Research progress of chromium solidification mechanism and preparation of inorganic materials by Cr-containing solid wastes from stainless steel industry
-
摘要: 我國不銹鋼工業近年來飛速發展,產生大量含鉻固廢。含Cr固廢的綜合利用工藝技術的開發,Cr元素的解毒/固化機理是需要考慮的關鍵問題。本文綜述了前人在該領域的相關研究工作,包括國內外不銹鋼工業固廢的化學和物相組成、鉻在不同含鉻固廢中的存在形式、鉻在環境中的循環富集規律和毒性。探討了含Cr礦相的演變規律、Cr在不同礦相中的固化機理。總結了目前利用不銹鋼工業含鉻固廢制備水泥、微晶玻璃和燒結陶瓷等各類無機材料的研究進展。分析了目前利用不銹鋼工業含鉻固廢制備各類無機材料過程中存在的瓶頸問題。以期為未來中國無害化、高值化、資源化處理不銹鋼含鉻固廢并實現產業化應用提供基礎借鑒。Abstract: In recent years, with the rapid development of the stainless steel industry in China, a large number of Cr-containing solid wastes are produced. Chromium resources in China are very scarce, and China mainly dependent on imported chromium. In the current situation of a limited supply of chromium ore in the world, determining the efficient utilization of chromium resources will become very important. The recovery of chromium in various solid wastes produced by the stainless steel industry has practical economic significance. In addition, an uncontrolled emission of Cr-containing solid wastes will endanger the ecological environment and hamper biological safety. Further, the large scale of China’s stainless steel industry has caused urgent environmental problems, i.e., the whole manufacturing process has produced a large number of Cr-containing solid wastes, including stainless steel slag, stainless steel dust, stainless steel rolled iron scale, and pickling sludge. The detoxification/solidification of Cr to obtain long-term safety performance is an important factor that must be considered in the development of a comprehensive utilization process technology for a large amount of Cr-containing solid wastes generated by the stainless steel industry. This paper reviewed the previous research work in this field, including the work regarding the chemical and phase compositions of the stainless steel industrial solid waste, the existing forms of chromium in different Cr-containing solid wastes, the cycle enrichment rule, and the toxicity of chromium in the environment. The evolution law of Cr-bearing mineral phases and the solidification mechanism of Cr in different mineral phases were discussed. The research progress of various inorganic materials such as cement, glass ceramics, and sintered ceramics prepared using Cr-containing solid wastes in the stainless steel industry was summarized. Bottleneck problems in the preparation of various inorganic materials from chromium-containing solid wastes in the stainless steel industry were analyzed to provide a basis for the future harmless, high-value, resource-based treatment of stainless steel Cr-containing solid wastes and the realization of industrial applications in China.
-
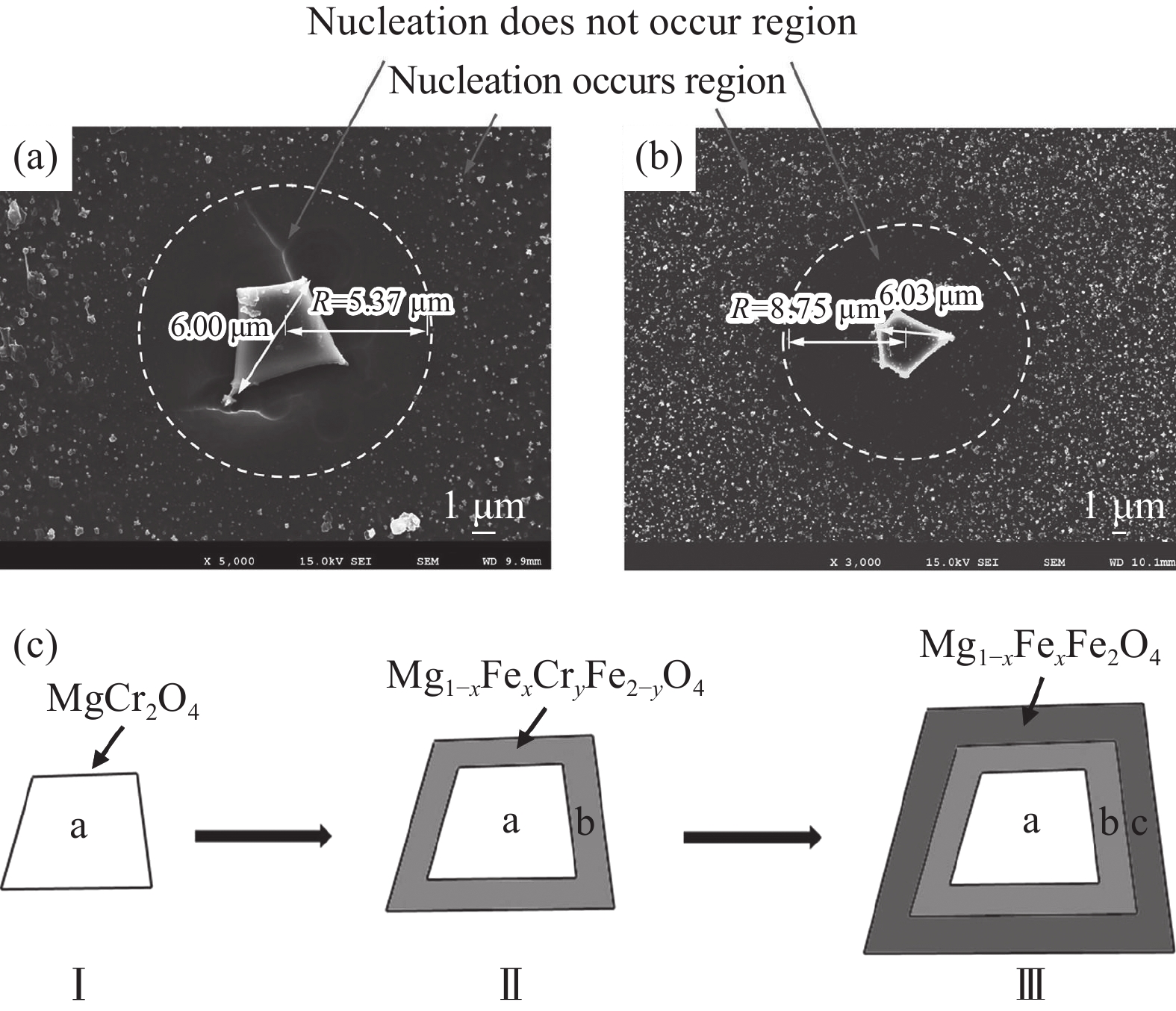
圖 2 (a) Fe/Si摩爾比為0.19 單晶尖晶石顯微結構[61]; (b) Fe/Si摩爾比為0.39單晶尖晶石顯微結構[61]; (c) 尖晶石冷卻過程形成示意圖[62]
Figure 2. (a) Microstructure of a single crystal spinel with Fe/Si mole ratios of 0.19[61]; (b) microstructure of a single crystal spinel with Fe/Si mole ratios of 0.39[61]; (c) growth diagram of the spinel during the cooling process[62]
表 1 不銹鋼行業含鉻固體廢物的化學成分(質量分數)
Table 1. Chemical composition of Cr-containing solid wastes in the stainless steel industry
% Types CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3/FeO MnO Cr2O3 NiO CaSO4 CaF2 Resource EAF slag 47.78 28.68 7.67 4.83 3.57 0.21 4.73 — — — [14] 46.5 28.0 7.4 4.3 2.7 1.7 8.0 — — — [15] 46.9 33.5 6.22 2.30 1.43 2.60 2.92 — — — [16] 36 32 4.4 7.9 1.6 5.8 10.4 — — — [17] AOD slag 64.02 26.51 4.68 1.54 0.28 0.47 0.43 — — — [14] 54.1 26.5 6.30 4.91 1.81 1.02 1.83 — — — [16] 56.4 29.7 8.5 1.6 1.1 0.3 1.6 — — — [18] 55.7 33.0 7.6 1.3 0.3 0.4 0.7 — — — [19] Stainless steel dust 28.70 0.70 3.71 0.12 22.18 / 13.19 0.03 — — [20] 10.8 3.42 2.12 1.45 47.6 / 11.1 2.12 — — [21] 19.3 5.8 3.2 0.5 37.1 / 16.3 2.98 — — [8] Stainless steel pickling sludge 14.68 0.17 0.99 11.48 20.09 / 4.12 0.96 51.61 8.92 [22] 7.95 1.15 0.92 / 17.5 / 5.07 3.18 8.50 42.7 [4] 14.61 2.37 0.38 0.88 15.48 / 6.12 1.03 5.32 13.86 [23] 表 2 不銹鋼工業含鉻固廢礦相組成
Table 2. Phase composition of Cr-containing solid wastes in the stainless steel industry
Types Phase composition Resource AOD slag (Mg,Fe)Cr2O4, Ni?Cr metal, Ca2SiO4, Cuspidine, MgO, CaF2 [16] MgCr2O4, Ca2SiO4, Cuspidine, Ca3Mg2O8, CaO [15] Ca2SiO4, MgO, Ni metal, Fe3O4 [24] Ca3Mg2O8, Cuspidine, MgO, β-Ca2SiO4, CaSiO3,CaF2 [19] γ-Ca2SiO4, Ca3Al2O6, MgAl2O4, Mg2SiO4 [25] EAF slag (Mg,Fe)2SiO4, Ca2SiO4, CaCrO4, CaCr2O4,Ni?Cr metal, MgCr2O4 [26] glass, MgCr2O4, CaTiO3,Ca2SiO4, [27] Ca3Mg2O8, MgCr2O4, γ-Ca2SiO4, [28] (Mg,Fe)Cr2O4, Ca3Mg2O8, Ca2SiO4,CaO [29] Ca2SiO4, Ca3Mg2O8, MgCr2O4, MgO, Ni?Cr metal [30] Stainless steel dust Fe2O3, Fe3O4, NiO, CrO, FeCr2O4, NiMn2O4, CuFe2O4, ZnCr2O4 [31] Fe2O3, Fe3O4, FeCr2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnO [32] Stainless steel pickling sludge Fe2O3, FeCr2O4, Cr(OH)3, NiCr2O4, Cr2O3, Cr, Ni(OH)2, CaF2, CaSO4·2H2O, CaCO3, CaCrO4, [33] Fe2O3, Fe3O4, FeCr2O4, NiO, NiFe2O4, CaCO3, SiO2 [34] 表 3 利用不銹鋼含鉻固廢制備微晶玻璃研究現狀
Table 3. Research status of the glass ceramic prepared from Cr-containing solid wastes of the stainless steel industry
Solid waste Main mineral phase Cr mass content and addition mass fraction of raw material Preparation heat treatment Properties Reference AOD stainless steel slag Diopside?akermanite?gehlenite 40%–80%AOD slag(2.1% Cr2O3) Melted at 1500 ℃ for 1 h and heated at the required temperatures Bending strength:137.83
MPa, acid and alkali resistances: 99.919% and 99.991%[94] Stainless steel slag Wollastonite?augite 1.82% Cr2O3 Melted at 1450 ℃ for 3 h and heated at the required temperatures Bending strength 176.21 MPa [95] Heavy metal gypsum and pickling sludge Akermanite Pickling sludge (4.55%Cr2O3) Melted at 1460 ℃ for 2.5 h, nucleated at 700 ℃ for 2 h, and crystallized at 900 ℃ for 1 h Bending strength: 206 MPa, [96] Fly ash and pickling sludge Diopside 22% pickling sludge Melted at 1400 ℃ for 3 h, nucleated and crystallized at 800 ℃ for 0.5 h Bending strength 135.84 MPa, acid and alkali resistances 98.65% and 99.88% [97] www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Ma G, Garbers-Craig A M. Cr(VI) containing electric furnace dusts and filter cake from a stainless steel waste treatment plant: Part 1 - Characteristics and microstructure. Ironmak Steelmak, 2006, 33(3): 229 doi: 10.1179/174328106X94816 [2] Zhang H W, Hong X. An overview for the utilization of wastes from stainless steel industries. Resour Conserv Recycl, 2011, 55(8): 745 doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.03.005 [3] Zhang H. Preparation of ecological activated carbon based on steel slag-modified biomass waste material and its formaldehyde degradation performance. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(2): 172張浩. 鋼渣改性生物質廢棄材料制備生態活性炭及其降解甲醛性能. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(2):172 [4] Sun D W, Deng J. Chlorine gas absorption performance of steel-slag-based biomass-activated carbon prepared via modified discarded walnut shell. Chin J Eng, 2021, 43(7): 946孫大為, 鄧軍. 特殊鋼渣超微粉改性廢棄核桃殼制備鋼渣基生物質活性炭及其吸收氯氣的性能. 工程科學學報, 2021, 43(7):946 [5] McClelland J M, Metius G E. Recycling ferrous and nonferrous waste streams with FASTMET. JOM, 2003, 55(8): 30 doi: 10.1007/s11837-003-0101-3 [6] Hara Y, Ishiwata N, Itaya H, et al. Smelting reduction process with a coke packed bed for steelmaking dust recycling. ISIJ Int, 2000, 40(3): 231 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.231 [7] Ye G Z, Burstr?m E, Kuhn M, et al. Reduction of steel-making slags for recovery of valuable metals and oxide materials. Scand J Metall, 2003, 32(1): 7 doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0692.2003.00526.x [8] Zhao H Q, Qi Y H, Shi Y L, et al. A test research on treatment of stainless steel dust by Oxycup. J Mater Metall, 2017, 16(1): 58趙海泉, 齊淵洪, 史永林, 等. Oxycup工藝處理不銹鋼粉塵的試驗研究. 材料與冶金學報, 2017, 16(1):58 [9] Khater G A. Influence of Cr2O3, LiF, CaF2 and TiO2 nucleants on the crystallization behavior and microstructure of glass-ceramics based on blast-furnace slag. Ceram Int, 2011, 37(7): 2193 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.03.011 [10] Hao X Y, Fan P H, Cui D, et al. Method for Preparing Ceramic Color Glaze with Chromium-Containing Waste Liquid: China Patent, CN104788128B. 2017-03-01郝小勇, 范盤華, 崔棟, 等. 一種利用含鉻廢液制備陶瓷色釉料的方法: 中國專利, CN104788128B. 2017-03-01 [11] Ma M L, Sun X N, Quan Z G, et al. Research progress on resource utilization of ceramsite prepared from industrial solid waste in China. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2020, 39(8): 2492馬明亮, 孫曉南, 權宗剛, 等. 我國工業固廢制備陶粒資源化利用的研究進展. 硅酸鹽通報, 2020, 39(8):2492 [12] Jiao H Z, Wang S F, Wu A X, et al. Cementitious property of NaAlO2-activated Ge slag as cement supplement. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2019, 26(12): 1594 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1901-y [13] Mukiza E, Zhang L L, Liu X M. Durability and microstructure analysis of the road base material prepared from red mud and flue gas desulfurization fly ash. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2020, 27(4): 555 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1915-5 [14] Wang Z J, Yang J, Pan D A, et al. Present state of stainless steel slag resources disposal technique. J Iron Steel Res, 2015, 27(2): 1汪正潔, 楊健, 潘德安, 等. 不銹鋼渣資源化利用技術研究現狀. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2015, 27(2):1 [15] Wang X, Geysen D, Van Gerven T, et al. Characterization of landfilled stainless steel slags in view of metal recovery. Front Chem Sci Eng, 2017, 11(3): 353 doi: 10.1007/s11705-017-1656-9 [16] Shen H T, Forssberg E, Nordstr?m U. Physicochemical and mineralogical properties of stainless steel slags oriented to metal recovery. Resour Conserv Recycl, 2004, 40(3): 245 doi: 10.1016/S0921-3449(03)00072-7 [17] Jung S S, Kim G B, Sohn I. Understanding the solidification of stainless steel slag and dust mixtures. J Am Ceram Soc, 2017, 100(8): 3771 doi: 10.1111/jace.14891 [18] Visuri V V, J?rvinen M, Savolainen J, et al. A mathematical model for the reduction stage of the AOD process. part II: Model validation and results. ISIJ Int, 2013, 53(4): 613 [19] Iacobescu R I, Malfliet A, Machiels L, et al. Stabilisation and microstructural modification of stainless steel converter slag by addition of an alumina rich by-product. Waste Biomass Valorization, 2014, 5(3): 343 doi: 10.1007/s12649-013-9287-y [20] Li X L, Liu X L, Li W C, et al. Experimental study on magnetic separation and reduction of stainless steel EAF dust. Chin J Process Eng, 2013, 13(3): 424李心林, 劉旭隆, 李文才, 等. 不銹鋼粉塵磁選?還原實驗研究. 過程工程學報, 2013, 13(3):424 [21] Wu T. Separation and Recovery of Cr from Typical Solid Waste of Stainless Steel Industry and Control of Reduction Reaction End Point [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019吳拓. 不銹鋼工業典型固廢中鉻的分離回收與還原反應終點控制[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2019 [22] Li X M, Jia L F, Zou C, et al. Progress and trend on comprehensive utilization of stainless steel pickling sludge. Iron Steel, 2019, 54(10): 1李小明, 賈李鋒, 鄒沖, 等. 不銹鋼酸洗污泥資源化利用技術進展及趨勢. 鋼鐵, 2019, 54(10):1 [23] Wang P, Yang X Y, Luo Q G, et al. A Treatment Method of Stainless Steel Pickling Sludge Type: China Patent, CN111560522A. 2020-8-21王攀, 楊賢有, 羅啟貴, 等. 一種不銹鋼酸洗污泥處理方法: 中國專利, CN111560522A. 2020-8-2 [24] Zhen C L, Na X Z, Qi Y H, et al. Basic research of stainless steel slag property and risk assessment on resource reclamation. Steelmaking, 2012, 28(4): 74甄常亮, 那賢昭, 齊淵洪, 等. 不銹鋼渣基礎性能研究及資源化利用風險評價. 煉鋼, 2012, 28(4):74 [25] Xu Y, Zhang Z Z, Wang B, et al. Curing influence factors and mechanism of stainless steel slag in AOD. Iron Steel, 2017, 52(8): 43許瑩, 張孜孜, 王變, 等. 不銹鋼AOD渣固化效果影響因素及其機理. 鋼鐵, 2017, 52(8):43 [26] Lü Y, Na X Z, Qi Y H. Industrial test on online detoxification of EAF stainless steel slag by silicothermic reduction process. Steelmaking, 2015, 31(2): 62呂巖, 那賢昭, 齊淵洪. 電爐不銹鋼渣硅熱法在線還原解毒的工業試驗. 煉鋼, 2015, 31(2):62 [27] Mostafaee S, Andersson M, J?nsson P. Petrographic and thermodynamic study of slags in EAF stainless steelmaking. Ironmak Steelmak, 2010, 37(6): 425 doi: 10.1179/030192310X12646889256022 [28] Engstr?m F, Adolfsson D, Yang Q, et al. Crystallization behaviour of some steelmaking slags. Steel Res Int, 2010, 81(5): 362 doi: 10.1002/srin.200900154 [29] Zhang W C, Wu X R, Wang W, et al. Enrichment of chromium in stainless steel slag by modification. J Anhui Univ Technol (Nat Sci) , 2012, 29(1): 12張文超, 武杏榮, 王偉, 等. 含鉻不銹鋼渣的改性與鉻的富集. 安徽工業大學學報(自然科學版), 2012, 29(1):12 [30] Gao Z Y, Li J G, Liu B, et al. Mineralogical composition of EAF slag and its short-term leaching characteristics. Ind Saf Environ Prot, 2017, 43(11): 80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.11.021高志遠, 李俊國, 劉寶, 等. EAF渣礦相組成及其短期淋溶特性. 工業安全與環保, 2017, 43(11):80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.11.021 [31] Peng B, Peng J. Physical and chemical characteristics of dust from electric arc furnace stainless steelmaking and mechanism of its formation. J North China Univ Technol, 2003, 15(1): 34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5477.2003.01.008彭兵, 彭及. 不銹鋼電弧爐粉塵的物理化學特性及形成機理探討. 北方工業大學學報, 2003, 15(1):34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5477.2003.01.008 [32] Wei F R, Zhang Y L, Wei W J, et al. Chemical composition of dust from stainless steel smelting and existing forms of Cr and Ni. Chin J Process Eng, 2011, 11(5): 786魏芬絨, 張延玲, 魏文潔, 等. 不銹鋼粉塵化學組成及其Cr、Ni存在形態. 過程工程學報, 2011, 11(5):786 [33] Yang C C, Pan J, Zhu D Q, et al. Pyrometallurgical recycling of stainless steel pickling sludge: A review. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2019, 26(6): 547 doi: 10.1007/s42243-019-00278-y [34] Liu P J, Liu Z G, Chu M S, et al. Green and efficient utilization of stainless steel dust by direct reduction and self-pulverization. J Hazard Mater, 2021, 413: 125403 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125403 [35] Albertsson G J, Engstr?m F, Teng L D. Effect of the heat treatment on the chromium partition in Cr-containing industrial and synthetic slags. Steel Res Int, 2014, 85(10): 1418 doi: 10.1002/srin.201300231 [36] Kriskova L, Pontikes Y, Pandelaers L, et al. Effect of high cooling rates on the mineralogy and hydraulic properties of stainless steel slags. Metall Mater Trans B, 2013, 44(5): 1173 doi: 10.1007/s11663-013-9894-9 [37] Li W L, Xue X X. Effect of cooling regime on phase transformation and chromium enrichment in stainless-steel slag. Ironmak Steelmak, 2019, 46(7): 642 doi: 10.1080/03019233.2018.1436890 [38] Albertsson G, Teng L D, Bj?rkman B, et al. Effect of low oxygen partial pressure on the chromium partition in CaO?MgO?SiO2?Cr2O3?Al2O3 synthetic slag at elevated temperatures. Steel Res Int, 2013, 84(7): 670 doi: 10.1002/srin.201200214 [39] Li J L, Zhu H Y, Xue Z L. Investigation on the effect of cooling condition on chromium elution from stainless steel slag. Adv Mater Res, 2014, 968: 101 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.968.101 [40] Yang Z H, Lin Q, Lu S C, et al. Effect of CaO/SiO2 ratio on the preparation and crystallization of glass-ceramics from copper slag. Ceram Int, 2014, 40(5): 7297 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.071 [41] Albertsson G J, Teng L D, Engstr?m F, et al. Effect of the heat treatment on the chromium partition in CaO?MgO?SiO2?Cr2O3 synthetic slags. Metall Mater Trans B, 2013, 44(6): 1586 doi: 10.1007/s11663-013-9939-0 [42] Ma J, Fu G Q, Li W, et al. Influence of TiO2 on the melting property and viscosity of Cr-containing high-Ti melting slag. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2020, 27(3): 310 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1914-6 [43] Zhao X, Fourie A, Qi C C. Mechanics and safety issues in tailing-based backfill: A review. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2020, 27(9): 1165 doi: 10.1007/s12613-020-2004-5 [44] James B R. Peer reviewed: The challenge of remediating chromium-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol, 1996, 30(6): 248A doi: 10.1021/es962269h [45] Bartlett R J. Chromium cycling in soils and water: Links, gaps, and methods. Environ Heal Perspect, 1991, 92: 17 doi: 10.1289/ehp.919217 [46] James B R. Remediation-by-reduction strategies for chromate-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Hlth, 2001, 23(3): 175 doi: 10.1023/A:1012477901521 [47] Apte A D, Verma S, Tare V, et al. Oxidation of Cr(III) in tannery sludge to Cr(VI): Field observations and theoretical assessment. J Hazard Mater, 2005, 121(1-3): 215 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.02.010 [48] Arnfalk P, Wasay S A, Tokunaga S. A comparative study of Cd, Cr(III), Cr(VI), Hg, and Pb uptake by minerals and soil materials. Water Air Soil Pollut, 1996, 87(1-4): 131 doi: 10.1007/BF00696833 [49] Eary L E, Rai D. Chromate reduction by subsurface soils under acidic conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 1991, 55(3): 676 doi: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500030007x [50] Dhal B, Thatoi H N, Das N N, et al. Chemical and microbial remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and mining/metallurgical solid waste: A review. J Hazard Mater, 2013, 250-251: 272 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.048 [51] Chaurand P, Rose J, Proux O, et al. Environmental impact of steel slag reused as aggregates in road manufacturing: Molecular mechanisms of chromium and vanadium release. AIP Conf Proc, 2007, 882(1): 199 [52] De Windt L, Chaurand P, Rose J. Kinetics of steel slag leaching: Batch tests and modeling. Waste Manag, 2011, 31(2): 225 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.05.018 [53] Liao C Z, Tang Y Y, Liu C S, et al. Double-barrier mechanism for chromium immobilization: A quantitative study of crystallization and leachability. J Hazard Mater, 2016, 311: 246 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.020 [54] Cao L H, Liu C J, Zhao Q, et al. Analysis on the stability of chromium in mineral phases in stainless steel slag. Metall Res Technol, 2017, 115(1): 114 [55] García-Ramos E, Romero-Serrano A, Zeifert B, et al. Immobilization of chromium in slags using MgO and Al2O3. Steel Res Int, 2008, 79(5): 332 doi: 10.1002/srin.200806135 [56] Cao L H, Liu C J, Zhao Q, et al. Effect of Al2O3 modification on enrichment and stabilization of chromium in stainless steel slag. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2017, 24(3): 258 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30038-9 [57] Cao L H, Liu C J, Zhao Q, et al. Growth behavior of spinel in stainless steel slag during cooling process. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2018, 25(11): 1131 doi: 10.1007/s42243-018-0058-7 [58] Brime C, Eberl D D. Growth mechanisms of low-grade illites based on the shapes of crystal thickness distributions. Schweiz Mineral Petrogr Mitt, 2002, 82: 203 [59] Li J L, Xu A J, He D F, et al. Effect of FeO on the formation of spinel phases and chromium distribution in the CaO?SiO2?MgO?Al2O3?Cr2O3 system. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2013, 20(3): 253 doi: 10.1007/s12613-013-0720-9 [60] Bai Z T, Qiu G B, Peng B, et al. Synthesis and characterization of glass-ceramics prepared from high-carbon ferrochromium slag. RSC Adv, 2016, 6(58): 52715 doi: 10.1039/C6RA06245H [61] Zeng Q, Li J L, Mou Q Q, et al. Effect of FeO on spinel crystallization and chromium stability in stainless steel-making slag. JOM, 2019, 71(7): 2331 doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03465-0 [62] Zhao M Z, Cao J W, Wang Z, et al. Insight into the dual effect of Fe2O3 addition on the crystallization of CaO?MgO?Al2O3?SiO2 glass-ceramics. J Non Cryst Solids, 2019, 513: 144 doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.03.021 [63] Mou Q Q, Li J L, Zeng Q, et al. Effect of Fe2O3 on the size and components of spinel crystals in the CaO?SiO2?MgO?Al2O3?Cr2O3 system. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2019, 26(9): 1113 doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1822-9 [64] Shu Q F, Luo Q Y, Wang L J, et al. Effects of MnO and CaO/SiO2 Mass ratio on phase formations of CaO?Al2O3?MgO?SiO2?CrOx Slag at 1673 K and PO2=10–10 atm. Steel Res Int, 2015, 86(4): 391 doi: 10.1002/srin.201400117 [65] Wang Z J, Sohn I. Immobilizing chromium in stainless steel slags with MnO addition. J Am Ceram Soc, 2021, 104(2): 697 doi: 10.1111/jace.17473 [66] Wang Z J, Sohn I. Selective elemental concentration during the solidification of stainless steel slags for increased Cr recovery with MnO addition. J Am Ceram Soc, 2020, 103(10): 6012 doi: 10.1111/jace.17296 [67] Lin Y, Luo Q Y, Yan B J, et al. Effect of B2O3 addition on mineralogical phases and leaching behavior of synthetic CaO?SiO2?MgO?Al2O3?CrOx slag. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag, 2020, 22(4): 1208 doi: 10.1007/s10163-020-01015-4 [68] Lin Y, Yan B J, Fabritius T, et al. Immobilization of chromium in stainless steel slag using low zinc electric arc furnace dusts. Metall Mater Trans B, 2020, 51(2): 763 doi: 10.1007/s11663-020-01777-0 [69] Wang Z J, Sohn I. Understanding the solidification and leaching behavior of synthesized Cr-containing stainless steel slags with varying Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratios. Ceram Int, 2021, 47(8): 10918 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.211 [70] Fang J H, Yang F, Zuo M Y, et al. Glassification of chromium slag for curing chromium ions. Glass Enamel, 2014, 42(4): 5方久華, 楊峰, 左明揚, 等. 鉻渣玻璃化固化鉻離子. 玻璃與搪瓷, 2014, 42(4):5 [71] Li J B, Li Y, Li B J, et al. The effect of chromate doped on borosilicate glass's structure. J Funct Mater, 2017, 48(7): 7209李江波, 李揚, 李寶軍, 等. 摻加鉻對硼硅酸鹽玻璃固化體結構影響. 功能材料, 2017, 48(7):7209 [72] Zhang Y X, Liu S L, OuYang S L, et al. Transformation of unstable heavy metals in solid waste into stable state by the preparation of glass-ceramics. Mater Chem Phys, 2020, 252: 123061 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123061 [73] Kindness A, Macias A, Glasser F P. Immobilization of chromium in cement matrices. Waste Manag, 1994, 14(1): 3 doi: 10.1016/0956-053X(94)90016-7 [74] Wei J X, Yao J Y, Yu Q J, et al. Chemical form of Cr existing in hardened Portland cement. J Chin Ceram Soc, 2009, 37(7): 1118 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.07.010韋江雄, 堯璟云, 余其俊, 等. 硅酸鹽水泥硬化體中Cr的存在形態分析. 硅酸鹽學報, 2009, 37(7):1118 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.07.010 [75] Lin C K, Chen J N, Lin C C. An NMR, XRD and EDS study of solidification/stabilization of chromium with Portland cement and C3S. J Hazard Mater, 1997, 56(1-2): 21 doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(97)00032-0 [76] Zhang M T, Yang C H, Zhao M, et al. Immobilization of Cr(VI) by hydrated Portland cement pastes with and without calcium sulfate. J Hazard Mater, 2018, 342: 242 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.039 [77] Wang X, Yan B L, Wang L, et al. The research on capturing several heavy metal irons and its stability of C?S?H with different Ca/Si. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2012, 31(6): 1356王昕, 顏碧蘭, 汪瀾, 等. 不同鈣硅比C?S?H對多種重金屬離子的俘獲及其穩定性. 硅酸鹽通報, 2012, 31(6):1356 [78] Tantawy M A, El-Roudi A M, Salem A A. Immobilization of Cr(VI) in bagasse ash blended cement pastes. Constr Build Mater, 2012, 30: 218 doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.12.016 [79] Zhang J G, Provis J L, Feng D W, et al. Geopolymers for immobilization of Cr6+, Cd2+, and Pb2+. J Hazard Mater, 2008, 157(2-3): 587 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.053 [80] Giergiczny Z. Effect of fly ash from different sources on the properties of hardened cement composites. Silic Ind, 2005, 70(3): 35 [81] Giergiczny Z, Król A. Immobilization of heavy metals (Pb, Cu, Cr, Zn, Cd, Mn) in the mineral additions containing concrete composites. J Hazard Mater, 2008, 160(2-3): 247 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.007 [82] Bakhshi N, Sarrafi A, Ramezanianpour A A. Immobilization of hexavalent chromium in cement mortar: Leaching properties and microstructures. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2019, 26(20): 20829 doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05301-z [83] Spanka M, Mansfeldt T, Bialucha R. Influence of natural and accelerated carbonation of steel slags on their leaching behavior. Steel Res Int, 2016, 87(6): 798 doi: 10.1002/srin.201500370 [84] Zhang H N, Wei C, Dong J P. Inhibition kinetics of chromium leaching by calcite coating on the surface of stainless steel slag via the gas?solid accelerated carbonation process. Waste Biomass Valorization, 2021, 12(1): 475 doi: 10.1007/s12649-020-00988-5 [85] Jiang Y, Ling T C, Shi C J, et al. Characteristics of steel slags and their use in cement and concrete—A review. Resour Conserv Recycl, 2018, 136: 187 doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.023 [86] Zhang W S, Zhang J T, Ye J Y, et al. Structure and activity of dicalcium silicate. J Chin Ceram Soc, 2019, 47(11): 1663張文生, 張江濤, 葉家元, 等. 硅酸二鈣的結構與活性. 硅酸鹽學報, 2019, 47(11):1663 [87] Moon E J, Choi Y C. Development of carbon-capture binder using stainless steel argon oxygen decarburization slag activated by carbonation. J Clean Prod, 2018, 180: 642 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.189 [88] Dai W B, Li Y, Cang D Q, et al. Research on a novel modifying furnace for converting hot slag directly into glass-ceramics. J Clean Prod, 2018, 172: 169 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.039 [89] Wang Y J, Li J G, Zhang Y Z, et al. Effect of leaching atmosphere on dynamic leaching characteristic of chromium in AOD stainless steel slag. Iron Steel, 2021, 56(07): 145王亞軍, 李俊國, 張玉柱, 等. 淋溶氣氛對AOD不銹鋼渣中鉻動態淋溶的影響. 鋼鐵, 2021, 56(07):145 [90] Li J X. Effect of Modification at High Temperature on the Composition, Structure and Property of Steel Slag [Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2011李建新. 高溫重構對鋼渣組成、結構與性能影響的研究[學位論文]. 廣州: 華南理工大學, 2011 [91] Hao Y D, Wu L. Characteristics and practice of the new technology of hot pressing and suffocating treatment of waste heat from steel slag roll crushing // The 4th Metallurgical Slag Solid Waste Recovery, Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction and Comprehensive Utilization of Resources Summit Forum. Hanzhong, 2019: 75郝以黨, 吳龍, 鋼渣輥壓破碎余熱有壓熱悶處理新技術的特點及實踐//第四屆冶金渣固廢回收、節能減排及資源綜合利用高峰論壇會. 漢中, 2019: 75 [92] Barbieri L, Leonelli C, Manfredini T, et al. Solubility, reactivity and nucleation effect of Cr2O3 in the CaO?MgO?Al2O3?SiO2 glassy system. J Mater Sci, 1994, 29(23): 6273 doi: 10.1007/BF00354571 [93] Zhang S, Zhang Y L, Wu T. Effect of Cr2O3 on the crystallization behavior of synthetic diopside and characterization of Cr-doped diopside glass ceramics. Ceram Int, 2018, 44(9): 10119 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.231 [94] Zhang S, Zhang Y L, Qu Z M. Physicochemical property and chromium leaching behavior in different environments of glass ceramics prepared from AOD stainless steel slag. J Alloys Compd, 2019, 805: 1106 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.065 [95] Deng L B, Yun F, Jia R D, et al. Effect of SiO2/MgO ratio on the crystallization behavior, structure, and properties of wollastonite-augite glass-ceramics derived from stainless steel slag. Mater Chem Phys, 2020, 239: 122039 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122039 [96] Pan D A, Li L J, Yang J, et al. Production of glass-ceramics from heavy metal gypsum and pickling sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol, 2015, 12(9): 3047 doi: 10.1007/s13762-015-0758-5 [97] Zhao S Z, Liu B, Ding Y J, et al. Study on glass-ceramics made from MSWI fly ash, pickling sludge and waste glass by one-step process. J Clean Prod, 2020, 271: 122674 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122674 [98] Yang J, Liu B, Zhang S G, et al. Glass-ceramics one-step crystallization accomplished by building Ca2+ and Mg2+ fast diffusion layer around diopside crystal. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 688: 709 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.027 [99] Zou C M, Cao J W, Zhao M Z, et al. Combined sodium and fluorine promote diopside continuous growth to achieve one-step crystallization in CaO?Al2O3?SiO2?Fe2O3 glass-ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2019, 39(15): 4979 doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.07.033 [100] Liang Y W, Zhang S, Zhang Y L. Effect of alumina content on the microstructure and properties of cast stone prepared by one-step method. Jiangxi Metall, 2021, 41(4): 1梁益瑋, 張帥, 張延玲. 氧化鋁含量對一步法制備鑄石微觀結構與性能的影響. 江西冶金, 2021, 41(4):1 [101] Liu M K, Ma G J, Zhang X, et al. Preparation of black ceramic tiles using waste copper slag and stainless steel slag of electric arc furnace. Materials, 2020, 13(3): 776 doi: 10.3390/ma13030776 [102] Zong Y B, Li Y, Cang D Q. Experimental study on stainless steel slag used in ceramic making. Adv Mater Res, 2010, 105-106: 758 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.105-106.758 [103] Liu C B, Liu L B, Tan K F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of porous cordierite ceramics prepared from ferrochromium slag. Ceram Int, 2016, 42(1): 734 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.174 [104] Zhu M X, Bai H, Liu D R. Preparation and properties of ceramsite from stainless steel pickling sludge and clay. J Wuhan Univ Sci Technol, 2016, 39(3): 185朱明旭, 白皓, 劉德榮. 不銹鋼酸洗污泥?黏土基陶粒的制備及性能研究. 武漢科技大學學報, 2016, 39(3):185 -




 下載:
下載: