-
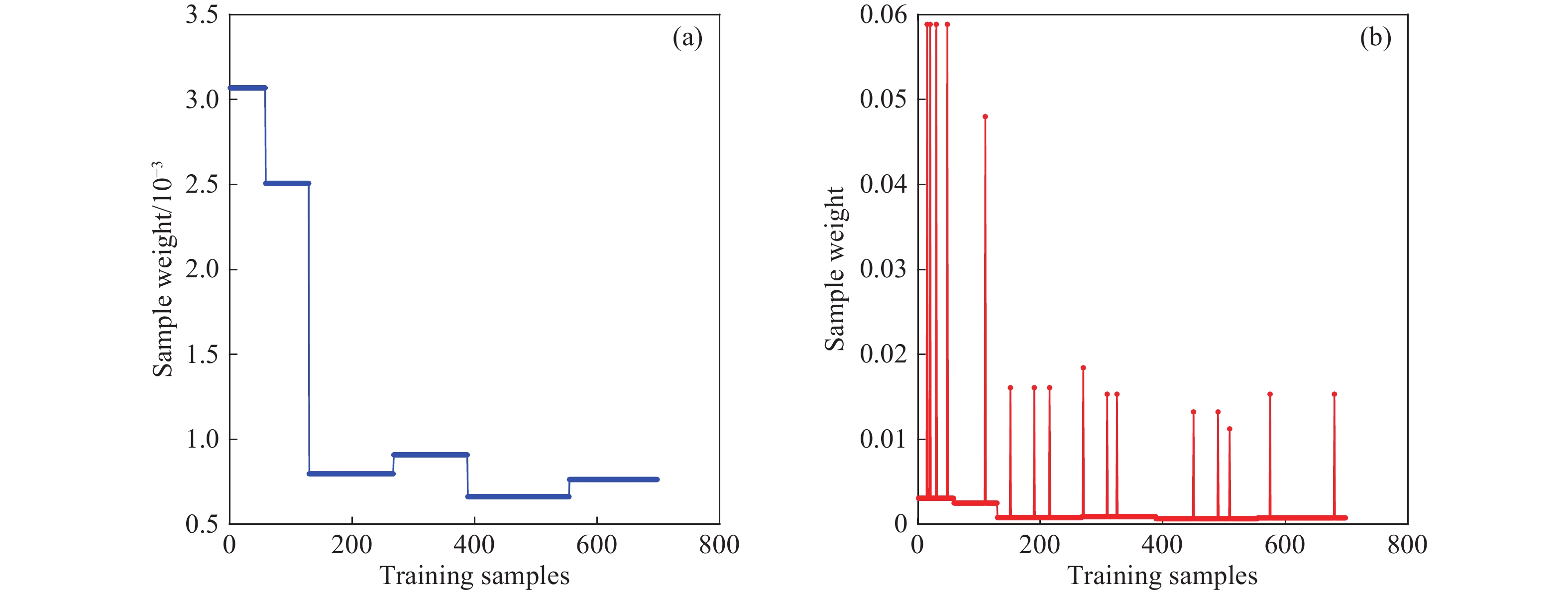
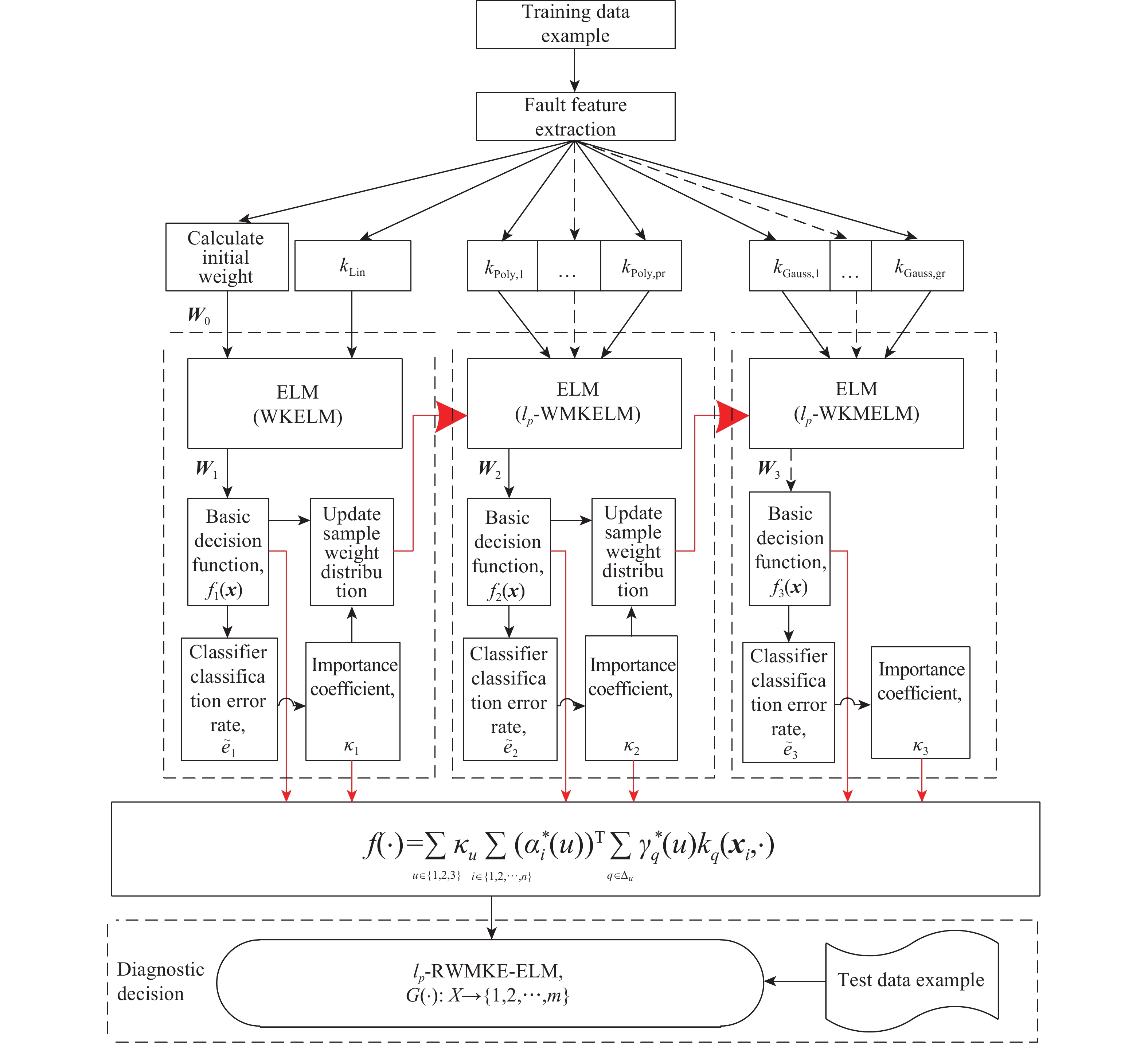
摘要: 針對裝備各類故障樣本分布不平衡、現有算法故障診斷精度較低的問題,通過引入p范數約束多核極限學習機和基于AdaBoost的集成學習策略,定義了一種p范數約束下正則化加權多核集成極限學習機的故障診斷模型。首先,在p范數約束下,基于各類故障樣本自身規模,分別進行了兩種自適應的樣本權重分配;其次,在每層分類器的優化中,將多核學習的多源數據融合能力和極限學習機運算高效的特點相結合,同時,將樣本的權重
$ {\boldsymbol{W}} $ 更新融入到多核極限學習機的優化進程;最后,通過Adaboost集成策略,自適應提升富含信息的樣本在模型中的權重,從而顯著提升故障診斷的精度。以6個UCI公共數據集以及1個實裝案例為例,進行了故障診斷實驗。結果表明,與核極限學習機、加權核極限學習機(使用$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\left( 1 \right)}} $ 和$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\left( 2 \right)}} $ 加權方式)以及多核極限學習機(在1范數和p范數約束下)相比,診斷精度有顯著提升;范數約束形式對模型的診斷性能影響有限。Abstract: As the service time of military equipment increases, equipment failure data is continuously accumulated during events such as routine maintenance, training, and combat readiness exercises, and the data presented is often imbalanced to varying degrees and consists of small samples. In addition, due to fault tolerances of various electrical component parameters in the equipment and widespread nonlinearity and feedback loops of the circuit, it is often difficult to accurately express the fault mechanism using mathematical models. This poses new challenges for the fault diagnosis of equipment. To address the aforementioned problems, machine learning methods are widely used for fault diagnosis. The essence of such methods is that they transform a fault diagnosis problem into a pattern recognition problem. By learning the characteristic data of normal modes and various failure modes, a diagnosis model is constructed and, ultimately, a diagnosis strategy is formed. Aiming at the problems of the unbalanced distribution of various fault samples from equipment and low fault diagnosis accuracy of existing algorithms, in this paper, we define a regularized weighted multiple kernel ensemble under a p-norm constraint by introducing a p-norm constraint weighted multicore extreme learning machine and an ensemble learning strategy based on the AdaBoost fault diagnosis model of extreme learning machine. Under the p-norm constraint, the model performed two types of adaptive sample weight distribution based on the size of various fault samples; simultaneously, the model combines the multisource data fusion and extreme learning abilities of the multiple kernel learning machine with high efficiency. The weight of a sample, W , is integrated into the optimization objective function of the multiple kernel extreme learning machine. Through the Adaboost integration strategy, the information-rich sample in the model is adaptively improved. Thus, the weight of a sample significantly improves the accuracy of fault diagnosis. Taking 6 UCI public data sets and 1 actual installation case as examples, a fault diagnosis experiment was conducted. The results of the experiment show that the model constructed in this study has significantly improved diagnostic accuracy compared with other models such as kernel extreme learning machine, weighted kernel extreme learning machine ($ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\left( 1 \right)}} $ and$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\left( 2 \right)}} $ weighting method), and weighted multiple kernel extreme learning machine under 1-norm constraint, and the model’s diagnostic performance impact is limited. -
表 1 混淆矩陣
Table 1. Confusion matrix
The true situation Classification result Positive Negative Positive TP (True positive) FN(False negative) Negative FP (False positive) TN(True false negative) Datasets Instances Number of classes Number of features Size of classes Diabetes 768 2 8 268, 500 Ionosphere 351 2 34 126, 225 Vowel 871 6 3 72, 89, 172, 151, 207, 180 Cancer 683 2 9 444, 239 Bupa 345 2 6 145, 200 Thyroid 215 3 5 150, 35, 30 表 3 各模型在各個UCI數據集上診斷性能比較
Table 3. Comparison of the diagnostic performance of various models on various UCI data sets
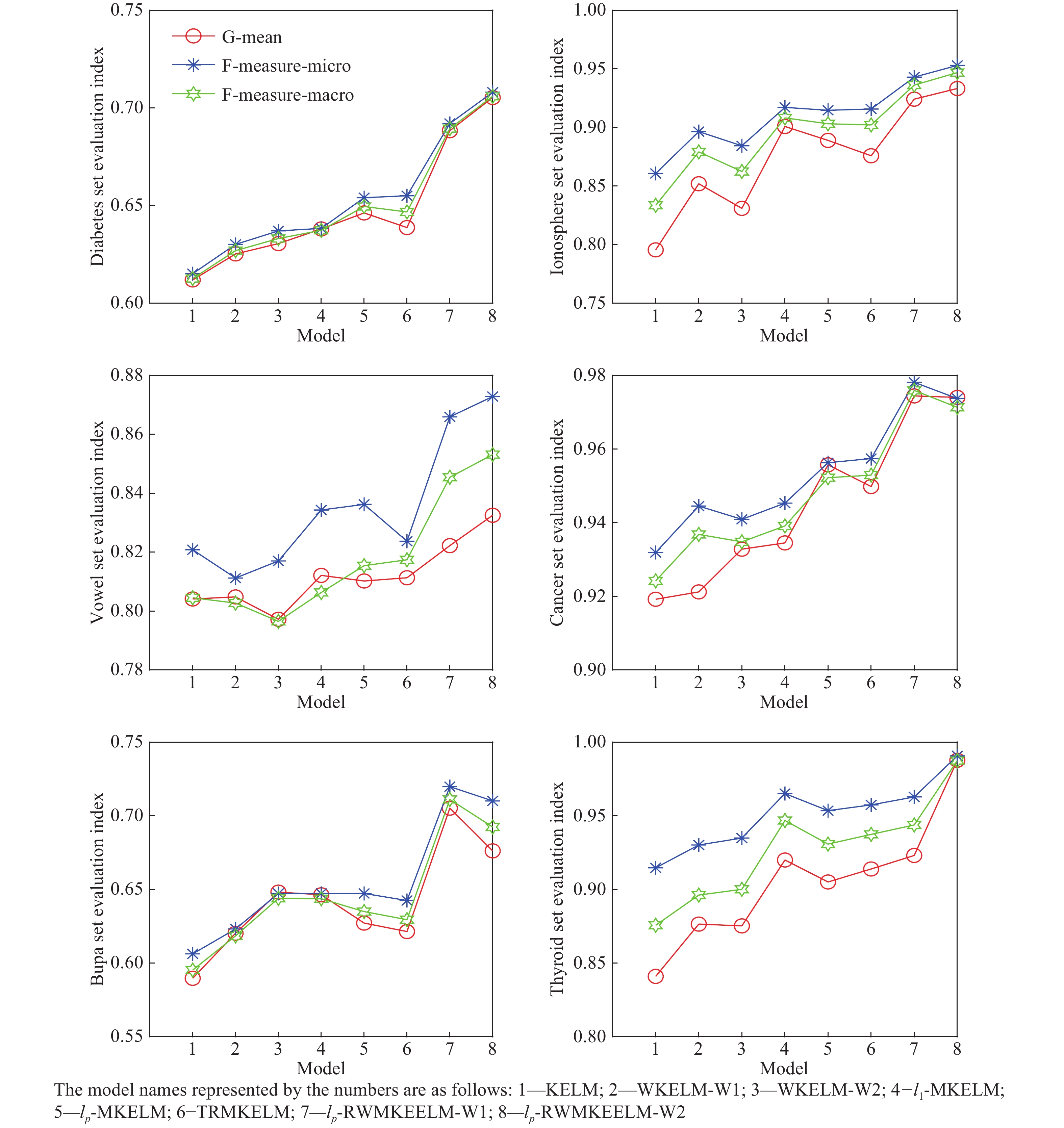
Datasets Model G-mean F-measure-micro F-measure-macro Parameter,C Diabetes KELM 0.6119±0.0418 0.615±0.0432 0.6126±0.0425 2(6) WKELM-W1 0.6252±0.0529 0.6301±0.0529 0.6269±0.053 2(8) WKELM-W2 0.6305±0.0431 0.6370±0.0432 0.6331±0.0429 2(9) l1-MKELM 0.638±0.0332 0.6383±0.0343 0.6373±0.0338 2(3) lp-MKELM 0.6462±0.0131 0.654±0.0152 0.6495±0.0135 2(10) ITDSMM-KELM 0.6387±0.0241 0.655±0.0243 0.6467±0.0238 2(13) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.6883±0.0612 0.6920±0.0581 0.6894±0.0596 2(3) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.7053±0.0588 0.7080±0.0567 0.7059±0.0575 2(3) Ionosphere KELM 0.7955±0.0552 0.8607±0.0353 0.8335±0.0452 2(5) WKELM-W1 0.8519±0.0555 0.8964±0.0356 0.8791±0.0447 2(9) WKELM-W2 0.8309±0.0706 0.8843±0.0362 0.8624±0.0512 2(8) l1-MKELM 0.9008±0.0315 0.9171±0.0221 0.9081±0.0259 2(3) lp-MKELM 0.8889±0.0265 0.9146±0.0169 0.9031±0.0201 2(9) ITDSMM-KELM 0.8758±0.0461 0.9157±0.0305 0.9021±0.0379 2(14) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.9241±0.0337 0.9429±0.0286 0.9361±0.0321 2(3) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.9332±0.0346 0.9529±0.0234 0.9468±0.0268 2(3) Vowel KELM 0.8041±0.0356 0.8208±0.0259 0.8045±0.0275 2(6) WKELM-W1 0.8048±0.0149 0.8112±0.0273 0.8027±0.0217 2(5) WKELM-W2 0.7972±0.0176 0.817±0.0273 0.7965±0.0225 2(10) l1-MKELM 0.8121±0.0318 0.8343±0.0273 0.8063±0.0329 2(2) lp-MKELM 0.8102±0.065 0.8362±0.0261 0.8154±0.0335 2(5) ITDSMM-KELM 0.8113±0.0358 0.8237±0.025 0.8174±0.0279 2(15) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.8222±0.0499 0.8659±0.0336 0.8454±0.0389 2(3) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.8325±0.0341 0.8728±0.0187 0.8531±0.0247 2(3) Cancer KELM 0.9192±0.0252 0.9319±0.0171 0.9242±0.0198 2(8) WKELM-W1 0.9212±0.0276 0.9445±0.0179 0.9368±0.0213 2(7) WKELM-W2 0.9328±0.0203 0.9409±0.0159 0.9348±0.0179 2(6) l1-MKELM 0.9345±0.0289 0.9453±0.021 0.9391±0.0241 2(5) lp-MKELM 0.9557±0.0161 0.9562±0.0137 0.9522±0.015 2(9) ITDSMM-KELM 0.9498±0.0614 0.9574±0.0142 0.9529±0.0158 2(11) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.9744±0.0198 0.9781±0.0052 0.9759±0.0056 2(4) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.974±0.0154 0.9737±0.0151 0.9713±0.0165 2(3) Bupa KELM 0.5897±0.0462 0.6063±0.0424 0.5953±0.0443 2(5) WKELM-W1 0.6203±0.0498 0.6232±0.0523 0.6185±0.05 2(9) WKELM-W2 0.6482±0.0404 0.6473±0.0418 0.644±0.0412 2(11) l1-MKELM 0.6464±0.0418 0.6473±0.0464 0.6437±0.0434 2(5) lp-MKELM 0.6272±0.049 0.6473±0.0586 0.635±0.0554 2(9) ITDSMM-KELM 0.6214±0.0614 0.6425±0.0731 0.6295±0.068 2(11) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.7052±0.0459 0.7198±0.0586 0.7111±0.0537 2(4) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.6762±0.0478 0.7101±0.0383 0.6924±0.0432 2(3) Thyroid KELM 0.841±0.0861 0.9147±0.0433 0.8757±0.066 2(7) WKELM-W1 0.8765±0.0759 0.9302±0.0347 0.8962±0.0524 2(6) WKELM-W2 0.8753±0.0662 0.9349±0.0264 0.9±0.0428 2(7) l1-MKELM 0.92±0.0712 0.9651±0.0353 0.9468±0.0507 2(3) lp-MKELM 0.9051±0.0877 0.9535±0.0329 0.9308±0.051 2(3) ITDSMM-KELM 0.9139±0.0796 0.9574±0.0373 0.9374±0.0559 2(6) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.9231±0.0471 0.9628±0.0127 0.9438±0.0221 2(2) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.9877±0.0217 0.9907±0.0127 0.9875±0.0171 2(4) 表 4 范數約束形式對模型診斷性能的影響
Table 4. Influence of norm-constrained forms on model diagnostic performance
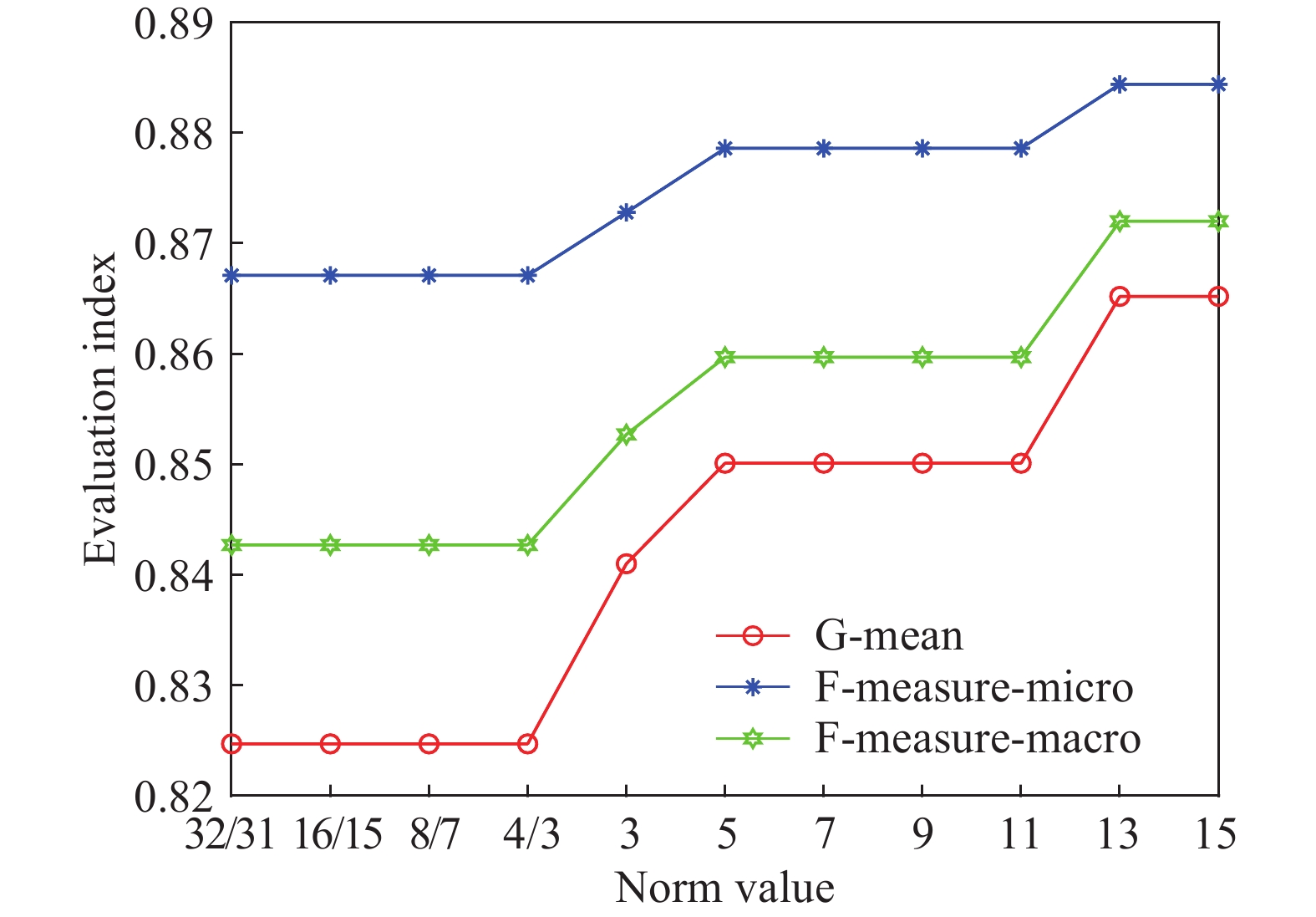
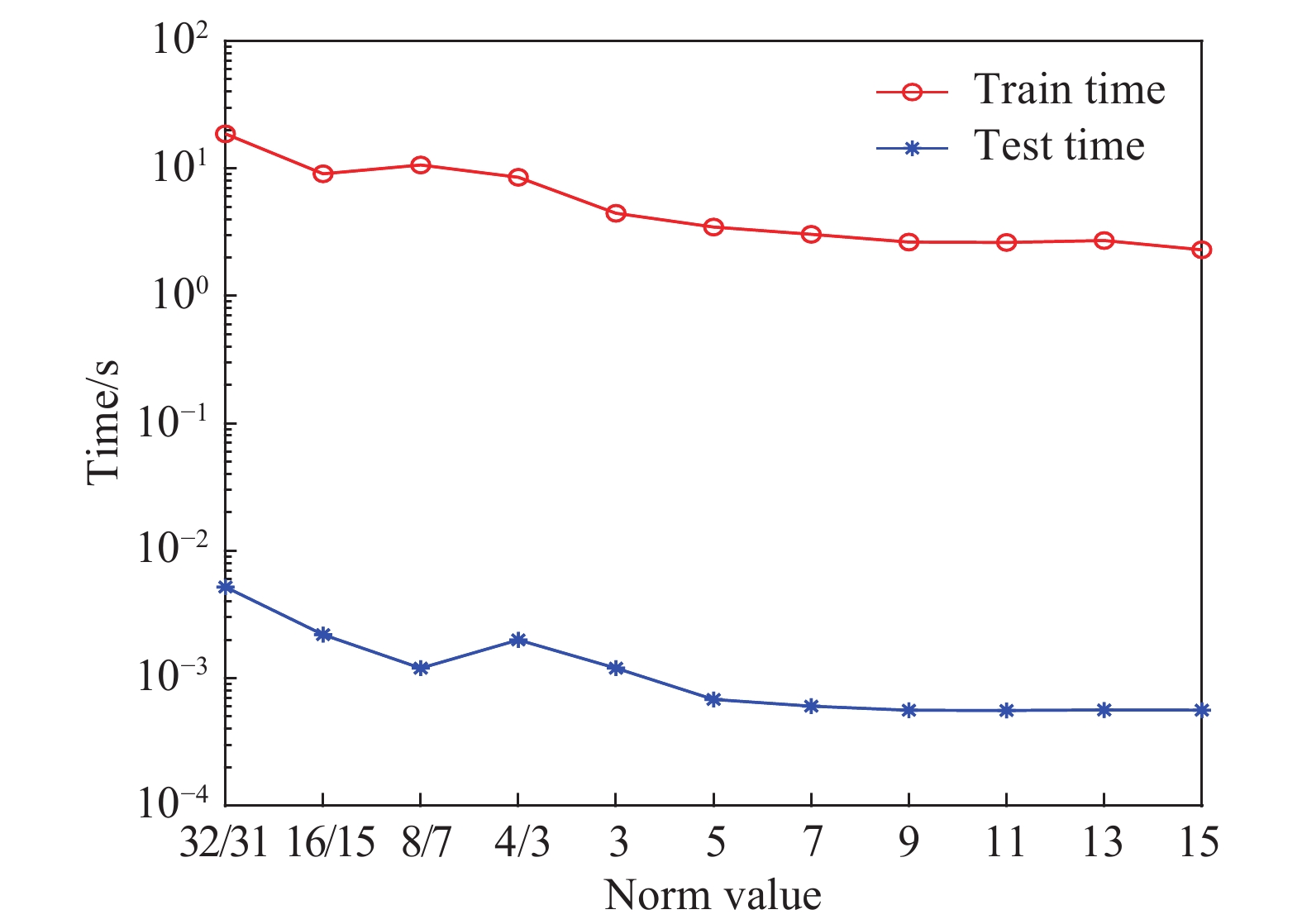
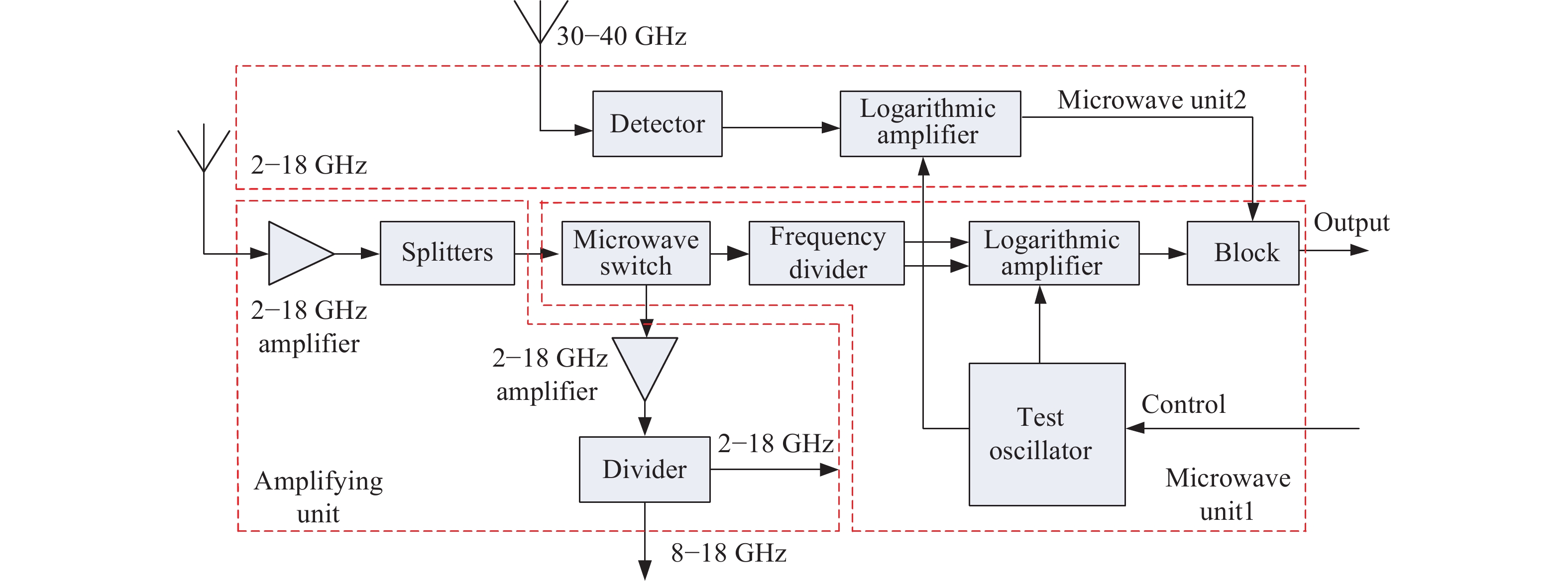
Evaluation index, p Training time/s Testing time/s G-mean F-measure-micro F-measure-macro 32/31 18.7024 0.0052 0.8247 0.8671 0.8427 16/15 9.0874 0.0022 0.8247 0.8671 0.8427 8/7 10.6509 0.0012 0.8247 0.8671 0.8427 4/3 8.5322 0.002 0.8247 0.8671 0.8427 3 4.4538 0.0012 0.841 0.8728 0.8527 5 3.4717 6.82×10?4 0.8501 0.8786 0.8597 7 3.0447 6.04×10?4 0.8501 0.8786 0.8597 9 2.6461 5.61×10?4 0.8501 0.8786 0.8597 11 2.6282 5.59×10?4 0.8501 0.8786 0.8597 13 2.7207 5.64×10?4 0.8652 0.8844 0.872 15 2.3017 5.62×10?4 0.8652 0.8844 0.872 表 5 前端接收機數據集
Table 5. The front-end receiver data set
Serial number Feature 1 Feature 2 Feature 3 Feature 4 Feature 5 Feature 6 Feature 7 Feature 8 Feature 9 Feature 10 Feature 11 Feature 12 State 1 0.108 0.092 0.28 0.912 0.108 0.698 0.777 0.641 0.609 0.627 0.357 0.702 Normal 2 0.263 0.689 0.165 0.901 0.193 0.377 0.108 0.567 0.521 0.225 0.736 0.438 3 0.073 0.371 0.344 0.486 0.1 0.889 0.524 0.545 0.474 0.05 0.238 0.724 … 46 0.701 0.477 0.367 0.741 0.427 0.836 0.151 0.791 0.927 0.788 0.684 0.583 Fault 48 0.798 0.329 0.278 0.766 0.558 0.869 0.509 0.545 0.1 0.283 0.704 0.328 … 121 0.671 0.685 0.029 0.473 0.555 0.328 0.914 0.742 0.23 0.665 0.401 0.752 122 0.947 0.444 0.145 0.342 0.8 0.56 0.484 0.602 0.12 0.089 0.363 0.126 123 0.044 0.532 0.226 0.336 0.718 0.246 0.484 0.064 0.627 0.198 0.846 0.649 表 6 前端接收機的診斷精度
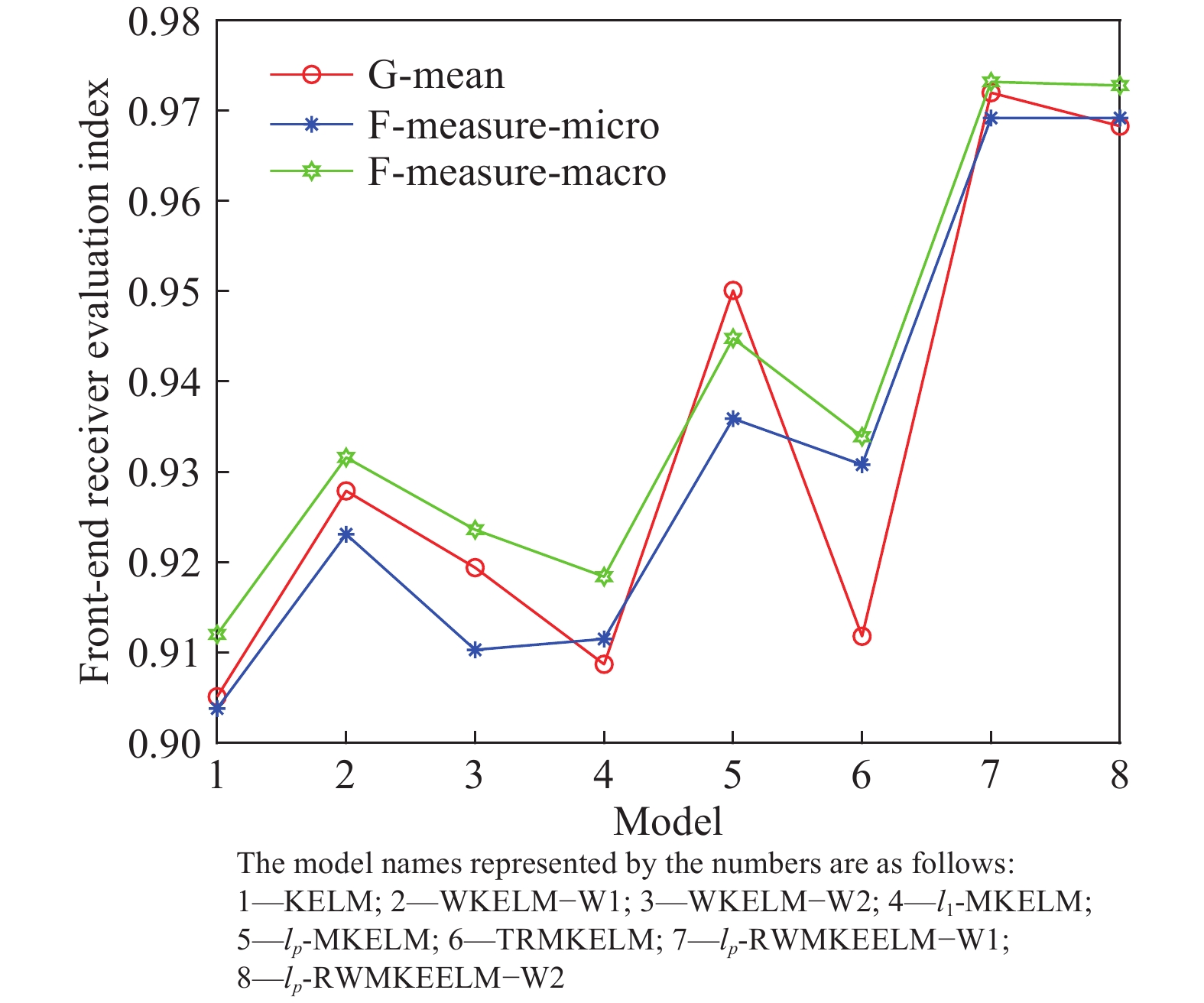
Table 6. Diagnostic accuracy of the front-end receiver
Model G-mean F-measure-micro F-measure-macro Parameter,C KELM 0.9051±0.054 0.9038±0.0458 0.912±0.0447 2(4) WKELM-W1 0.9279±0.0635 0.9231±0.0666 0.9316±0.0593 2(10) WKELM-W2 0.9194±0.0098 0.9103+0.0222 0.9236±0.0153 2(10) l1-MKELM 0.9087±0.061 0.9115±0.0575 0.9184±0.0551 2(7) lp-MKELM 0.9501±0.022 0.9359±0.0222 0.9448±0.0198 2(7) ITDSMM-KELM 0.9118±0.0474 0.9308±0.0322 0.9339±0.0337 2(17) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.972±0.0298 0.9692±0.0322 0.9732±0.028 2(3) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.9683±0.0307 0.9691±0.0322 0.9728±0.0282 2(3) 表 7 前端接收機診斷時間開銷
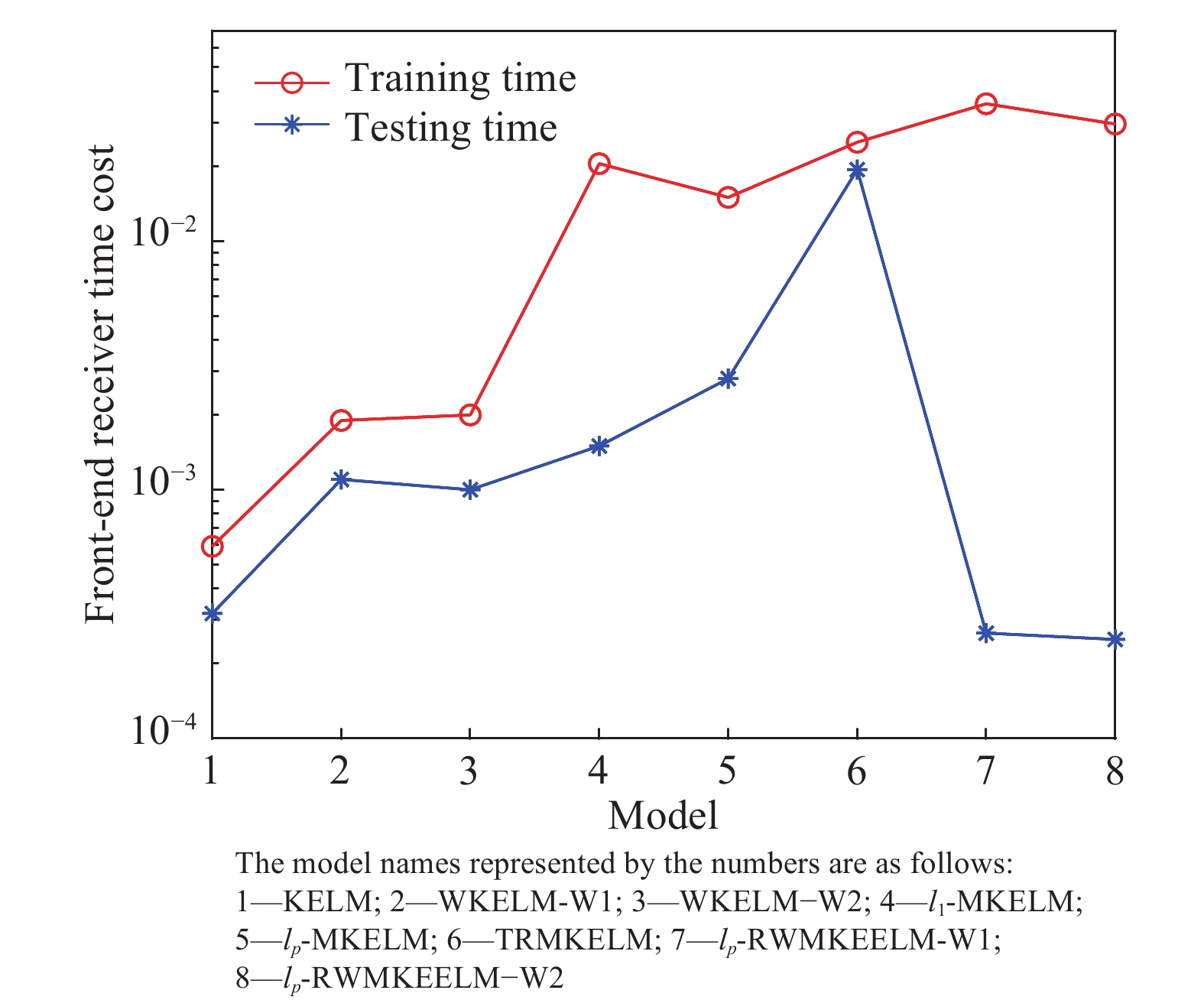
Table 7. Diagnosis time cost of the front-end receiver
Model Training time/s Testing time/s Parameter,C ELM 5.92E-04 3.18×10?4 2(4) WKELM-W1 0.0019 0.0011 2(10) WKELM-W2 0.002 1.0010?3 2(10) l1-MKELM 0.0205 0.0015 2(7) lp-MKELM 0.015 0.0028 2(7) ITDSMM-KELM 0.025 0.0194 2(17) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W1 0.0357 2.65×10?4 2(3) lp-RWMKE-ELM-W2 0.0296 2.50×10?4 2(3) www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Ao Y C, Shi Y B, Zhang W, et al. An approximate calculation of ratio of normal variables and its application in analog circuit fault diagnosis. J Electron Test, 2013, 29(4): 555 doi: 10.1007/s10836-013-5382-z [2] Han H, Wang H J, Tian S L, et al. A new analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on improved mahalanobis distance. J Electron Test, 2013, 29(1): 95 doi: 10.1007/s10836-012-5342-z [3] Tang X F, Xu A Q. Practical analog circuit diagnosis based on fault features with minimum ambiguities. J Electron Test, 2016, 32(1): 83 doi: 10.1007/s10836-015-5561-1 [4] Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feed forward neural networks // Proceedings of 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest, 2004: 985 [5] Qin H Y, Zhou H P, Cao J W. Imbalanced learning algorithm based intelligent abnormal electricity consumption detection. Neurocomputing, 2020, 402: 112 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.085 [6] He H B, Garcia E A. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, 2009, 21(9): 1263 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2008.239 [7] Akbani R, Kwek S, Japkowicz N. Applying support vector machines to imbalanced datasets // Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Machine Learning. Pisa, 2004: 39 [8] Zheng L K, Xiang Y, Sheng C X. Optimization-based improved kernel extreme learning machine for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng, 2019, 41: 619 [9] Deng W Y, Zheng Q H, Chen L. Regularized extreme learning machine // IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining (CIDM 09). Nashville, 2009: 389 [10] Zong W W, Huang G B, Chen Y Q. Weighted extreme learning machine for imbalance learning. Neurocomputing, 2013, 101: 229 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.08.010 [11] Mirza B, Lin Z P, Toh K A. Weighted online sequential extreme learning machine for class imbalance learning. Neural Process Lett, 2013, 38(3): 465 doi: 10.1007/s11063-013-9286-9 [12] Mao W T, Wang J W, Xue Z N. An ELM-based model with sparse-weighting strategy for sequential data imbalance problem. Int J Mach Learn Cybern, 2017, 8(4): 1333 doi: 10.1007/s13042-016-0509-z [13] Yu H Y, Sun X Y, Yan X Z. Sequential prediction for imbalanced data stream via weighted OS-ELM and dynamic GAN. Intell Data Anal, 2019, 23(6): 1191 doi: 10.3233/IDA-184377 [14] Zhang Y, Liu B, Cai J, et al. Ensemble weighted extreme learning machine for imbalanced data classification based on differential evolution. Neural Comput Appl, 2017, 28: 259 doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2342-4 [15] Zhang W, Xu A Q. Application of MKL model incorporated within-class scatter in analog circuit diagnosis. Comput Eng Appl, 2018, 54(9): 5 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1712-0425張偉, 許愛強. 集成散度的MKL模型在模擬電路診斷中的應用. 計算機工程與應用, 2018, 54(9):5 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1712-0425 [16] Ergul U, Bilgin G. MCK-ELM: multiple composite kernel extreme learning machine for hyper spectral images. Neural Comput Appl, 2020, 32(11): 6809 doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04044-9 [17] Yu H Y, Sun X Y, Wang J. Ensemble OS-ELM based on combination weight for data stream classification. Appl Intell, 2019, 49(6): 2382 doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-01403-2 [18] Zhou Z H, Liu X Y. Training cost-sensitive neural networks with methods addressing the class imbalance problem. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, 2006, 18(1): 63 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2006.17 [19] Raghuwanshi B S, Shukla S. Class-specific cost-sensitive boosting weighted ELM for class imbalance learning. Memetic Comput, 2019, 11(3): 263 doi: 10.1007/s12293-018-0267-4 [20] Mirza B, Lin Z P, Liu N. Ensemble of subset online sequential extreme learning machine for class imbalance and concept drift. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 316 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.03.075 [21] Li K, Kong X F, Lu Z, et al. Boosting weighted ELM for unbalanced learning. Neurocomputing, 2014, 128: 15 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.051 [22] Huang G B, Zhou H M, Ding X J, et al. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern, 2012, 42(2): 513 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2168604 [23] Liu X W, Wang L, Huang G B, et al. Multiple kernel extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 253 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.09.072 [24] Vong C M, Ip W F, Wong P K, et al. Predicting minority class for suspended particulate matters level by extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 2014, 128: 136 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.11.056 [25] Zhang P B, Yang Z X. A novel AdaBoost framework with robust threshold and structural optimization. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2018, 48(1): 64 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2623900 [26] Phoungphol P, Zhang Y Q, Zhao Y C. Robust multiclass classification for learning from imbalanced biomedical data. Tsinghua Sci Technol, 2012, 17(6): 619 doi: 10.1109/TST.2012.6374363 -









 下載:
下載: