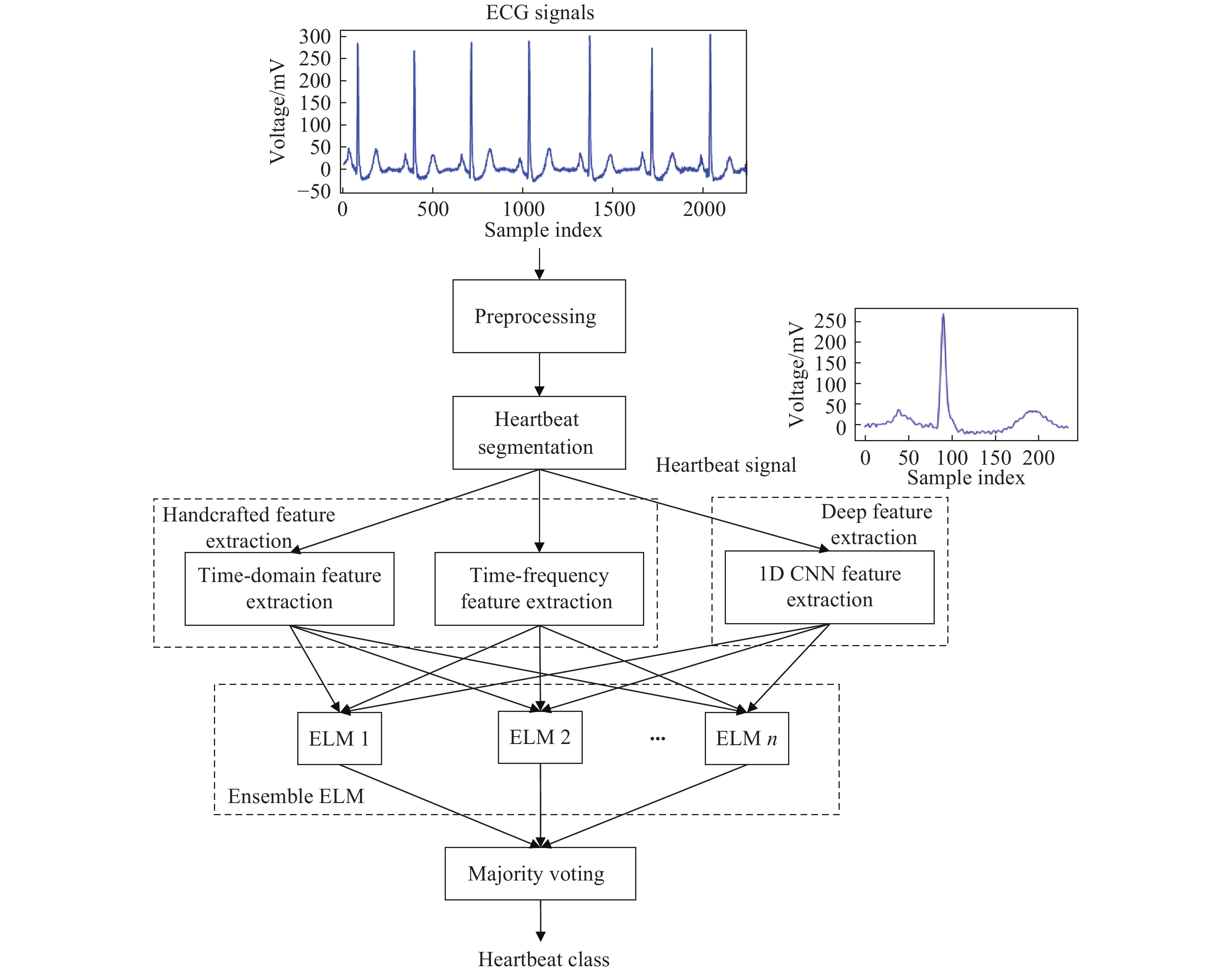
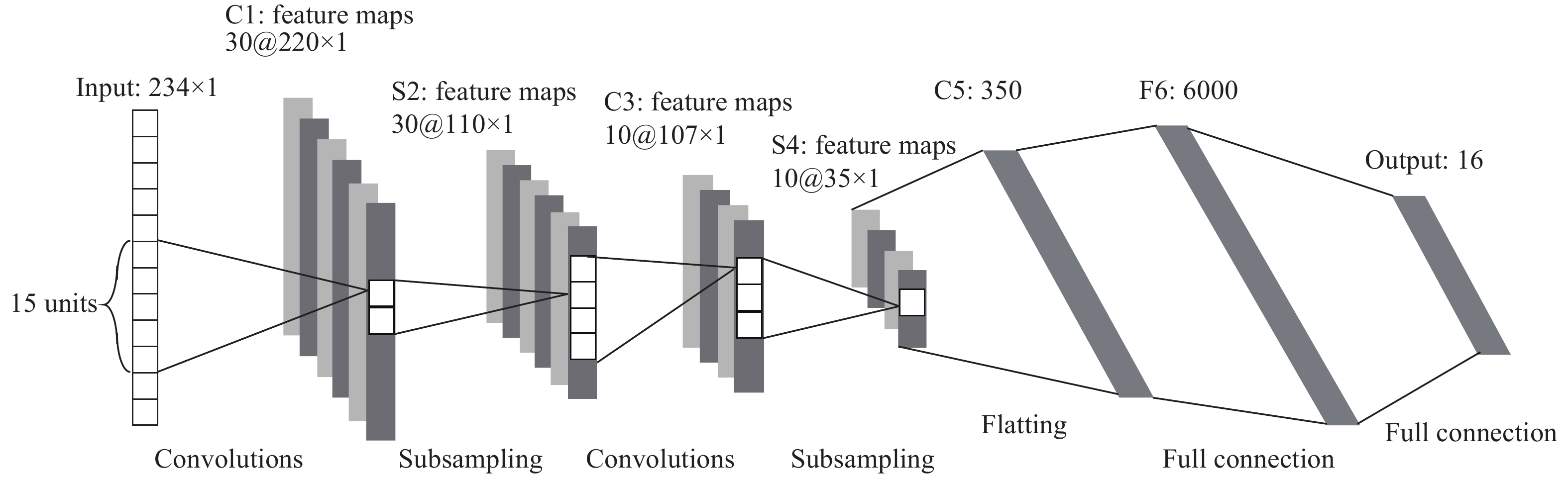
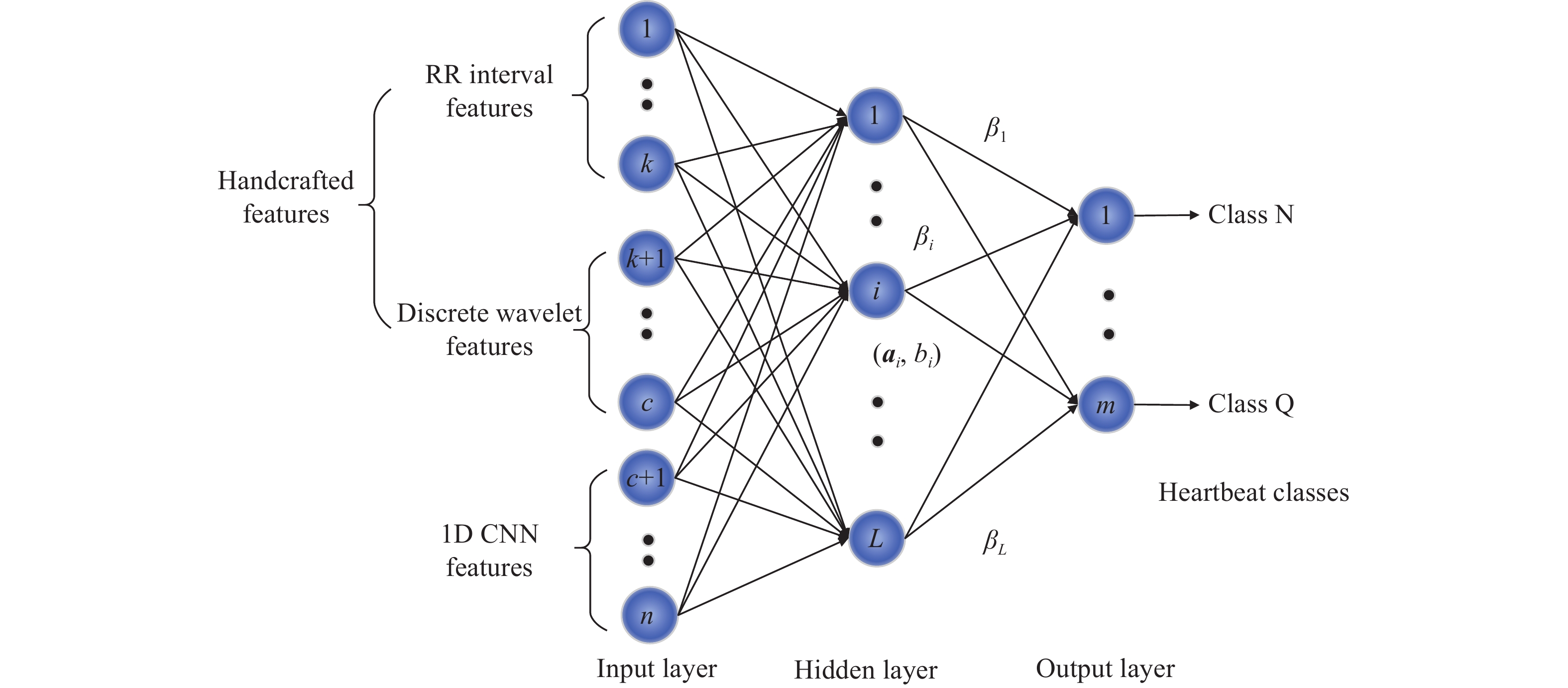
Ensemble extreme learning machine approach for heartbeat classification by fusing 1d convolutional and handcrafted features
-
摘要: 融合手工特征和深度特征,提出了一種集成超限學習機心跳分類方法。手工提取的特征明確地表征了心電信號的特定特性,如相鄰心跳時間間隔反映了心跳信號的時域特性,小波系數反映了心跳信號的時頻特性。同時設計了一維卷積神經網絡對心跳信號特征進行自動提取。基于超限學習機(Extreme leaning machine,ELM),將上述特征融合進行心跳分類。由于ELM初始參數的隨機給定可能導致其性能不穩定,進一步提出了一種基于袋裝(Bagging)策略的多個ELM集成方法,使分類結果更加穩定且模型泛化能力更強。利用麻省理工心律失常公開數據集對所提方法進行了驗證,分類準確率達到了99.02%,實驗結果也表明基于融合特征的分類準確率高于基于單獨特征的分類準確率。Abstract: Arrhythmia is a common cardiovascular disease whose occurrence is mainly related to two factors: cardiac pacing and conduction. Some severe arrhythmias can even threaten human life. An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the changes in electrical activity generated during each cardiac cycle of the heart, which can reflect the human cardiac health status and help diagnose arrhythmias. However, because of the brevity of conventional ECGs, arrhythmias, which occasionally occur in daily life, cannot be detected easily. Automatic ECG analysis-based long-term heartbeat monitoring is of great significance for the effective detection of accidental arrhythmias and then for taking indispensable measures to prevent cardiovascular diseases in time. An ensemble extreme learning machine (ELM) approach for heartbeat classification that fuses handcrafted features and deep features was proposed. The manually extracted features clearly characterize the heartbeat signal, where RR interval features reflect the time-domain characteristic, and the wavelet coefficient features reflect the time–frequency characteristic. A 1D convolutional neural network (1D CNN) was designed to automatically extract deep features for heartbeat signals. These features were fused by an ELM for heartbeat classification. Because of the instability caused by the random assignment of ELM hidden layer parameters, the bagging ensemble strategy was introduced to integrate multiple ELMs to achieve stable classification performance and good generalization ability. The proposed approach was validated on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia public dataset. The classification accuracy reaches 99.02%, and the experimental results show that the performance of the proposed approach with fused features is better than those with only deep features and only handcrafted features.
-
表 1 MIT?BIH數據集的詳細描述和劃分
Table 1. Detailed description and division of the MIT?BIH dataset
Heartbeat type (abbreviation) Annotation Total
number of
samplesNumber of training samples Number of testing samples Normal beat (NOR) N 75023 9753 65270 Left bundle branch block (LBBB) L 8072 3229 4843 Right bundle branch block (RBBB) R 7255 2902 4353 Atrial premature contraction (APC) A 2546 1018 1528 Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) V 7129 2852 4277 Paced beat (PACE) / 7026 2810 4216 Aberrated atrial premature beat (AP) a 150 75 75 Ventricular flutter
wave (VF)! 472 236 236 Fusion of ventricular and normal beat (VFN) F 802 401 401 Blocked atrial premature beat (BAP) x 193 96 97 Nodal (junctional) escape beat (NE) j 229 114 115 Fusion of paced and normal beat (FPN) f 982 491 491 Ventricular escape
beat (VE)E 106 53 53 Nodal (junctional) premature beat (NP) J 83 42 41 Atrial escape beat (AE) e 16 8 8 Unclassifiable beat (UN) Q 33 16 17 Total 16 110117 24096 86021 表 2 每類心跳的召回率和精確率
Table 2. Recall and precision for each heartbeat class
Heartbeat type Number of test samples Recall/% Precision/% N 65270 99.58 99.43 L 4843 99.71 99.67 R 4353 99.61 99.34 A 1528 86.45 94.90 V 4277 97.80 95.57 / 4216 99.69 99.41 a 75 65.33 92.45 ! 236 93.64 92.47 F 401 79.55 87.40 x 97 86.60 94.38 j 115 87.83 71.13 f 491 91.65 96.98 E 53 94.34 98.04 J 41 90.24 97.37 e 8 12.50 100.00 Q 17 5.88 50.00 Total 86021 99.02 99.02 表 3 混淆矩陣
Table 3. Confusion matrix
Predict labels N L R A V / a ! F x j f E J e Q True labels N 64996 9 3 58 126 1 0 8 28 4 32 4 0 0 0 1 L 6 4829 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 R 8 0 4336 6 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 A 169 1 20 1321 9 0 0 1 0 0 6 1 0 0 0 0 V 62 4 1 2 4183 0 1 5 18 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 / 5 0 0 0 1 4203 0 0 0 0 1 6 0 0 0 0 a 11 2 0 4 7 0 49 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ! 8 0 0 0 5 0 1 221 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 F 54 0 1 0 27 0 0 0 319 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 x 4 0 0 1 4 0 1 2 0 84 1 0 0 0 0 0 j 12 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 101 0 0 1 0 0 f 16 0 0 0 1 24 0 0 0 0 0 450 0 0 0 0 E 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 50 0 0 0 J 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 37 0 0 e 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Q 10 0 1 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 表 4 提出的方法與其他方法的比較結果
Table 4. Comparison results of the proposed approach with other approaches
Reference Features + Classifier Accuracy/
%Manual features only DWT, RR + ELM (Single) 98.28 Deep feature only 1D CNN 98.50 Feature fusion
(Without ensemble)DWT, RR, 1D Convolution +
ELM (Single)98.81 Ye[9] ICA, Wavelet, RR + SVM
(One-against-one)98.72 Our proposed approach DWT, RR, 1D Convolution + ELM
(Bagging ensemble)99.02 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Thaler M S. The Only EKG Book You’ll Ever Need. 9th Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017[2] Gawlowska J, Wranicz J K, Norman J. “Jeff ” Holter (1914—1983). Cardiol J, 2009, 16(4): 386 [2] Chazal P d, Reilly R B. A patient-adapting heartbeat classifier using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2006, 53(12): 2535 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.883802 [3] Mondéjar-Guerra V, Novo J, Rouco J, et al. Heartbeat classification fusing temporal and morphological information of ECGs via ensemble of classifiers. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2019, 47: 41 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2018.08.007 [4] Chazal P d, O'Dwyer M, Reilly R B. Automatic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51(7): 1196 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.827359 [5] Tuncer T, Dogan S, P?awiak P, et al. Automated arrhythmia detection using novel hexadecimal local pattern and multilevel wavelet transform with ECG signals. Knowl Based Syst, 2019, 186: 104923 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.104923 [6] Sahoo S, Kanungo B, Behera S, et al. Multiresolution wavelet transform based feature extraction and ECG classification to detect cardiac abnormalities. Measurement, 2017, 108: 55 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.022 [7] Afkhami R G, Azarnia G, Tinati M A. Cardiac arrhythmia classification using statistical and mixture modeling features of ECG signals. Pattern Recognit Lett, 2016, 70: 45 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2015.11.018 [8] Marinho L B, Nascimento N M M, Souza J W M, et al. A novel electrocardiogram feature extraction approach for cardiac arrhythmia classification. Future Gener Comput Syst, 2019, 97: 564 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.03.025 [9] Ye C, Vijaya Kumar B V K, Coimbra M T. Heartbeat classification using morphological and dynamic features of ECG signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2012, 59(10): 2930 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2213253 [10] Castillo O, Melin P, Ramírez E, et al. Hybrid intelligent system for cardiac arrhythmia classification with Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbors and neural networks combined with a fuzzy system. Expert Syst Appl, 2012, 39(3): 2947 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.08.156 [11] Girshick R. Fast R?CNN // 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, 2015: 1440 [12] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks // 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, 2017: 2261 [13] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2015, 37(9): 1904 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [14] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions // 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, 2015: 1 [15] Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering // 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, 2015: 815 [16] Ding C X, Tao D C. Trunk-branch ensemble convolutional neural networks for video-based face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2018, 40(4): 1002 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2700390 [17] He R, Wu X, Sun Z N, et al. Wasserstein CNN: Learning invariant features for NIR-VIS face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2019, 41(7): 1761 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2842770 [18] Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(4): 640 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [19] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [20] Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1-3): 489 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 [21] Huang G B, Chen L, Siew C K. Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 2006, 17(4): 879 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2006.875977 [22] Anthimopoulos M, Christodoulidis S, Ebner L, et al. Lung pattern classification for interstitial lung diseases using a deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1207 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2535865 [23] Li J Y, Zhao Y K, Xue Z E, et al. A survey of model compression for deep neural networks. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(10): 1229李江昀, 趙義凱, 薛卓爾, 等. 深度神經網絡模型壓縮綜述. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(10):1229 [24] Ji S W, Xu W, Yang M, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2013, 35(1): 221 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 [25] Bartlett P L. The sample complexity of pattern classification with neural networks: The size of the weights is more important than the size of the network. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1998, 44(2): 525 doi: 10.1109/18.661502 [26] PhysioNet. MIT−BIH Arrhythmias Database [J/OL]. PhysioNet Online (2020-04-15) [2021-01-12] https://physionet.org/files/mitdb/1.0.0 [27] Moody G B, Mark R G. The impact of the mit-bih arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag, 2001, 20(3): 45 doi: 10.1109/51.932724 -




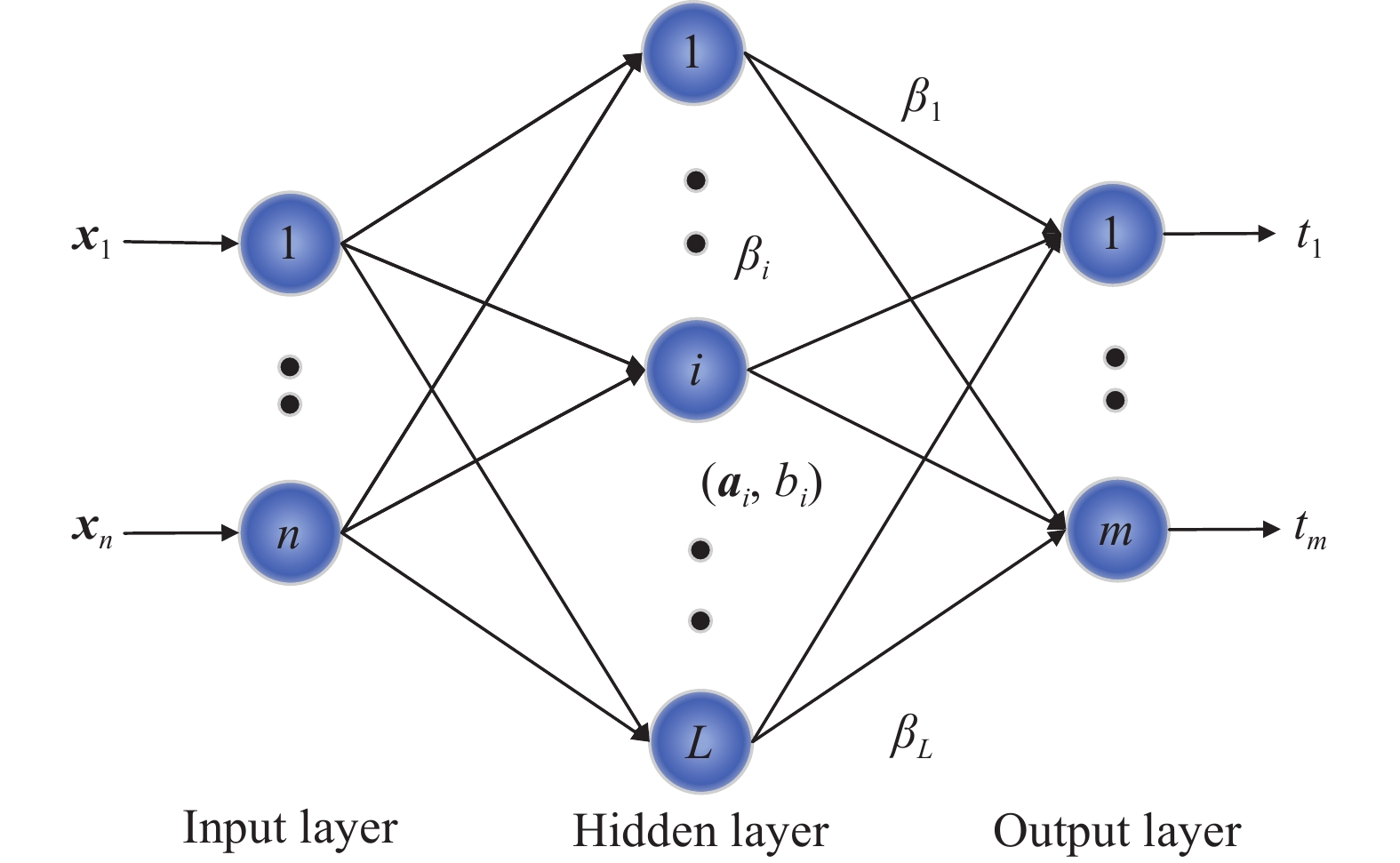
 下載:
下載: