Survey of simultaneous localization and mapping based on environmental semantic information
-
摘要: 同步定位與地圖構建技術(SLAM)是當前機器人領域的重要研究熱點,傳統的SLAM技術雖然在實時性方面已經達到較高的水平,但在定位精度和魯棒性等方面還存在較大缺陷,所構建的環境地圖雖然一定程度上滿足了機器人的定位需要,但不足以支撐機器人自主完成導航、避障等任務,交互性能不足。隨著深度學習技術的發展,利用深度學習方法提取環境語義信息,并與SLAM技術結合,越來越受到學者的關注。本文綜述了環境語義信息應用到同步定位與地圖構建領域的最新研究進展,重點介紹和總結了語義信息與傳統視覺SLAM在系統定位和地圖構建方面結合的突出研究成果,并對傳統視覺SLAM算法與語義SLAM算法做了深入的對比研究。最后,展望了語義SLAM研究的發展方向。
-
關鍵詞:
- 視覺同步定位與地圖構建技術 /
- 深度學習 /
- 系統定位 /
- 地圖構建 /
- 語義同步定位與地圖構建技術
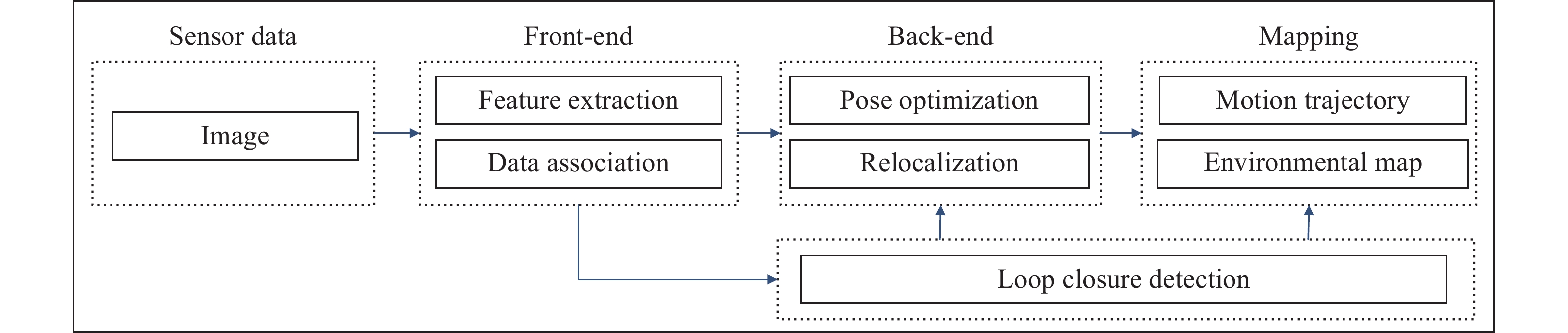
Abstract: The simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technique is an important research direction in robotics. Although the traditional SLAM has reached a high level of real-time performance, major shortcomings still remain in its positioning accuracy and robustness. Using traditional SLAM, a geometric environment map can be constructed that can satisfy the pose estimation of robots. However, the interactive performance of this map is insufficient to support a robot in completing self-navigation and obstacle avoidance. One popular practical application of SLAM is to add semantic information by combining deep learning methods with SLAM. Systems that introduce environmental semantic information belong to semantic SLAM systems. Introduction of semantic information is of great significance for improving the positioning performance of a robot, optimizing the robustness of the robot system, and improving the scene-understanding ability of the robot. Semantic information improves recognition accuracy in complex scenes, which brings more optimization conditions for an odometer, pose estimation, and loop detection, etc. Therefore, positioning accuracy and robustness is improved. Moreover, semantic information aids in the promotion of data association from the traditional pixel level to the object level so that the perceived geometric environmental information can be assigned with semantic tags to obtain a high-level semantic map. This then aids a robot in understanding an autonomous environment and human–computer interaction. This paper summarized the latest researches that apply semantic information to SLAM. The prominent achievements of semantics combined with the traditional visual SLAM of localization and mapping were also discussed. In addition, the semantic SLAM was compared with the traditional SLAM in detail. Finally, future research topics of advanced semantic SLAM were explored. This study aims to serve as a guide for future researchers in applying semantic information to tackle localization and mapping problems. -
表 1 面向場景的語義地圖與面向對象的語義地圖對比
Table 1. Comparison of scene-oriented semantic maps with object-oriented semantic maps
表 2 傳統SLAM算法與語義SLAM算法對比
Table 2. Comparison of traditional SLAM algorithm and semantic SLAM algorithm
Name Traditional SLAM Semantic SLAM Data scale Small Large Information utilization Low High Generalization Weak Strong Visualization Low High Latency Low High Robustness Weak Strong Path planning Weak intelligence Strong intelligence Application scene Static, strong texture, and unchanged lighting Static or dynamic, texture, and lighting unlimited www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Smith R C, Cheeseman P. On the representation and estimation of spatial uncertainty. Int J Rob Res, 1986, 5(4): 56 doi: 10.1177/027836498600500404 [2] Cadena C, Carlone L, Carrillo H, et al. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Trans Rob, 2016, 32(6): 1309 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2624754 [3] Davison A J, Reid I D, Molton N D, et al. MonoSLAM: real-time single camera SLAM. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2007, 29(6): 1052 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1049 [4] Liu Q, Duan F H, Sang Y, et al. A survey of loop-closure detection method of visual SLAM in complex environments. Robot, 2019, 41(1): 112劉強, 段富海, 桑勇, 等. 復雜環境下視覺SLAM閉環檢測方法綜述. 機器人, 2019, 41(1):112 [5] Hess W, Kohler D, Rapp H, et al. Real-time loop closure in 2D LIDAR SLAM // Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Stockholm, 2016: 1271 [6] Chen X, L?be T, Milioto A, et al. OverlapNet: Loop closing for LiDAR-based SLAM // Proceeding of Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS). Corvalis, 2020 [7] Liu H M, Zhang G F, Bao H J. A survey of monocular simultaneous localization and mapping. J Computer-Aided Des Comput Graph, 2016, 28(6): 855 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.06.001劉浩敏, 章國鋒, 鮑虎軍. 基于單目視覺的同時定位與地圖構建方法綜述. 計算機輔助設計與圖形學學報, 2016, 28(6):855 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.06.001 [8] Taketomi T, Uchiyama H, Ikeda S. Visual SLAM algorithms: a survey from 2010 to 2016. IPSJ Trans Comput Vision Appl, 2017, 9(1): 16 doi: 10.1186/s41074-017-0027-2 [9] Fuentes-Pacheco J, Ruiz-Ascencio J, Rendón-Mancha J M. Visual simultaneous localization and mapping: a survey. Artif Intell Rev, 2015, 43(1): 55 doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9365-8 [10] Zhao Y, Liu G L, Tian G H, et al. A survey of visual SLAM based on deep learning. Robot, 2017, 39(6): 889趙洋, 劉國良, 田國會, 等. 基于深度學習的視覺SLAM綜述. 機器人, 2017, 39(6):889 [11] Xia L L, Cui J S, Shen R, et al. A survey of image semantics-based visual simultaneous localization and mapping: application-oriented solutions to autonomous navigation of mobile robots. Int J Adv Rob Syst, 2020, 17(3): 4158 [12] Ding W D, Xu D, Liu X L, et al. Review on visual odometry for mobile robots. Acta Autom Sin, 2018, 44(3): 385丁文東, 徐德, 劉希龍, 等. 移動機器人視覺里程計綜述. 自動化學報, 2018, 44(3):385 [13] Wei H, Lü Q, Lin H C, et al. Survey on multi-robot SLAM back-end optimization algorithm. Syst Eng Electron, 2017, 39(11): 2553 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.11.24衛恒, 呂強, 林輝燦, 等. 多機器人SLAM后端優化算法綜述. 系統工程與電子技術, 2017, 39(11):2553 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.11.24 [14] Qin T, Li P L, Shen S J. Relocalization, global optimization and map merging for monocular visual-inertial SLAM // 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, 2018: 1197 [15] Shotton J, Glocker B, Zach C, et al. Scene coordinate regression forests for camera relocalization in RGB-D images // Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, 2013: 2930 [16] Strasdat H, Montiel J M M, Davison A J. Scale drift-aware large scale monocular SLAM // Robotics: science and Systems VI. Zaragoza, 2010: 7 [17] Frost D, Prisacariu V, Murray D. Recovering stable scale in monocular SLAM using object-supplemented bundle adjustment. IEEE Trans Rob, 2018, 34(3): 736 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2820722 [18] Felzenszwalb P F, Girshick R B, McAllester D, et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2010, 32(9): 1627 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 [19] Sucar E, Hayet J B. Bayesian scale estimation for monocular SLAM based on generic object detection for correcting scale drift // 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, 2018: 5152 [20] Bowman S L, Atanasov N, Daniilidis K, et al. Probabilistic data association for semantic SLAM // 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore, 2017: 1722 [21] Lianos K N, Schonberger J L, Pollefeys M, et al. VSO: Visual semantic odometry // Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, 2018: 234 [22] Mur-Artal R, Tardos J D. ORB-SLAM2: an open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Trans Rob, 2017, 33(5): 1255 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [23] Alismail H, Browning B, Lucey S. Photometric bundle adjustment for vision-based SLAM // Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Taipei, 2016: 324 [24] Bavle H, Manthe S, de la Puente P, et al. Stereo visual odometry and semantics based localization of aerial robots in indoor environments // 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, 2018: 1018 [25] Nicholson L, Milford M, Sünderhauf N. QuadricSLAM: dual quadrics from object detections as landmarks in object-oriented SLAM. IEEE Rob Autom Lett, 2019, 4(1): 1 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2866205 [26] Yang S C, Scherer S. CubeSLAM: monocular 3D object SLAM. IEEE Trans Rob, 2019, 35(4): 925 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2909168 [27] Yang S C, Scherer S. Monocular object and plane SLAM in structured environments. IEEE Rob Autom Lett, 2019, 4(4): 3145 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2924848 [28] Yang S C, Song Y, Kaess M, et al. Pop-up SLAM: semantic monocular plane SLAM for low-texture environments // 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Daejeon, 2016: 1222 [29] Lin D H, Fidler S, Urtasun R. Holistic scene understanding for 3D object detection with RGBD cameras // Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, 2013: 1417 [30] Gawel A, Don C D, Siegwart R, et al. X-View: graph-based semantic multi-view localization. IEEE Rob Autom Lett, 2018, 3(3): 1687 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2801879 [31] Tsintotas K A, Bampis L, Gasteratos A. Assigning visual words to places for loop closure detection // 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, 2018: 5979 [32] Zhang K J, Zhang Y Z, Lü G H, et al. Loop closure detection based on local semantic topology for visual SLAM system. Robot, 2019, 41(5): 649張括嘉, 張云洲, 呂光浩, 等. 基于局部語義拓撲圖的視覺SLAM閉環檢測. 機器人, 2019, 41(5):649 [33] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2018-04-08)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767. [34] Engel J, Sch?ps T, Cremers D. LSD-SLAM: large-scale direct monocular SLAM // European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, 2014: 834 [35] Ganti P, Waslander S L. Visual SLAM with network uncertainty informed feature selection [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2019-08-26)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.11946v1. [36] Xue L, Huang N T, Zhao S Y, et al. Low redundancy feature selection using conditional mutual information for short-term load forecasting. J Northeast Dianli Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2019, 39(2): 30薛琳, 黃南天, 趙樹野, 等. 基于條件互信息的低冗余短期負荷預測特征選擇. 東北電力大學學報, 2019, 39(2):30 [37] Qin T, Chen T Q, Chen Y L, et al. AVP-SLAM: semantic visual mapping and localization for autonomous vehicles in the parking lot [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2020-07-08)[ 2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.01813. [38] Stenborg E, Toft C, Hammarstrand L. Long-term visual localization using semantically segmented images // 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, 2018: 6484 [39] Sch?nberger J L, Pollefeys M, Geiger A, et al. Semantic visual localization // Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, 2018: 6896 [40] Naseer T, Oliveira G L, Brox T, et al. Semantics-aware visual localization under challenging perceptual conditions // 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore, 2017: 2614 [41] Liang H J, Sanket N J, Fermüller C, et al. SalientDSO: bringing attention to direct sparse odometry. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng, 2019, 16(4): 1619 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2019.2900980 [42] Engel J, Koltun V, Cremers D. Direct sparse odometry. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2018, 40(3): 611 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2658577 [43] Han S Q, Xi Z H. Dynamic scene semantics SLAM based on semantic segmentation. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 43563 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2977684 [44] Cui L Y, Ma C W. SDF-SLAM: semantic depth filter SLAM for dynamic environments. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 95301 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2994348 [45] Yu C, Liu Z X, Liu X J, et al. DS-SLAM: a semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments // 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, 2018: 1168 [46] Bescos B, Fácil J M, Civera J, et al. DynaSLAM: tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Rob Autom Lett, 2018, 3(4): 4076 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039 [47] Brasch N, Bozic A, Lallemand J, et al. Semantic monocular SLAM for highly dynamic environments // 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, 2018: 393 [48] Cui L Y, Ma C Q. SOF-SLAM: a semantic visual SLAM for dynamic environments. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 166528 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952161 [49] Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(12): 2481 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [50] Wang S, Clark R, Wen H K, et al. End-to-end, sequence-to-sequence probabilistic visual odometry through deep neural networks. Int J Rob Res, 2018, 37(4-5): 513 doi: 10.1177/0278364917734298 [51] Vasudevan S, G?chter S, Nguyen V, et al. Cognitive maps for mobile robots—an object based approach. Rob Autonom Syst, 2007, 55(5): 359 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2006.12.008 [52] Galindo C, Saffiotti A, Coradeschi S, et al. Multi-hierarchical semantic maps for mobile robotics // 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Edmonton, 2005: 2278 [53] Lai K, Bo L F, Fox D. Unsupervised feature learning for 3D scene labeling // 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Hong Kong, 2014: 3050 [54] Mozos O M, Triebel R, Jensfelt P, et al. Supervised semantic labeling of places using information extracted from sensor data. J Rob Autonom Syst, 2007, 55(5): 391 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2006.12.003 [55] Kundu A, Li Y, Dellaert F, et al. Joint semantic segmentation and 3D reconstruction from monocular video // European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, 2014: 703 [56] Hermans A, Floros G, Leibe B. Dense 3D semantic mapping of indoor scenes from RSB-D images // 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Hong Kong, 2014: 2631 [57] Civera J, Gálvez-López D, Riazuelo L, et al. Towards semantic SLAM using a monocular camera // 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Francisco, 2011: 1277 [58] Gálvez-López D, Salas M, Tardós J D, et al. Real-time monocular object SLAM. Rob Autonom Syst, 2016, 75: 435 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2015.08.009 [59] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2020-04-23)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [60] McCormac J, Handa A, Davison A, et al. SemanticFusion: dense 3D semantic mapping with convolutional neural networks // 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and automation (ICRA). Singapore, 2017: 4628 [61] Runz M, Buffier M, Agapito L. MaskFusion: real-time recognition, tracking and reconstruction of multiple moving objects // 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR). Munich, 2018: 10 [62] Ma L N, Stückler J, Kerl C, et al. Multi-view deep learning for consistent semantic mapping with RGB-D cameras // 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, 2017: 598 [63] Xiang Y, Fox D. DA-RNN: semantic mapping with data associated recurrent neural networks [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2017-05-30)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03098v2. [64] Izadi S, Kim D, Hilliges O, et al. KinectFusion: real-time 3D reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth camera // Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. Santa Barbara, 2011: 559 [65] Mao M Y, Zhang H W, Li S M, et al. SEMANTIC-RTAB-MAP (SRM): a semantic SLAM system with CNNs on depth images. Math Found Comput, 2019, 2(1): 29 doi: 10.3934/mfc.2019003 [66] Labbe M, Michaud F. Appearance-based loop closure detection for online large-scale and long-term operation. IEEE Trans Rob, 2013, 29(3): 734 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2013.2242375 [67] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger // Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, 2017: 6517 [68] Cui X, Lu C G, Wang J X. 3D semantic map construction using improved ORB-SLAM2 for mobile robot in edge computing environment. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 67179 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2983488 [69] Rosinol A, Abate M, Chang Y, et al. Kimera: an open-source library for real-time metric-semantic localization and mapping // 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, 2020: 1689 [70] Webb A M, Brown G, Luján M. ORB-SLAM-CNN: lessons in adding semantic map construction to feature-based SLAM // Annual Conference Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems. London, 2019: 221 [71] Ehlers S F G, Stuede M, Nuelle K, et al. Map management approach for SLAM in large-scale indoor and outdoor areas // 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, 2020: 9652 [72] Sunderhauf N, Pham T T, Latif Y, et al. Meaningful maps with object-oriented semantic mapping // 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, 2017: 5079 [73] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector // European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, 2016: 21 [74] McCormac J, Clark R, Bloesch M, et al. Fusion++: volumetric object-level SLAM // 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Verona, 2018: 32 [75] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. Mask R-CNN // Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, 2017: 2961 [76] Hoang D C, Stoyanov T, Lilienthal A J. Object-RPE: dense 3D reconstruction and pose estimation with convolutional neural networks for warehouse robots // 2019 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR). Prague, 2019: 1 [77] Whelan T, Leutenegger S, Salas-Moreno R, et al. ElasticFusion: dense SLAM without a pose graph // Robotics: Science and Systems, Rome, 2015 [78] Hoang D C, Lilienthal A J, Stoyanov T. Panoptic 3D mapping and object pose estimation using adaptively weighted semantic information. IEEE Rob Autom Lett, 2020, 5(2): 1962 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2970682 [79] Li W, Gu J H, Chen B W, et al. Incremental instance-oriented 3D semantic mapping via RGB-D cameras for unknown indoor scene. J Discrete Dyn Nat Soc, 2020, 2020: 2528954 [80] Hosseinzadeh M, Latif Y, Pham T, et al. Structure aware SLAM using quadrics and planes // Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Perth, 2018: 410 [81] Hosseinzadeh M, Li K J, Latif Y, et al. Real-time monocular object-model aware sparse SLAM // 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, 2019: 7123 [82] Rünz M, Agapito L. Co-fusion: real-time segmentation, tracking and fusion of multiple objects // 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore, 2017: 4471 [83] Keller M, Lefloch D, Lambers M, et al. Real-time 3D reconstruction in dynamic scenes using point-based fusion // 2013 International Conference on 3D Vision-3DV 2013. Seattle, 2013: 1 [84] Xu B B, Li W B, Tzoumanikas D, et al. MID-Fusion: octree-based object-level multi-instance dynamic SLAM // 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, 2019: 5231 [85] Oberlander J, Uhl K, Zollner J M, et al. A region-based SLAM algorithm capturing metric, topological, and semantic properties // 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Pasadena, 2008: 1886 [86] Kostavelis I, Gasteratos A. Semantic mapping for mobile robotics tasks: a survey. Rob Autonom Syst, 2015, 66: 86 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.12.006 [87] Luo R C, Chiou M. Hierarchical semantic mapping using convolutional neural networks for intelligent service robotics. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 61287 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2873597 [88] Xie L H, Markham A, Trigoni N. SnapNav: learning mapless visual navigation with sparse directional guidance and visual reference // 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, 2020: 1682 [89] Wang X, Huang Q Y, Celikyilmaz A, et al. Reinforced cross-modal matching and self-supervised imitation learning for vision-language navigation // Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 6622 [90] Chaplot D S, Gandhi D, Gupta S, et al. Learning to explore using active neural SLAM [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2020-04-10)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05155. [91] Chaplot D S, Salakhutdinov R, Gupta A, et al. Neural topological SLAM for visual navigation // Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, 2020: 12872 [92] Li B Y, Zou D P, Sartori D, et al. TextSLAM: visual SLAM with planar text features // 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, 2020: 2102 [93] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation // 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, 2014: 580 [94] Masci J, Meier U, Cire?an D, et al. Stacked convolutional auto-encoders for hierarchical feature extraction // International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Espoo, 2011: 52 [95] Handa A, Bloesch M, P?tr?ucean V, et al. gvnn: neural network library for geometric computer vision // European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, 2016: 67 [96] Wang K, Lin Y M, Wang L W, et al. A unified framework for mutual improvement of SLAM and semantic segmentation // 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, 2019: 5224 [97] Zhi S F, Bloesch M, Leutenegger S, et al. SceneCode: monocular dense semantic reconstruction using learned encoded scene representations // Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, 2019: 11768 [98] Yamauchi B. A frontier-based approach for autonomous exploration // Proceedings 1997 IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation CIRA'97. 'Towards New Computational Principles for Robotics and Automation'. Monterey, 1997: 146 [99] Dai A N, Papatheodorou S, Funk N, et al. Fast frontier-based information-driven autonomous exploration with an MAV [J/OL]. arXiv preprint (2020-02-13)[2020-11-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.04440. -




 下載:
下載:









