-
摘要: 首先,從理論分析、實驗研究和數值模型三個方面概述了當前多孔介質細觀流動的研究現狀,重點圍繞納微孔隙中流體流動界面作用與細觀力學特性關系及表征、細觀?宏觀網絡仿真模擬、細觀尺度流體(油/水、氣/水)流動細觀動力學機制及數學模型等關鍵問題展開論述。在此基礎上介紹了當前細觀流動界面作用與細觀力學特性研究情況,明確了細觀尺度流體非線性流動機理,構建了反映微觀力作用下細觀尺度流動的數學模型,形成了網絡仿真模擬方法。將為非常規油氣開發過程中揭示影響流動細觀成因,進一步闡明不同條件下的動用機理,確定高效開發方法提供指導,同時促進滲流力學學科的發展,具有重要的理論和現實意義。Abstract: Porous media are widely found in underground rocks, biomimetic, and engineering materials. However, the current flow theory of fluids (liquid and gas, etc.) is incomplete to study flows in small and complex pores, thus a new theory is urgently needed for studying a large number of fluid flows in porous media. The theory of meso-scale flow in porous media is a “mysterious key” to unlock the flow of nano-micron porous media. At present, a large number of fluid flow problems need an immediate solution in porous media such as shale oil and gas development, soil seepage, human capillary network, and carbon nanotube (CNT). With the advancement of world petroleum engineering technology, unconventional oil and gas reservoirs have become the main areas of development in the petroleum industry. There are a large number of nano-scale pores in unconventional oil and gas reservoirs, and the existing macro-statistical methods of Darcy and non-Darcy percolation cannot reveal the nonlinear flow mechanism and effective production mechanism of fluid in mesopores. Thus, it is urgent to carry out theoretical research on meso-flow in porous media to provide a theoretical basis for unconventional oil and gas development. This paper summarizes the research results in this area, including those of the authors. The current research status of fine and meso flow in porous media is summarized from three aspects: (1) theoretical analysis, (2) experimental research, and (3) numerical model, focusing on key issues such as the relationship and characterization of meso-scale fluid flow interface and micro-mechanical properties, meso–macro network simulation, meso-scale fluid (oil/water, gas/water) flow, meso-dynamic mechanism, and mathematical models. On this basis, the importance of the research on the interface effect and meso-mechanical characteristics of fine and micro-scale fluid flow, the nonlinear flow mechanism of the fine and meso-scale fluids, the construction of a mathematical model reflecting the meso-scale flow under the action of micro-forces, and the formation of a network simulation method are introduced. The study provides certain guiding significance for unconventional oil and gas development processes, revealing the meso-causes affecting flow, clarifying the production mechanism under different conditions, and promoting further development of the discipline of seepage mechanics.
-
Key words:
- porous media /
- mesoscopic flow /
- interface effect /
- micro force /
- pore network model
-
表 1 不同尺度油氣滲流數學模型
Table 1. Mathematical models of oil and gas seepage in different scales
Scale Reservoir type Mathematical model of seepage Expression Literature Source Meso-Scale (l=10 nm–1 mm) Ultra-low permeability reservoirs, Shale reservoirs, Tight reservoirs Ultra-low permeabiliy shallow sandstone $ v = - \dfrac{k}{\mu }\left[ {\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}} - \lambda } \right] $ [54] Tight oil reservoir $ v = \left( {2am{k^r} + b} \right)\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{{{\lambda _{\text{c}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}} + {\lambda _{\text{c}}} - \lambda }}} \right) $ [55] Shale gas reservoir $ v = - \dfrac{{{k_{\text{o}}}}}{\mu }\left( {1 + \dfrac{{3{\text{π }}a}}{{16{k_{\text{o}}}}}\dfrac{{\mu {D_{\text{k}}}}}{p}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}}} \right) $ [56] Low permeability reservoir Power function fitting nonlinear segment
(Piecewise function)$\left\{ \begin{gathered} v = \dfrac{k}{\mu }\nabla p{\text{ }}|\nabla p| \leqslant b \hfill \\ v = \dfrac{k}{\mu }\nabla p\left( {1 - \dfrac{\lambda }{{|\nabla p|}}} \right){ ^n} a < |\nabla p| < b \hfill \\ v = 0 |\nabla p| \leqslant a \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.$ [57] Piecewise function $ \left\{\begin{array}{l}\text{Ultra-low speed zone}:\dfrac{\Delta p}{L}=0\\ \text{Low speed transition zone}:v=c{\left(\dfrac{\Delta p}{L}\right)}^{\frac{1}{2-n}}\\ \text{Darcy flow zone}:v=-\dfrac{k}{\mu }\Delta p\end{array} \right.$ [58] Two-parameter model
(Continuous model)$ v = \dfrac{k}{\mu }\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{a + b|\nabla p|}}} \right)\nabla p $ [59] Three-parameter model
(Continuous model)$ v\left( {{a_{\text{1}}} + \dfrac{{{a_{\text{2}}}}}{{1 + bv}}} \right) = - \nabla p $ [60] Three-parameter model
(Continuous model)$ v = {\left( {\dfrac{k}{\mu }} \right)_{\text{o}}}\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{{{\lambda _{\text{c}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{\text{d}}p}}{{{\text{d}}x}} + {\lambda _{\text{c}}} - \lambda }}} \right) $ [61] Medium permeability reservoir Darcy’s Law $ v = - \dfrac{k}{\mu }\Delta p $ [25] Macro-Scale
(l>1 mm)High permeability reservoir Darcy’s Law $v = - \dfrac{k}{\mu }\Delta p$ [25] Fractured reservoir Darcy’s Law $v = - \dfrac{k}{\mu }\Delta p$ [25] Note: v—fluid velocity, m·s?1; k—permeability, 10?3 μm; ko—oil permeability, 10?3 μm; μ—formation crude oil viscosity, mPa·s; p—formation pressure, MPa; λ—starting pressure gradient, MPa·m?1; λc—proposed start pressure gradient, MPa·m?1; a, b, c—constant coefficient, dimensionless; m=0.0186; r=?0.579; Dk—diffusion coefficient, cm2·s?1; a1, a2, n—constant coefficient, dimensionless; L—model length, cm. www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Tao R, Quan X B, Xu J Z. Several questions in research of micro scale flow. J Eng Thermophys, 2001, 22(5): 575 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2001.05.015陶然, 權曉波, 徐建中. 微尺度流動研究中的幾個問題. 工程熱物理學報, 2001, 22(5):575 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2001.05.015 [2] Chen Y L, Ma Y, Pan F, et al. Research progress in multi-scale mechanics of composite materials. Chin J Solid Mech, 2018, 39(1): 1陳玉麗, 馬勇, 潘飛, 等. 多尺度復合材料力學研究進展. 固體力學學報, 2018, 39(1):1 [3] Zhu W Y, Ma Q P, Song Z Y, et al. The effect of injection pressure on the microscopic migration characteristics by CO2 flooding in heavy oil reservoirs. Energy Sources Part A, 2019: 1 [4] Zhu W Y, Huang Y Z. The effect of porous media on gas-liquid phase behavior. Pet Explor Dev, 1988, 15(1): 51朱維耀, 黃延章. 多孔介質對氣-液相變過程的影響. 石油勘探與開發, 1988, 15(1):51 [5] Ju Y, Gong W B, Chang W, et al. Effects of pore characteristics on water-oil two-phase displacement in non-homogeneous pore structures: A pore-scale lattice Boltzmann model considering various fluid density ratios. Int J Eng Sci, 2020, 154: 103343 doi: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2020.103343 [6] Allen M B III, Behie G A, Trangenstein J A. Multiphase Flow in Porous Media. New York: Springer US, 1988 [7] Wang Q, Chen X, Jha A N, et al. Natural gas from shale formation?The evolution, evidences and challenges of shale gas revolution in United States. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev, 2014, 30: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.065 [8] Zhu W Y, Yue M, Liu Y F, et al. Research progress on tight oil exploration in China. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(9): 1103朱維耀, 岳明, 劉昀楓, 等. 中國致密油藏開發理論研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(9):1103 [9] Wang X F, Zhu W Y, Deng Q J, et al. Dynamic network model considering solid-liquid molecule interaction in porous media. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2014, 36(2): 145王小鋒, 朱維耀, 鄧慶軍, 等. 考慮固液分子作用的多孔介質動態網絡模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2014, 36(2):145 [10] Zhu W Y, Tian Y A, Yu M X, et al. Mechanism of microscopic fluid flow in microtubes. Sci Technol Rev, 2014, 32(27): 23 doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.27.003朱維耀, 田英愛, 于明旭, 等. 微圓管中流體的微觀流動機制. 科技導報, 2014, 32(27):23 doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.27.003 [11] Li Z H, Cui H H. Characteristics of micro scale flow. J Mech Strength, 2001, 23(4): 476 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2001.04.017李戰華, 崔海航. 微尺度流動特性. 機械強度, 2001, 23(4):476 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2001.04.017 [12] Qian X R, Shen H J. Developments on hydrokinetic of microfluidic flow. Aviat Precis Manuf Technol, 2005, 41(6): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2005.06.004錢曉蓉, 沈宏繼. 微流體動力學研究發展與現狀. 航空精密制造技術, 2005, 41(6):11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2005.06.004 [13] Wu P Y, Little W A. Measurement of friction factors for the flow of gases in very fine channels used for microminiature Joule-Thomson refrigerators. Cryogenics, 1983, 23(5): 273 doi: 10.1016/0011-2275(83)90150-9 [14] Terry S C. A Gas Chromatography System Fabricated on a Silicon Wafer Using Integrated Circuit Technology [Dissertation]. Palo Alto: Stanford University, 1975 [15] Harley J C, Huang Y F, Bau H H, et al. Gas flow in micro-channels. J Fluid Mech, 1995, 284: 257 doi: 10.1017/S0022112095000358 [16] Ho C M, Tai Y C. Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 1998, 30(1): 579 doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.579 [17] Barajas A M, Panton R L. The effects of contact angle on two-phase flow in capillary tubes. Int J Multiph Flow, 1993, 19(2): 337 doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(93)90007-H [18] Triplett K A, Ghiaasiaan S M, Abdel-Khalik S I, et al. Gas-liquid two-phase flow in microchannels Part I: Two-phase flow patterns. Int J Multiph Flow, 1999, 25(3): 377 doi: 10.1016/S0301-9322(98)00054-8 [19] Deng Q J, Zhu W Y, Wang X F, et al. Seepage model considering micro forces in porous media. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2014, 36(4): 415鄧慶軍, 朱維耀, 王小鋒, 等. 多孔介質中微觀力的作用及滲流模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2014, 36(4):415 [20] Koplik J, Banavar J R, Willemsen J F. Molecular dynamics of fluid flow at solid surfaces. Phys Fluids A, 1989, 1(5): 781 [21] Zhu W Y, Li B B, Liu Y J, et al. Solid-liquid interfacial effects on residual oil distribution utilizing three-dimensional micro network models. Energies, 2017, 10(12): 2059 doi: 10.3390/en10122059 [22] Cai Q, Buts A, Seaton N A, et al. A pore network model for diffusion in nanoporous carbons: Validation by molecular dynamics simulation. Chem Eng Sci, 2008, 63(13): 3319 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2008.03.032 [23] Wang S, Feng Q, Javadpour F, et al. Multiscale modeling of shale apparent permeability: an integrated study of molecular dynamics and pore network model // SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. San Antonio, 2017: SPE-187286-MS [24] Li Y F. Study on Boundary Slip at the Solid-Liquid Interface of the Rough Surfaces Immersed in Liquids with Low Surface Tension [Dissertation]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018李軼凡. 低表面張力液體下的粗糙表面固液界面邊界滑移的研究[學位論文]. 哈爾濱: 哈爾濱工業大學, 2018 [25] Hubbert M K. Darcy’s law and the field equations of the flow of underground fluids. Int Assoc Sci Hydrol Bull, 1957, 2(1): 222 [26] Allen M B. Basic Mechanics of Oil Reservoir Flows. New York: Springer Press, 1988 [27] Hu G Q, Li D Q. Multiscale phenomena in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Chem Eng Sci, 2007, 62(13): 3443 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2006.11.058 [28] Civan F. A triple-mechanism fractal model with hydraulic dispersion for gas permeation in tight reservoirs // SPE International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition in Mexico. Villahermosa, 2002: SPE-74368-MS [29] Roy S, Raju R, Chuang H F, et al. Modeling gas flow through microchannels and nanopores. J Appl Phys, 2003, 93(8): 4870 doi: 10.1063/1.1559936 [30] Li Z H, Zheng X. The problems and progress in the experimental study of micro/nano-scale flow. J Exp Fluid Mech, 2014, 28(3): 1 doi: 10.11729/syltlx20140018李戰華, 鄭旭. 微納米尺度流動實驗研究的問題與進展. 實驗流體力學, 2014, 28(3):1 doi: 10.11729/syltlx20140018 [31] Wang J L, Song H Q, Zhu W Y, et al. Flow characteristics and a permeability model in nanoporous media with solid-liquid interfacial effects. Interpretation, 2017, 5(1): SB1 doi: 10.1190/INT-2016-0009.1 [32] Keenan J H, Neumann E P. Measurements of friction in a pipe for subsonic and supersonic flow of air. J Appl Mech, 1946, 13(2): A91 doi: 10.1115/1.4009532 [33] Pfitzner J. Poiseuille and his law. Anaesthesia, 1976, 31(2): 273 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1976.tb11804.x [34] Zhang X L, Zhu W Y, Cai Q, et al. Analysis of weakly compressible fluid flow in nano /micro-size circular tubes considering solid wall force. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2014, 36(5): 569張雪齡, 朱維耀, 蔡強, 等. 考慮固壁作用力的微可壓縮流體納微米圓管流動分析. 北京科技大學學報, 2014, 36(5):569 [35] Bonaccurso E, Butt H J, Craig V S. Surface roughness and hydrodynamic boundary slip of a Newtonian fluid in a completely wetting system. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90(14): 144501 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.144501 [36] Shen W J, Song F Q, Hu X, et al. Experimental study on flow characteristics of gas transport in micro- and nanoscale pores. Sci Rep, 2019, 9: 10196 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46430-2 [37] Ou J, Rothstein J P. Direct velocity measurements of the flow past drag-reducing ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Phys Fluids, 2005, 17(10): 103606 doi: 10.1063/1.2109867 [38] Pak T, Butler I B, Geiger S, et al. Droplet fragmentation: 3D imaging of a previously unidentified pore-scale process during multiphase flow in porous media. PNAS, 2015, 112(7): 1947 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420202112 [39] Wang Y M, Pang Y M, Yang S F, et al. Study on classification of low-permealility sandstone reservoirs based on the starting pressure gradient. Geol J China Univ, 2005, 11(4): 617 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.019王渝明, 龐顏民, 楊樹鋒, 等. 基于啟動壓力梯度的低滲透砂巖儲層分類研究. 高校地質學報, 2005, 11(4):617 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.019 [40] Jerauld G R, Salter S J. The effect of pore-structure on hysteresis in relative permeability and capillary pressure: Pore-level modeling. Transp Porous Media, 1990, 5(2): 103 doi: 10.1007/BF00144600 [41] McDougall S R, Sorbie K S. The impact of wettability on waterflooding: Pore-scale simulation. SPE Reserv Eng, 1995, 10(3): 208 doi: 10.2118/25271-PA [42] Wang C, Nguyen N T, Wong T N, et al. Investigation of active interface control of pressure driven two-fluid flow in microchannels. Sens Actuators A, 2007, 133(2): 323 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2006.06.034 [43] Datta S S, Ramakrishnan T S, Weitz D A. Mobilization of a trapped non-wetting fluid from a three-dimensional porous medium. Phys Fluids, 2014, 26(2): 022002 doi: 10.1063/1.4866641 [44] Arif M, Mahmoud M, Zhang Y H, et al. X-ray tomography imaging of shale microstructures: A review in the context of multiscale correlative imaging. Int J Coal Geol, 2021, 233: 103641 doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2020.103641 [45] Deng Q J. Microscale Occurence and Recovery Mechanism of Remaining Oil in Sazhong Area at Extra-High Water Cut Stage of Daqing Field [Dissertation]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2015鄧慶軍. 大慶油田薩中開發區特高含水期微觀剩余油成因及動用機制研究[學位論文]. 大慶: 東北石油大學, 2015 [46] Xiong Q R, Baychev T G, Jivkov A P. Review of pore network modelling of porous media: Experimental characterisations, network constructions and applications to reactive transport. J Contam Hydrol, 2016, 192: 101 doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2016.07.002 [47] Fatt I. The network model of porous media. Trans AIME, 1956, 207(1): 144 doi: 10.2118/574-G [48] Dullien F A L, Lai F S Y, MacDonald I F. Hydraulic continuity of residual wetting phase in porous media. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1986, 109(1): 201 doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(86)90295-X [49] Zhang X L, Shi Y T, Kuang S Y, et al. Microscale effects of Bingham-plastic liquid behavior considering electroviscous effects in nano- or microsized circular tubes. Phys Fluids, 2019, 31(2): 022001 doi: 10.1063/1.5068774 [50] Zhang X L, Kuang S Y, Shi Y T, et al. Research progress on the nonlinear seepage characteristics of tight oil in nano-micron porous media. China Offshore Oil Gas, 2019, 31(4): 102張雪齡, 鄺頌雅, 師渝滔, 等. 致密油納微米孔隙介質非線性滲流特性研究進展. 中國海上油氣, 2019, 31(4):102 [51] Xie C Y, Xu K, Mohanty K, et al. Nonwetting droplet oscillation and displacement by viscoelastic fluids. Phys Rev Fluids, 2020, 5(6): 063301 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.063301 [52] Wang J X, Wu X D, Yang P H, et al. Calculating the imbibition relative permeability of a gas-liquid system by pore scale network model. Nat Gas Ind, 2003, 23(3): 8 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.03.003王金勛, 吳曉東, 楊普華, 等. 孔隙網絡模型法計算氣液體系吸吮過程相對滲透率. 天然氣工業, 2003, 23(3):8 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.03.003 [53] Han Q, Qu Z, Ye Z Y. Research status of shale multi-scale mechanical properties. Chin J Appl Mech, 2018, 35(3): 564韓強, 屈展, 葉正寅. 頁巖多尺度力學特性研究現狀. 應用力學學報, 2018, 35(3):564 [54] Ma Y J, Wang R F. Non-linear seepage models for sandstone reservoirs of ultra-low permeability and shallow layers. Gas Field, 2017, 24(4): 514馬勇軍, 王瑞飛. 超低滲淺層砂巖油藏儲層非線性滲流模型. 斷塊油氣田, 2017, 24(4):514 [55] Ma Q Z, Yang S L, Wang J R, et al. Non-linear seepage model of tight reservoir based on threshold pressure gradient. J Petrochem Univ, 2020, 33(1): 36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2020.01.007馬銓崢, 楊勝來, 王君如, 等. 基于啟動壓力梯度的致密油藏非線性滲流模型. 石油化工高等學校學報, 2020, 33(1):36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2020.01.007 [56] Deng J. Nonlinear Seepage Theory of Multistage Fractured Horizontal Wells for Shale Gas Reservoirs [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015鄧佳. 頁巖氣儲層多級壓裂水平井非線性滲流理論研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2015 [57] Huang Y Z. Nonlinear percolation feature in low permeability reservoir. Gas Reservoirs, 1997, 4(1): 9黃延章. 低滲透油層非線性滲流特征. 特種油氣藏, 1997, 4(1):9 [58] Yao Y D, Ge J L. Study on non-darcy flow pattern in low permeability oil reservoir. Xinjiang Pet Geol, 2000, 21(3): 213 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2000.03.010姚約東, 葛家理. 低滲透油層非達西滲流規律的研究. 新疆石油地質, 2000, 21(3):213 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2000.03.010 [59] Yang Q L, Yang Z M, Wang Y F, et al. Study on flow theory in ultra-low permeability oil reservoir. Drill Prod Technol, 2007, 30(6): 52 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2007.06.019楊清立, 楊正明, 王一飛, 等. 特低滲透油藏滲流理論研究. 鉆采工藝, 2007, 30(6):52 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2007.06.019 [60] Deng Y E, Liu C Q. Mathematical model of nonlinear flow law in low permeability porous media and its application. Acta Petrolei Sin, 2001, 22(4): 72 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2001.04.014鄧英爾, 劉慈群. 低滲油藏非線性滲流規律數學模型及其應用. 石油學報, 2001, 22(4):72 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2001.04.014 [61] Huang Y Z, Yang Z M, He Y, et al. Nonlinear porous flow in low permeability porous media. Mech Eng, 2013, 35(5): 1 doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-13-165黃延章, 楊正明, 何英, 等. 低滲透多孔介質中的非線性滲流理論. 力學與實踐, 2013, 35(5):1 doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-13-165 [62] Vinay G, Wachs A, Agassant J F. Numerical simulation of weakly compressible Bingham flows: The restart of pipeline flows of waxy crude oils. J Non Newton Fluid Mech, 2006, 136(2-3): 93 doi: 10.1016/j.jnnfm.2006.03.003 [63] Xiang D P, Deng X G, Mao M L. Study on a novel method for low Mach number flows computation. Acta Aerodyn Sin, 2002, 20(4): 373 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2002.04.001向大平, 鄧小剛, 毛枚良. 低馬赫數流動數值模擬方法的研究. 空氣動力學學報, 2002, 20(4):373 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2002.04.001 [64] Xiang D P, Deng X G, Mao M L. Study of slightly compressible model (SCM) and compressible N-S equations on low Mach number flow computation. Acta Aerodyn Sin, 2005, 23(2): 195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2005.02.012向大平, 鄧小剛, 毛枚良. 微可壓縮模型(SCM)與可壓縮NS方程數值計算對比研究. 空氣動力學學報, 2005, 23(2):195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2005.02.012 [65] Liu C Q. Generalized Maxwell Model of Non-Newtonian Fluid and Its Solution. Mech Pract, 1995, 17(2): 21劉慈群. 非牛頓流體的廣義Maxwell模型及其解. 力學與實踐, 1995, 17(2):21 [66] Huang Y Y, Shen Z Z, Wu Z R. Generalized kelvin model under different stress state. Chin J Appl Mech, 2007, 24(4): 588 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4939.2007.04.019黃耀英, 沈振中, 吳中如. 不同應力分量下廣義開爾文模型粘性系數探討. 應用力學學報, 2007, 24(4):588 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4939.2007.04.019 [67] Li X J, Ouyang J, Jiang T, et al. A WCCBSSU method for solving weakly compressible visco-elastic flow problems. Chin J Comput Mech, 2011, 28(4): 590 doi: 10.7511/jslx201104017栗雪娟, 歐陽潔, 蔣濤, 等. 模擬微可壓粘彈性流體的WCCBSSU方法. 計算力學學報, 2011, 28(4):590 doi: 10.7511/jslx201104017 [68] Venerus D C. Laminar capillary flow of compressible viscous fluids. J Fluid Mech, 2006, 555: 59 doi: 10.1017/S0022112006008755 [69] Liu X L, Peng X L, Du Z M, et al. Oil water two phases flow darcy-strokes mode. J Southwest Pet Univ, 2007, 29(6): 89劉學利, 彭小龍, 杜志敏, 等. 油水兩相流Darcy-Stokes模型. 西南石油大學學報, 2007, 29(6):89 [70] Wan Z. Preconditioning Technique in Slighly Compressible Model [Dissertation]. Mianyang: China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center, 2010萬釗. 微可壓縮模型預處理求解方法研究[學位論文]. 綿陽: 中國空氣動力研究與發展中心, 2010 [71] Zhang X L. Percolation Theory Research of Weakly Compressible Fluid Flow Considering Wall-Liquid Interaction [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015張雪齡. 考慮液—固界面作用的微可壓縮流體的滲流理論研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2015 [72] Liu C, Li Z G. Flow regimes and parameter dependence in nanochannel flows. Phys Rev E, 2009, 80(3): 036302 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.036302 [73] Yang C, Li D Q. Electrokinetic effects on pressure-driven liquid flows in rectangular microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1997, 194(1): 95 doi: 10.1006/jcis.1997.5091 [74] Zhu W Y, Wang Y Z, Yue M, et al. Micro circular pipe flow in micron-sized soft particle solution considering the effect of spatial configuration force. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(10): 1266朱維耀, 王亞震, 岳明, 等. 考慮空間位形力作用的微米軟顆粒溶液微圓管流動規律. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(10):1266 [75] Long Y Q, Zhu W Y, Liu Q P, et al. Flow characteristics of nano/micron-sized polymer particles aqueous solution through microporous membrane. J Southwest Pet Univ Sci Technol, 2015, 37(6): 144龍運前, 朱維耀, 劉啟鵬, 等. 納微米聚合物顆粒分散體系微孔濾膜流動特征. 西南石油大學學報(自然科學版), 2015, 37(6):144 [76] Zhu W Y, Ma Q, Deng J, et al. Mathematical model and application of gas flow in nano-micron pores. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2014, 36(6): 709朱維耀, 馬千, 鄧佳, 等. 納微米級孔隙氣體流動數學模型及應用. 北京科技大學學報, 2014, 36(6):709 [77] Hazlett R D. Simulation of capillary-dominated displacements in microtomographic images of reservoir rocks. Transp Porous Media, 1995, 20(1-2): 21 doi: 10.1007/BF00616924 [78] Coles M E, Hazlett R D, Spanne P, et al. Pore level imaging of fluid transport using synchrotron X-ray microtomography. J Petroleum Sci Eng, 1998, 19(1-2): 55 doi: 10.1016/S0920-4105(97)00035-1 [79] Joshi M Y. A Class of Stochastic Models for Porous Media[Dissertation]. Lawrence: University of Kansas, 1974. [80] Quiblier J A. A new three-dimensional modeling technique for studying porous media. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1984, 98(1): 84 doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(84)90481-8 [81] Xu M. Method of Digital Core Construction and Pore Network Extraction[Dissertation]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2017徐模. 數字巖心及孔隙網絡模型的構建方法研究[學位論文]. 成都: 西南石油大學, 2017 [82] Hazlett R D. Statistical characterization and stochastic modeling of pore networks in relation to fluid flow. Math Geol, 1997, 29(6): 801 doi: 10.1007/BF02768903 [83] Zhao X C, Yao J, Tao J, et al. A method of constructing digital core by simulated annealing algorithm. Appl Math A J Chin Univ (Sera) , 2007, 22(2): 127 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4424.2007.02.001趙秀才, 姚軍, 陶軍, 等. 基于模擬退火算法的數字巖心建模方法. 高校應用數學學報A輯, 2007, 22(2):127 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4424.2007.02.001 [84] Hidajat I, Rastogi A, Singh M, et al. Transport properties of porous media reconstructed from thin-sections. SPE J, 2002, 7(1): 40 doi: 10.2118/77270-PA [85] Wu K J, Dijke M I J, Couples G D, et al. 3D stochastic modelling of heterogeneous porous media-applications to reservoir rocks. Transp Porous Media, 2006, 65(3): 443 doi: 10.1007/s11242-006-0006-z [86] Hu X T, Li Y. Study of microcosmic distribution of residual oil with stochastic simulation in networks. Acta Petrolei Sin, 2000, 21(4): 46 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.04.009胡雪濤, 李允. 隨機網絡模擬研究微觀剩余油分布. 石油學報, 2000, 21(4):46 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.04.009 [87] Blunt M J, Jackson M D, Piri M, et al. Detailed physics, predictive capabilities and macroscopic consequences for pore-network models of multiphase flow. Adv Water Resour, 2002, 25(8-12): 1069 doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00049-0 [88] Xu S Y, Li H N. Evolvement of reservoir pore-throat-net and remaining oil distribution. Acta Petrolei Sin, 2003, 24(4): 48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2003.04.011徐守余, 李紅南. 儲集層孔喉網絡場演化規律和剩余油分布. 石油學報, 2003, 24(4):48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2003.04.011 [89] Wang K W, Sun J M, Guan J T, et al. Network model modeling of microcosmic remaining oil distribution after polymer flooding. J China Univ Pet Ed Nat Sci, 2006, 30(1): 72王克文, 孫建孟, 關繼騰, 等. 聚合物驅后微觀剩余油分布的網絡模型模擬. 中國石油大學學報(自然科學版), 2006, 30(1):72 [90] Yao J, Tao J, Li A F. Research on oil-water two-phase flow using 3D random network model. Acta Petrolei Sin, 2007, 28(2): 94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.02.018姚軍, 陶軍, 李愛芬. 利用三維隨機網絡模型研究油水兩相流動. 石油學報, 2007, 28(2):94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.02.018 [91] Zhang P W, Hu L M, Meegoda J, et al. Two-phase flow model based on 3D pore structure of geomaterials. Chin J Geotech Eng, 2020, 42(1): 37張鵬偉, 胡黎明, Jay N Meegoda, 等. 基于巖土介質三維孔隙結構的兩相流模型. 巖土工程學報, 2020, 42(1):37 [92] Yan W C, Sun J M. Analysis of research present situation of microscopic remaining oil. Prog Geophys, 2016, 31(5): 2198 doi: 10.6038/pg20160544閆偉超, 孫建孟. 微觀剩余油研究現狀分析. 地球物理學進展, 2016, 31(5):2198 doi: 10.6038/pg20160544 [93] Wang F F, Hu H G, He Z X. Remaining oil forming mechanism of occurrence research. Guangdong Chem Ind, 2013, 40(3): 66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.03.033王芳芳, 胡海光, 何志雄. 剩余油形成機理與賦存狀態研究綜述. 廣東化工, 2013, 40(3):66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2013.03.033 [94] Li T X, Song H Q, Wang J L, et al. An analytical method for modeling and analysis gas-water relative permeability in nanoscale pores with interfacial effects. Int J Coal Geol, 2016, 159: 71 doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.03.018 [95] Chatenever A, Calhoun J C Jr. Visual examinations of fluid behavior in porous media?part I. J Pet Technol, 1952, 4(6): 149 doi: 10.2118/135-G [96] Templeton C C. A study of displacements in microscopic capillaries. J Pet Technol, 1954, 6(7): 37 doi: 10.2118/307-G [97] Huang Y Z. Experimental Mechanics of Microscopic Seepage and its Application. Beijing: Petroleum industry press, 2001黃延章. 微觀滲流實驗力學及其應用. 北京: 石油工業出版社, 2001 [98] Zhang X L, Zhu W Y, Cai Q, et al. Compressible liquid flow in nano- or micro-sized circular tubes considering wall–liquid Lifshitz–van der Waals interaction. Phys Fluids, 2018, 30(6): 062002 doi: 10.1063/1.5023291 -




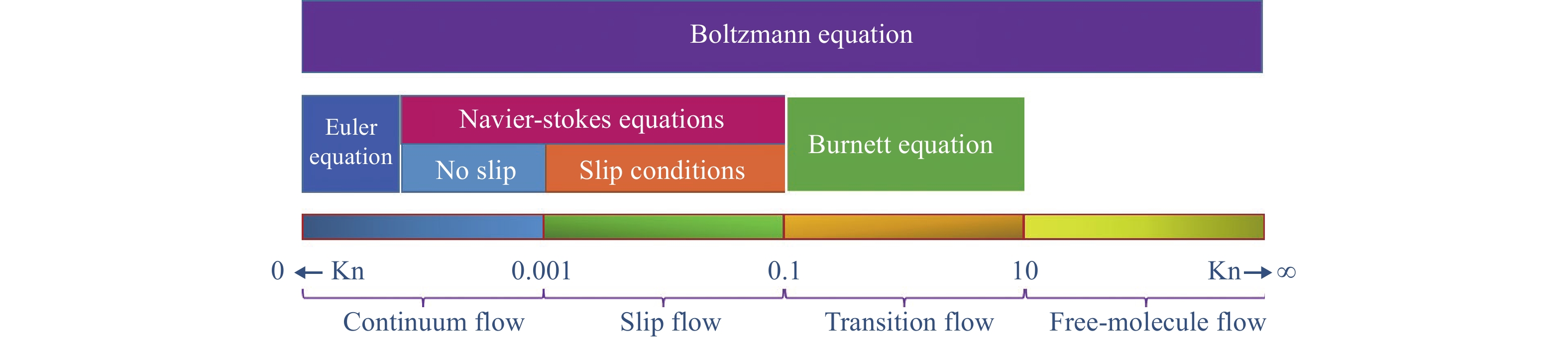
 下載:
下載: