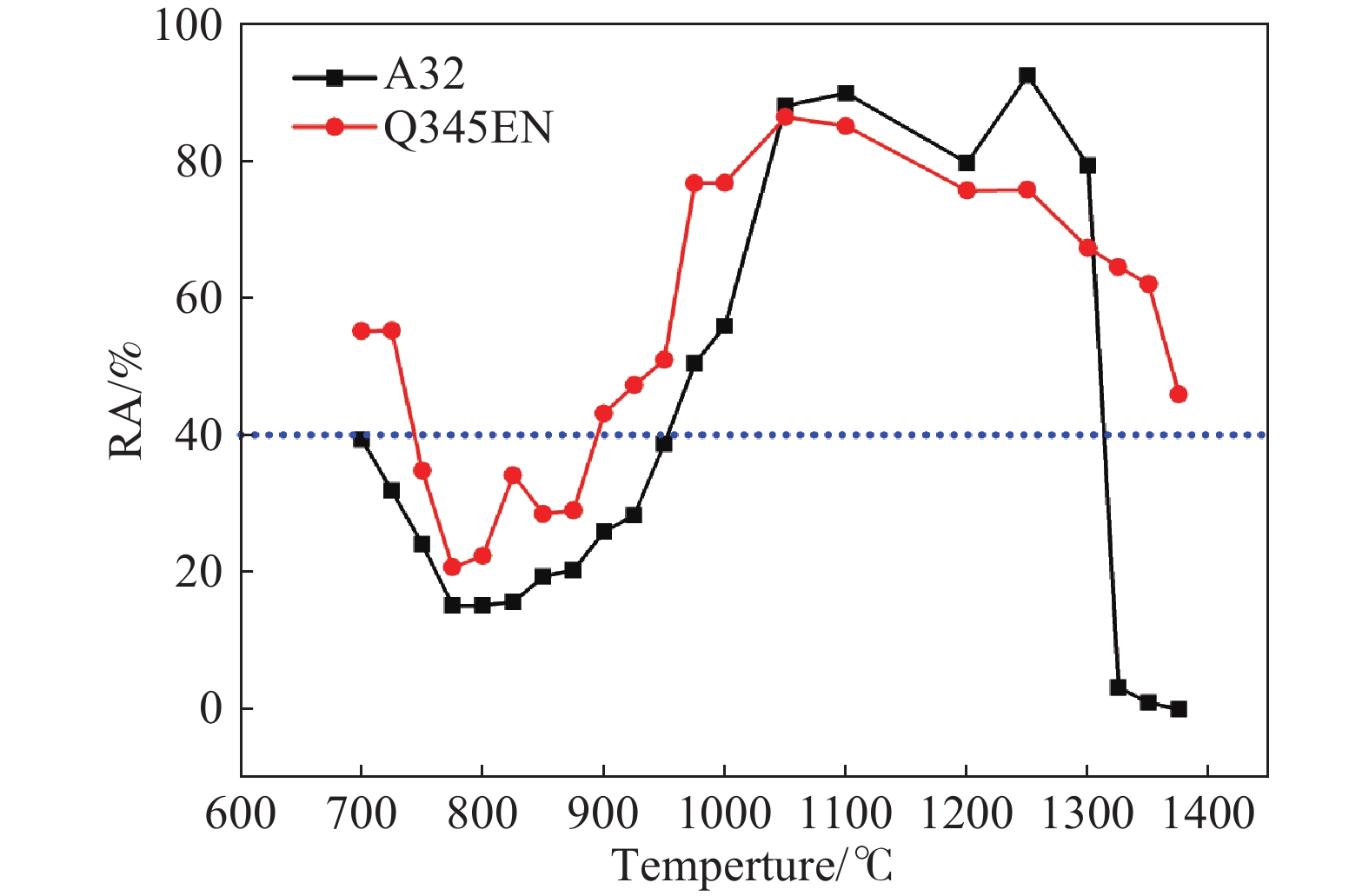
% Elements C Mn P S Si Nb V Ti Cu Alt N A32 0.16 1.11 0.0097 0.0067 0.242 0.0252 0.0039 0.0049 0.07 0.0319 0.0044 Q345EN 0.16 1.404 0.0076 0.0018 0.336 0.02296 0.0031 0.0123 0.05 0.0317 0.0033 表 2 混合澆注鋼種成分及其固?液相線溫度
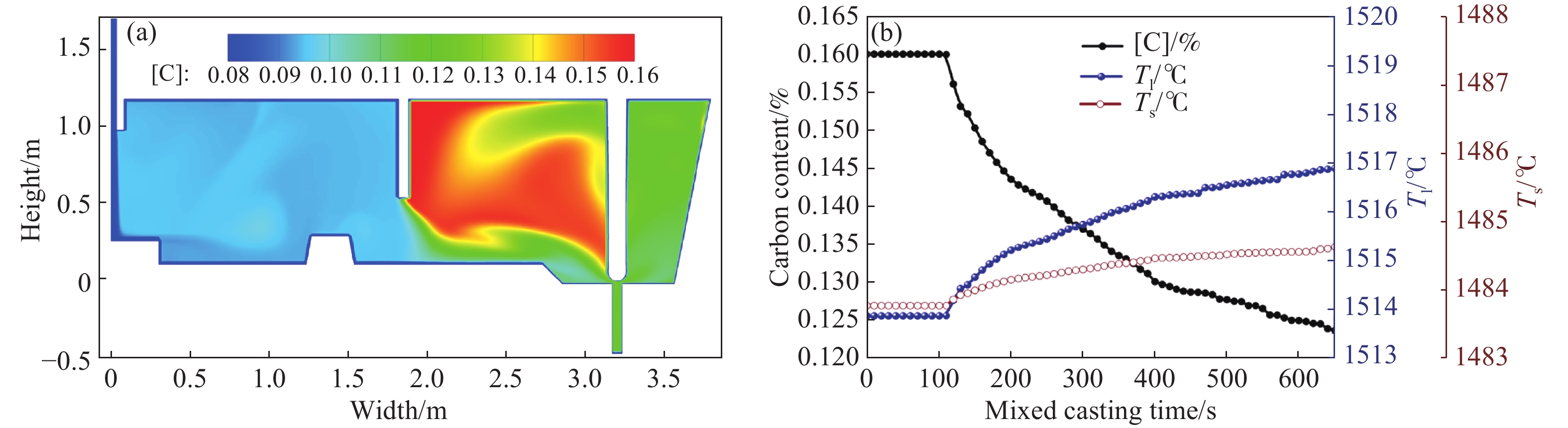
Table 2. Composition of mixed cast steel and solid–liquid phase line temperature
Steel grades w/% Tl/℃ Ts/℃ C Si Mn P S Before mixed (AH36) 0.16 0.15 1.50 0.015 0.01 1514 1482 After mixed (Q345) 0.08 0.27 1.30 0.02 0.025 1520 1486 表 3 模型上線前后軋后缺陷率統計
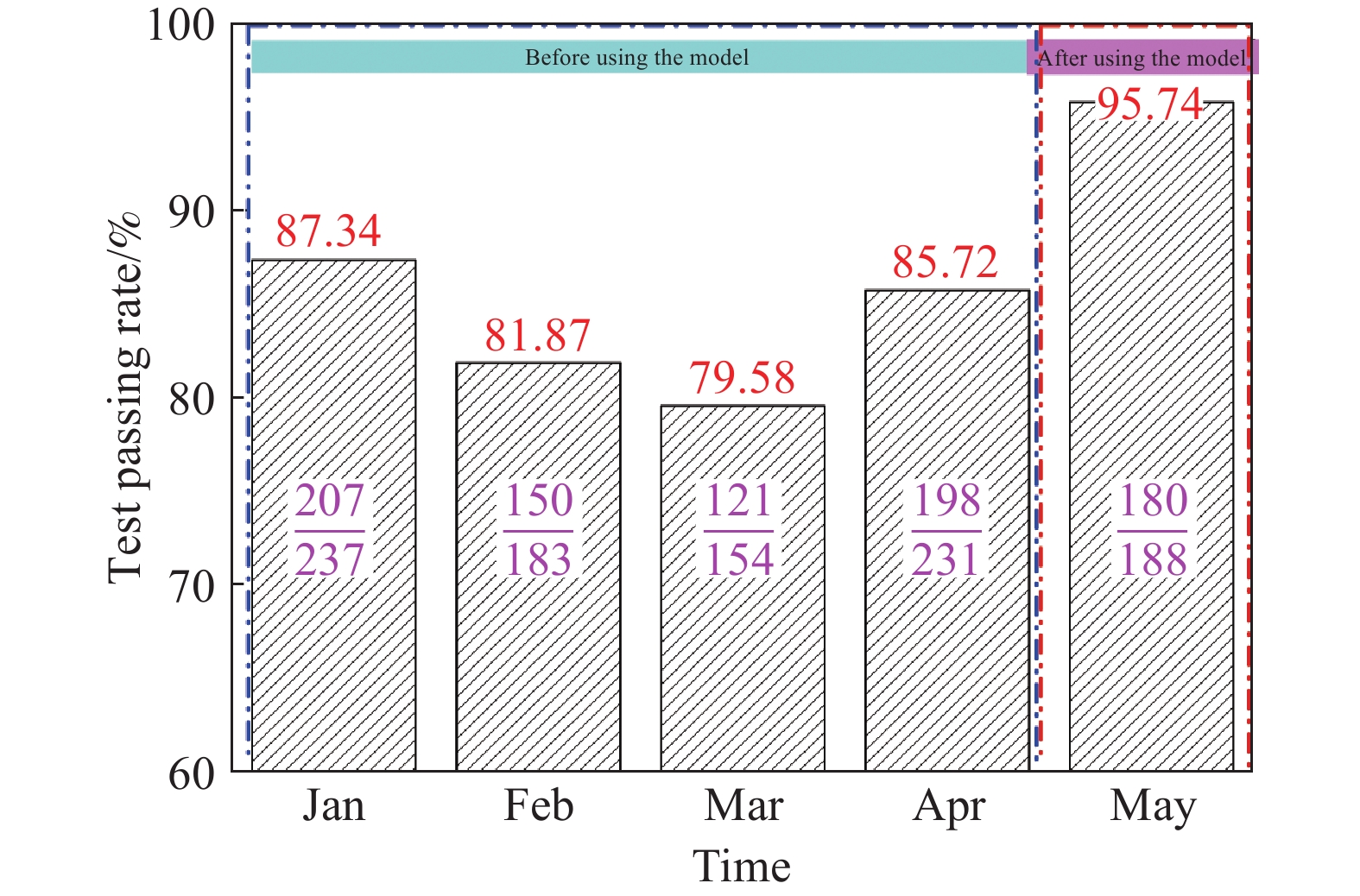
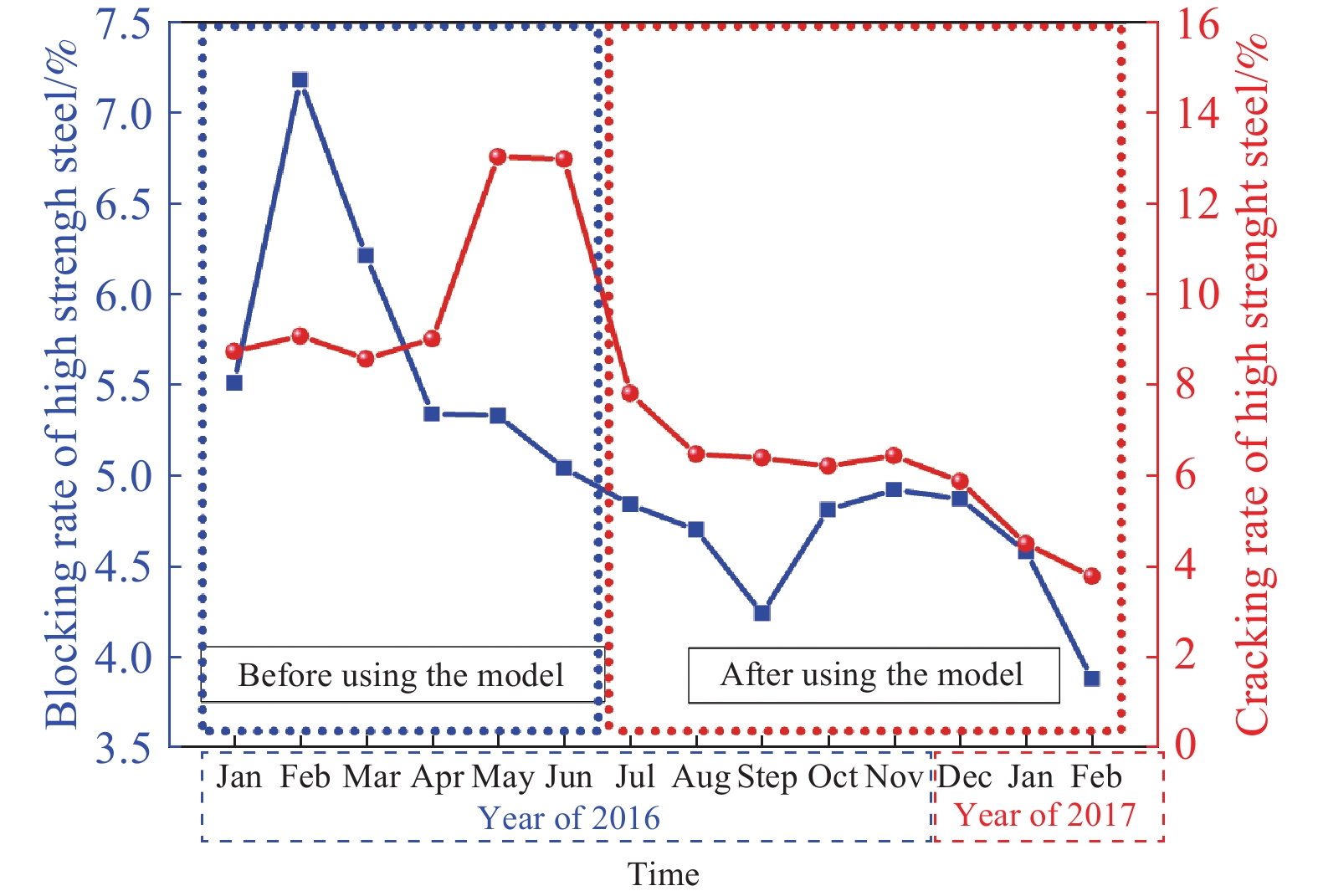
Table 3. Crack rate before and after using the model
Low-alloyed statistics of
the crack after rolling/ %Hot-rolled plate statistics of
the crack after rolling/ %Before use After use Before use After use 0.92 0.38 0.78 0.3 0.95 0.46 0.75 0.28 0.93 0.37 0.71 0.19 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Wu G R, Xie X, Chen G. Slab corner crack control of high strength automobile frame steel // The 3rd Vanadium and Titanium Microalloyed High Strength Steel Development and Application Technology and the 4th Vanadium Industry Advanced Technology Exchange Conference. Chongqing, 2017: 93吳國榮, 謝鑫, 陳剛. 高強汽車梁板鋼寬厚板坯角橫裂紋控制. 第三屆釩鈦微合金化高強鋼開發應用技術暨第四屆釩產業先進技術交流會論文集. 重慶, 2017: 93 [2] Ding Z Y, Feng C B. Practice in controlling centerline segregation of continuous casting slab for heavy plate. Continuous Cast, 2018, 43(2): 32丁占元, 馮長寶. 控制厚板連鑄板坯中心偏析的實踐. 連鑄, 2018, 43(2):32 [3] Qu S T. Study on optimization of continuous casting secondary cooling process and crack control at corner of the billet. Shanxi Metall, 2021, 44(1): 131渠松濤. 連鑄二冷工藝優化與鑄坯角部裂紋控制研究. 山西冶金, 2021, 44(1):131 [4] Zhou D, Zhang S W, Gong Y K, et al. Analysis on transverse corner crack of medium plate. Henan Metall, 2020, 28(4): 38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2020.04.013周丹, 張守偉, 鞏彥坤, 等. 中厚板角部橫裂紋缺陷分析. 河南冶金, 2020, 28(4):38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2020.04.013 [5] Zhao D, Cheng Y, Li B, et al. Practice process of reducing surface transverse crack of aluminum containing steel. Continuous Cast, 2020, 45(2): 14趙迪, 程業, 李博, 等. 降低含鋁鋼表面橫裂紋的工藝實踐. 連鑄, 2020, 45(2):14 [6] Lu D H, Wang Z P, Zhang H. Development of production technology of micro-alloyed steel continuous casting billet without corner defects. Continuous Cast, 2020, 45(5): 66路殿華, 王振鵬, 張慧. 微合金化鋼連鑄坯邊角部無缺陷生產技術開發. 連鑄, 2020, 45(5):66 [7] Song J X, Zhang F B. Study of temperature distribution of continuous casting chamfer mold based on heat flux distribution model. Steelmaking, 2019, 35(6): 35宋景欣, 張發斌. 基于熱流密度分布模型的連鑄倒角結晶器溫度分布研究. 煉鋼, 2019, 35(6):35 [8] Yang X S, Zhang P. Development and application of chamfered mold technology. Continuous Cast, 2018, 43(2): 26楊曉山, 張鵬. 倒角結晶器技術開發及應用. 連鑄, 2018, 43(2):26 [9] Yin H B. Solidifying shell waviness during continuous casting of AHSS slabs. IOP Conf Ser:Mater Sci Eng, 2019, 529(1): 012073 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/529/1/012073 [10] Yang L, Li Y, Xue Z L, et al. Effect of different thermal schedules on ductility of microalloyed steel slabs during continuous casting. Metals, 2019, 9(1): 37 doi: 10.3390/met9010037 [11] Yang X G, Zhang L F, Lai C B, et al. A method to control the transverse corner cracks on a continuous casting slab by combining microstructure analysis with numerical simulation of the slab temperature field. Steel Res Int, 2018, 89(5): 1700480 doi: 10.1002/srin.201700480 [12] Wang Y, Li G Q, Liu Y L, et al. Effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of normalized bands of grain oriented silicon steel. Materials Reports, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.TB.20210809.1551.016.html汪勇, 李光強, 劉玉龍, 等. Nb微合金化取向硅鋼常化板中析出物特征及其對組織和織構的影響. 材料導報, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1078.TB.20210809.1551.016.html [13] Yuan H, Yang S F, Wang T T, et al. Research progress of transverse corner crack on hypo-peritectic micro-alloyed steel slab. China Metall, 2020, 30(10): 1袁航, 楊樹峰, 王田田, 等. 亞包晶微合金鋼連鑄板坯角部橫裂紋研究進展. 中國冶金, 2020, 30(10):1 [14] Zhang Z F, Xing L D, Wang M, et al. Analysis of precipitation behavior of TiN in low carbon micro-alloyed steel. Continuous Cast, 2020, 45(5): 38張澤峰, 邢立東, 王敏, 等. 低碳微合金鋼中TiN的析出行為分析. 連鑄, 2020, 45(5):38 [15] Xu S Q, Zhao H P. Influence of solution treatment on precipitate bearing Nb in S30432 austenitic heat resistant steel. Iron Steel, 2018, 53(5): 86徐松乾, 趙海平. 固溶處理對S30432奧氏體耐熱鋼中含鈮析出相的影響. 鋼鐵, 2018, 53(5):86 [16] Du C, Zhang J, Wen J, et al. Hot ductility trough elimination through single cycle of intense cooling and reheating for microalloyed steel casting. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2016, 43(5): 331 doi: 10.1179/1743281215Y.0000000044 [17] Pascon F, Habraken A M. Finite element study of the effect of some local defects on the risk of transverse cracking in continuous casting of steel slabs. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng, 2007, 196(21-24): 2285 doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2006.07.017 [18] Ma F J, Wen G H, Tang P, et al. Causes of transverse corner cracks in microalloyed steel in vertical bending continuous slab casters. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2010, 37(1): 73 doi: 10.1179/030192309X12506804200465 [19] Guo G, Qiao J F. Continuous Casting Process Control Theory and Technology. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2003郭戈, 喬俊飛. 連鑄過程控制理論與技術. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2003 [20] Sun Y K, Wang J. Fundamentals of Metallurgical Process Automation. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006孫一康, 王京. 冶金過程自動化基礎: 冶金過程自動化技術叢書. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2006 [21] Jiang G S, Boyle J R. Computer dynamic control of the secondary cooling during continuous casting // Conference on Continuous Casting of Steel in Developing Countries. Beijing, 1993: 567 [22] Laitinen E, Neittaanm?ki P. On numerical simulation of the continuous casting process. J Eng Math, 1988, 22(4): 335 doi: 10.1007/BF00058513 [23] Okuno K, Naruwa H, Kuribayashi T, et al. Dynamic spray cooling control system for continuous casting. Iron Steel Eng, 1987, 64(4): 34 [24] Han Y S, Zhang J S, Zou L L, et al. Effect of nozzle spray distance on the secondary cooling uniformity of continuous casting billet. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(6): 739韓延申, 張江山, 鄒雷雷, 等. 噴嘴噴淋距離對連鑄小方坯二冷均勻性的影響. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(6):739 [25] Zhu M Y, Lin Q Y. Light reduction technology for continuous casting slab. Angang Technol, 2004(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2004.01.001朱苗勇, 林啟勇. 連鑄坯的輕壓下技術. 鞍鋼技術, 2004(1):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2004.01.001 [26] Brent A D, Voller V R, Reid K J. Enthalpy-porosity technique for modeling convection-diffusion phase change: Application to the melting of a pure metal. Numer Heat Transfer, 1988, 13(3): 297 doi: 10.1080/10407788808913615 [27] Louhenkilpi S, Laitinen E, Nieminen R. Real-time simulation of heat transfer in continuous casting. Metall Mater Trans B, 1993, 24(4): 685 doi: 10.1007/BF02673184 [28] Tao W Q. Numerical Heat Transfer. 2nd Ed. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 2001陶文銓. 數值傳熱學. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大學出版社, 2001 [29] Song W X. Metalology. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1989宋維錫. 金屬學. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 1989 [30] Chen L. Continuous Cast Steel. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994陳雷. 連續鑄鋼. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 1994 [31] Clyne T W, Kurz W. Solute redistribution during solidification with rapid solid state diffusion. Metall Trans A, 1981, 12(6): 965 doi: 10.1007/BF02643477 [32] Yin Y B, Zhang J M, Ma H T, et al. Large eddy simulation of transient flow, particle transport, and entrapment in slab mold with double-ruler electromagnetic braking. Steel Res Int, 2021, 92(5): 2000582 doi: 10.1002/srin.202000582 [33] Launder B E, Spalding D B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng, 1974, 3(2): 269 doi: 10.1016/0045-7825(74)90029-2 [34] Zhang X Z. Principles of Metallurgical Transmission. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1991張先棹. 冶金傳輸原理. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 1991 -




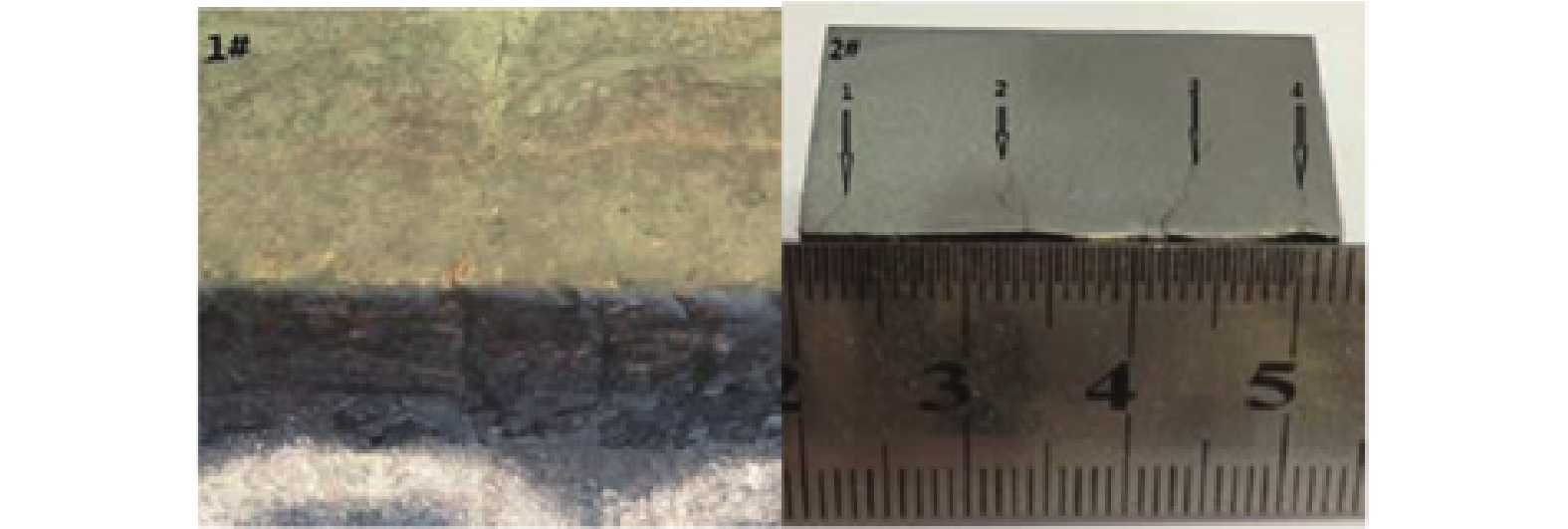
 下載:
下載: