Research progress on three kinds of classic process interface technologies in steelmaking-continuous casting section
-
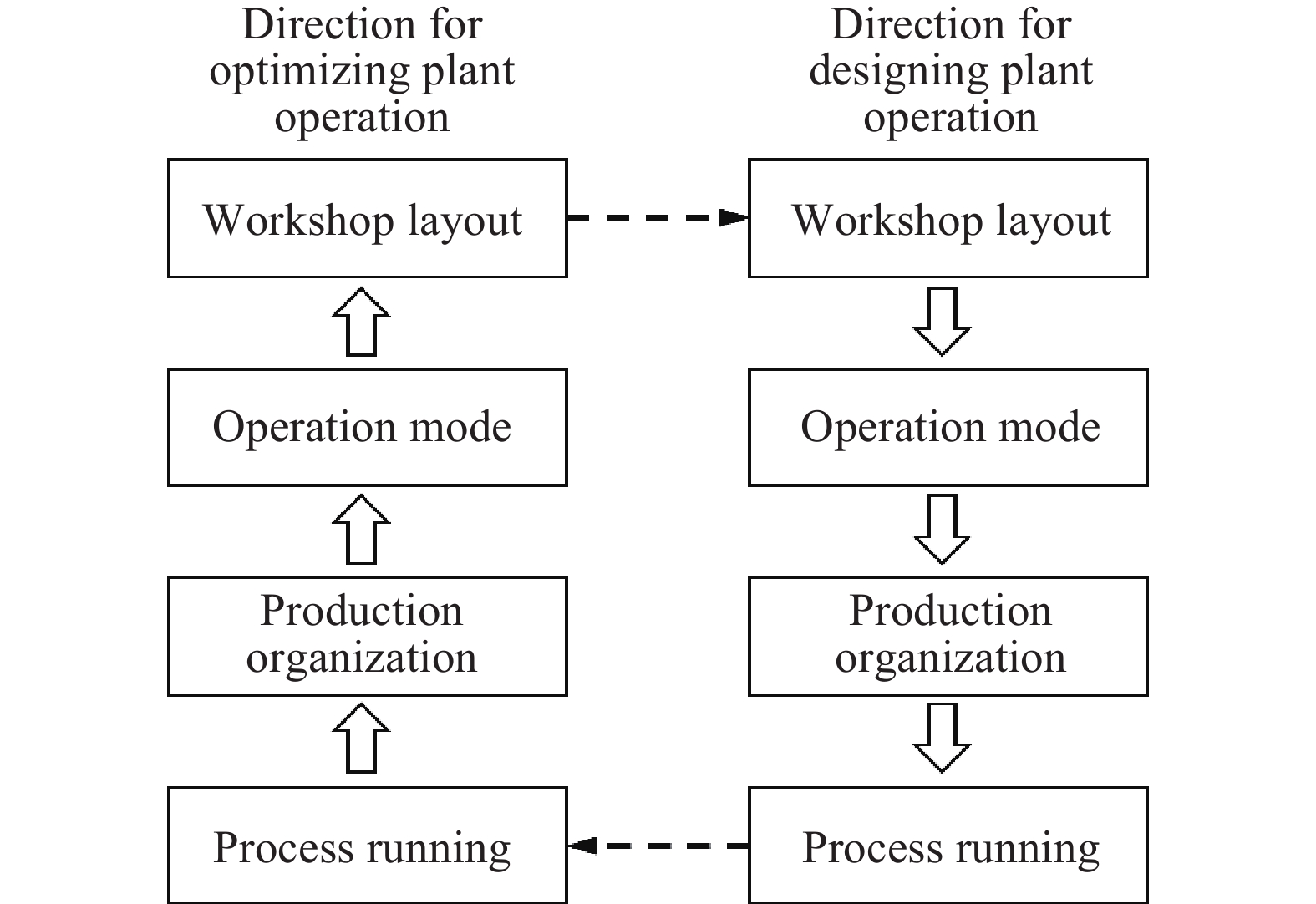
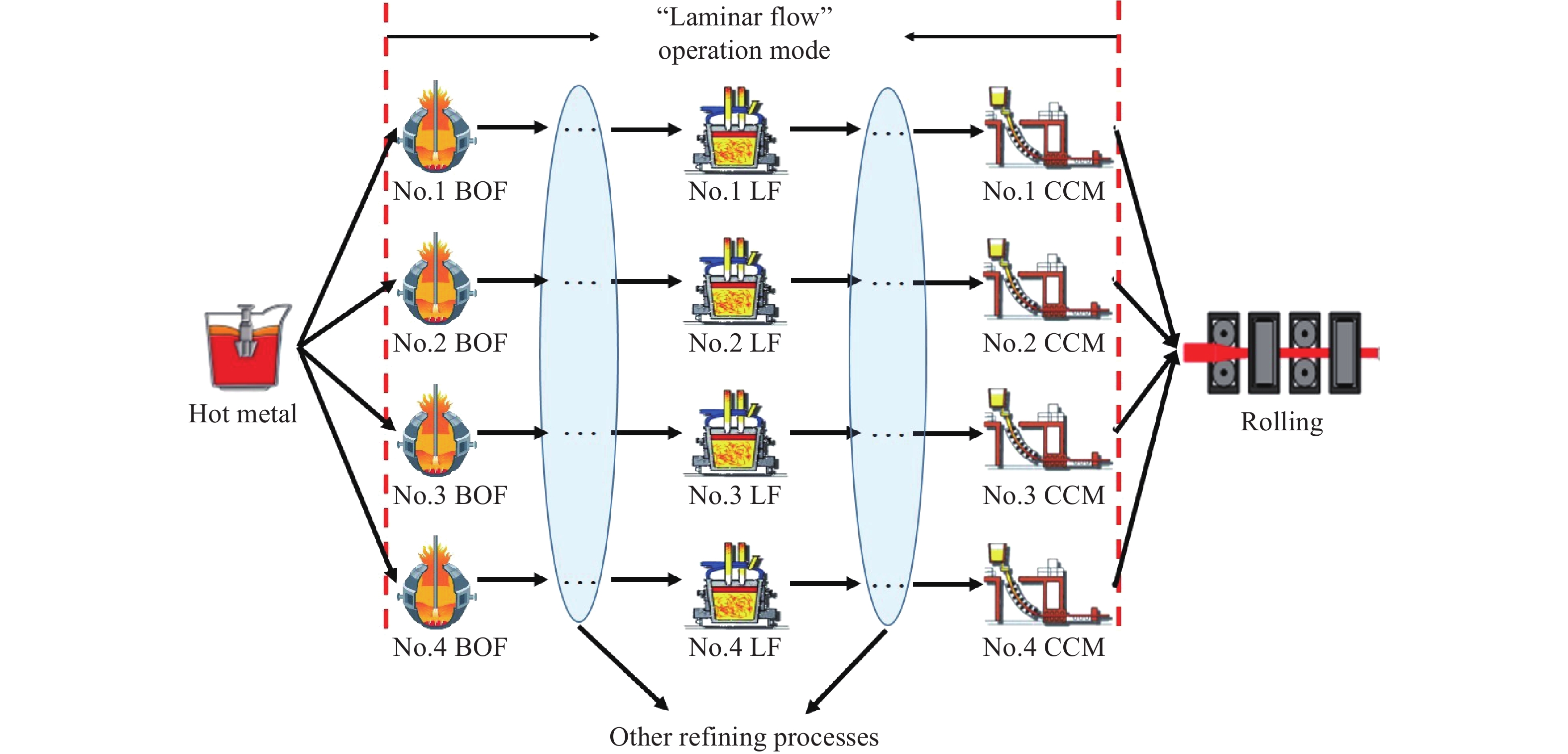
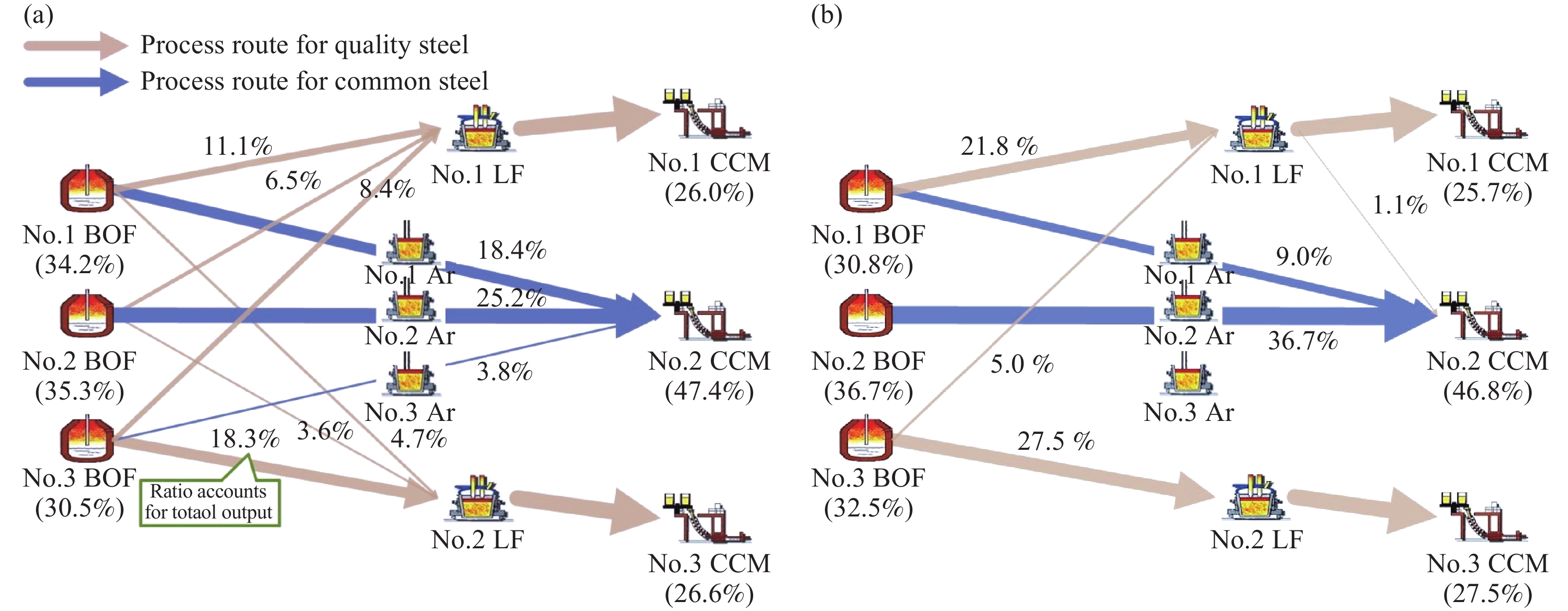
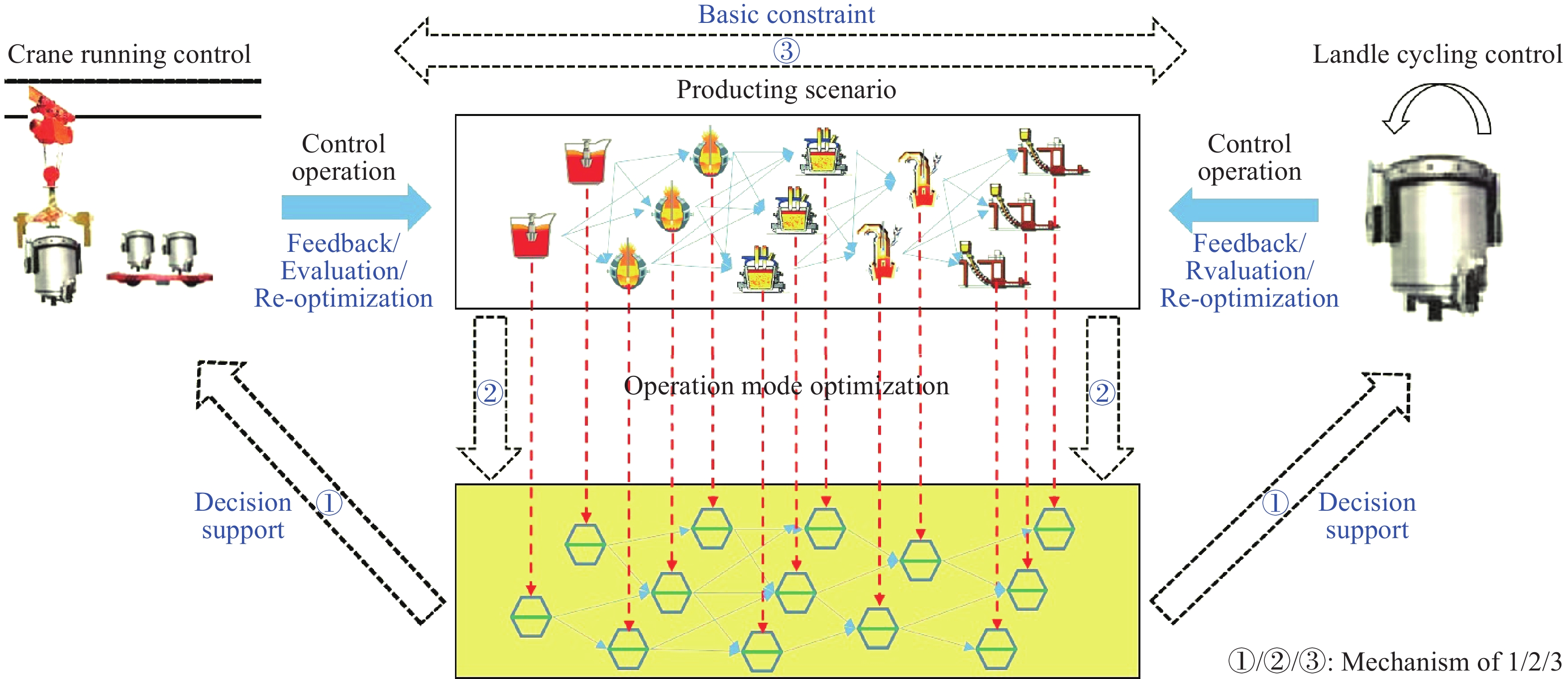
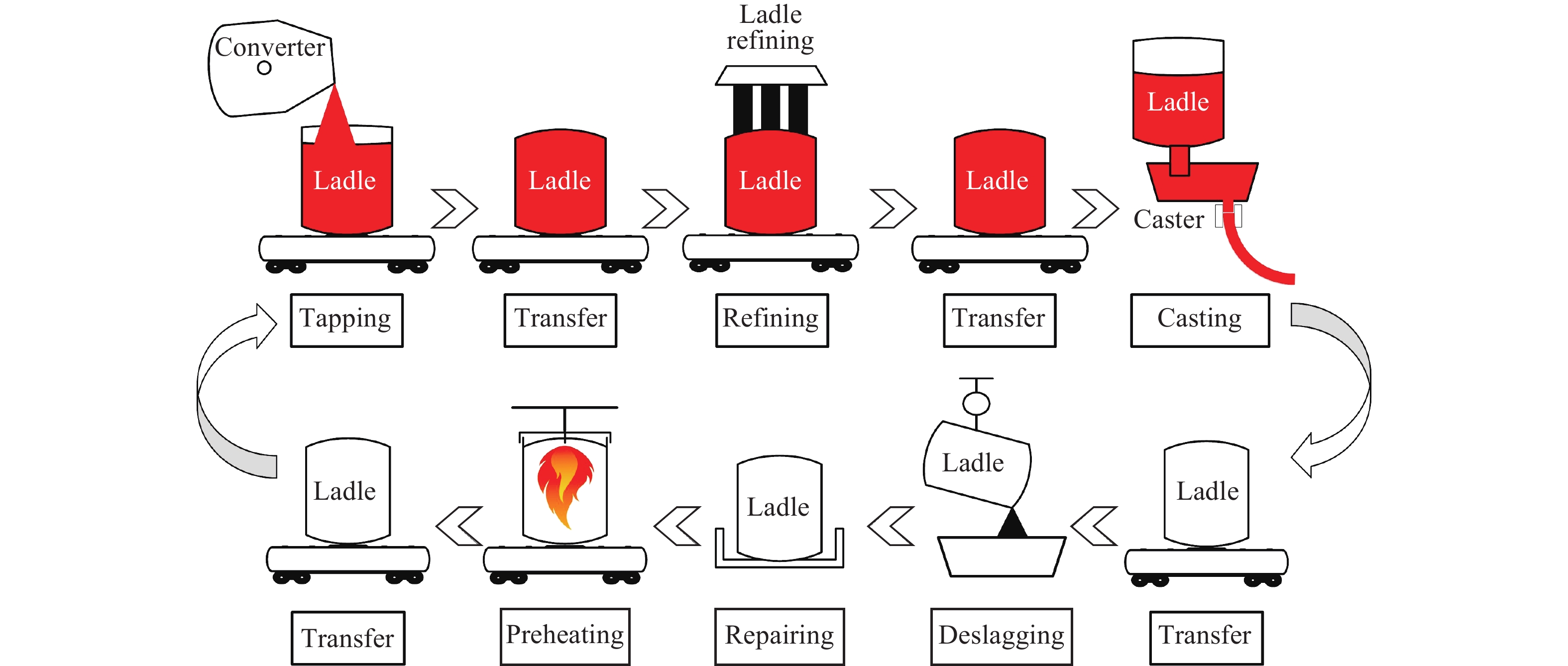
摘要: 面對鋼廠智能化發展的時代要求,煉鋼–連鑄區段工序界面技術受到越來越多冶金學者的關注,其不僅是解決工序關系集合協同–優化問題的重要手段,也影響著工序功能集合解析–優化和流程工序集合重構–優化的效果。本文對煉鋼–連鑄區段3種典型工序界面技術,即鋼包運行控制、天車運行控制和生產運行模式優化的研究進展進行闡述,其中,鋼包運行控制包括鋼包熱狀態監測、鋼包選配以及鋼包調度,天車運行控制包括吊運任務的分配和同跨/異跨天車的協同調度,生產運行模式優化包括工序/設備產能、時間節奏與爐–機對應模式的匹配設計。此外,針對煉鋼–連鑄區段多工序協同運行的制約因素,指出工序界面技術協同的必要性,并對上述工序界面技術的協同機制與協同方案進行了闡述。Abstract: Metallurgical process engineering proposed by academician Ruiyu Yin is a new branch in the field of metallurgy, which deals with the physical nature, structure, and global behavior of metallurgical manufacturing process. Process interface technology used in steelmaking-continuous casting section (SCCS) is developed from metallurgical process engineering. It is used to study and analyze the running dynamics of mass flow in steelmaking plants. In recent years, the intelligent and green production in steelmaking plants has become the demand and necessity of the time because of the rapid development of intelligent manufacturing represented by Industry 4.0 in Germany. Nowadays, the automation control of single-process has been realized in most steelmaking plants at home and abroad, which is a stepping zone and has created the foundation for the intelligent and green production. But at the same time, importance also should be given for the improvement in the multi-process operation of SCCS considering the global optimization on steelmaking production. Undoubtedly the process interface technology is an important method to deal with the collaboration-optimization of process relationship set, but also it has a greater influence on the analysis-optimization of process function set and the reconstruction-optimization of process set. Therefore, the process interface technology has created lot of interest and drawn greater attention from scholars and experts of metallurgy, which results in the great improvement of the multi-process operation in SCCS. Currently, three kinds of classic process interface technologies, including ladle cycling control, crane running control, and operation mode optimization, have become the most important research areas because of their significant effect on the high-efficient connection of mass flow among multi-process. The scope of ladle cycling control includes the monitoring of thermal state and the matching and scheduling of ladles. The task assignment and multi-crane collaborative scheduling are the most important components of crane running control and it is of great interest to research further. When operation mode optimization is considered, the improvement of furnace-caster coordinating mode based on the matching of capacity and rhythm can be regarded as the most interesting research area. It is known that the operation mode is the fundamental for ladle cycling and crane running, and moreover, the status of ladle cycling and crane running also can guide the further optimization of operation mode. Based on above analysis, this paper presented a detailed overview of progress made in the research on abovementioned three kinds of classic process interface technologies in SCCS. Further, the necessity of collaboration between process interface technologies was also illustrated, aiming at unfavorable restraints of multi-process collaborative operation. In addition, the collaboration mechanisms and schemes of all three kinds of classic process interface technologies were described in detail. Finally, it is expected that this review could offer some reference and guidance for the improvements in multi-process operation of SCCS.
-
表 1 鋼包熱狀態影響因素的研究
Table 1. Study on influence factors on thermal state of ladles
No. Authors (Year) Influencing factors Methods (tools)/Model types Refs. 1 Xia (2001) Initial temperature of ladle lining, heat dissipation rate of slag layer, and bottom blowing or not CFX software/Two dimensional
heat transfer model[22-23] 2 Volkova (2003) Lining thickness and working layer materials Two dimensional heat transfer model [24] 3 Bj?rn (2011) Lining thickness, distance from cover to ladle edge,
and preheating timeCOMSOL software/Two dimensional
heat transfer model[25] 4 Tripathi (2012) Thickness of slag layer, tapping temperature, ladle life,
and initial temperature of ladle liningSoftware of Gambit and Fluent/Two
dimensional heat transfer model[26] 5 Huang (2016) Repair time, preheating time, baking gas temperature,
and cooling timeTwo dimensional heat transfer model [27] 6 Phanomchoeng (2016) Thermal resistance for different materials and thermal resistance for the same material with different temperatures Bounded Jacobian nonlinear observer/One dimensional heat transfer model [28] 7 Gong (2016) Online/offline preheating time, cooling time, and erosion degree of ladle lining Ansys software with ParaMesh/Two
dimensional heat transfer model[29] 8 Wang (2017) Materials and structures of ladle lining Fluent software/Three dimensional
heat transfer model[30] 9 Yuan (2018) Ladle preheating methods Fluent software/Three dimensional
heat transfer model[31] 10 Santos (2018) Working layer materials and insulation layer or not Abaqus software/Two dimensional
heat transfer model[32] 11 Hou (2018) Thickness and thermal conductivity of ladle lining Abaqus software and Taguchi approaches/Two dimensional heat transfer model [33] 表 2 近年來關于天車調度的代表性研究工作
Table 2. Study on crane scheduling in recent years
No. Authors (Year) Modeling methods Solving methods Characteristics Refs. 1 Xu (2007) Cellular automata Heuristic and genetic algorithms Verify the feasibility of results through
cellular automata[55] 2 Ma (2010) Multi-agent Heuristic algorithm Improve the reliability of results by frequent interaction among different agents and
parallel computing strategy[56] 3 Liu (2011) Mathematical programming Heuristic algorithm Coordinated scheduling between
ladles and cranes[57] 4 Sun (2011) Mixed-timed Petri Net Branch-and-cutmethod Transform crane scheduling problem
into the linear model[58] 5 Xie (2012) Mathematical programming Variable neighborhood search algorithm Optimize algorithm parameters by
artificial neural network[59] 6 Yu (2012) Mathematical programming Genetic and heuristic algorithms Solve the static and dynamic crane scheduling models respectively by genetic
and heuristic algorithms[60] 7 Zhu (2013) Petri Net with UML Heuristic algorithm Make up the deficiency of UML on formal expression by Petri Net [61] 8 Zheng (2013) Mathematical programming Immune genetic algorithm Prominent local search ability of the algorithm and strong global diversity of solutions [62] 9 Wang (2014) Mathematical programming Improved Memetic algorithm Design decoding operator based on task allocation and conflicts eliminating rules [63] 10 Jiang (2016) Mathematical programming Improved genetic algorithm Design encoding operator based on matrix form, and solve task priority and crane
selection in parallel[64] 11 Gao (2017) Mathematical programming Improved genetic algorithm Minimize the total transfer times of tasks and balance the task allocations among cranes [65] 12 Li (2019) Mathematical programming Heuristic algorithm Apply the predictive reactive
rescheduling strategy[66] 13 Pang (2019) Mathematical programming Heuristic algorithm Apply analytical hierarchy process (AHP) fuzzy comprehensive evaluation to
analyze crane scheduling[67] 14 Yang (2019) Plant simulation Heuristic algorithm Coordinated scheduling among ladles,
cranes, and heat plans[68] www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Zhong R Y, Xu X, Klotz E, et al. Intelligent manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0: a review. Engineering, 2017, 3(5): 616 doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.015 [2] Yin R Y. A discussion on “smart” steel plant—view from physical system side. Iron Steel, 2017, 52(6): 1殷瑞鈺. 關于智能化鋼廠的討論—從物理系統一側出發討論鋼廠智能化. 鋼鐵, 2017, 52(6):1 [3] Yin R Y. Metallurgical Process Engineering. 2nd Ed. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011殷瑞鈺. 冶金流程工程學. 2版. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2011 [4] Liu Q, Tian N Y, Yin R Y. Running control for steelmaking workshop. Iron Steel, 2003, 38(9): 14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2003.09.004劉青, 田乃媛, 殷瑞鈺. 煉鋼廠的運行控制. 鋼鐵, 2003, 38(9):14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2003.09.004 [5] Semura K, Matsuura H. Past development and future prospects of secondary refining technology. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2014, 100(4): 456 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane.100.456 [6] Wang F, Tian N Y, He D F, et al. Discussion on effective utilization coefficient of online two-operating position LF. Steelmaking, 2011, 27(1): 71王鋒, 田乃媛, 賀東風, 等. 在線雙工位LF有效利用系數的討論. 煉鋼, 2011, 27(1):71 [7] Wang G, Wang B, Wang B, et al. Scheduling model for steelmaking-continuous casting process based on “furnace-caster matching” principle. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(8): 1080王剛, 王彬, 王寶, 等. 基于“爐機對應”原則的煉鋼–連鑄調度模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(8):1080 [8] Yu X Z, Yang J P, Li X, et al. Optimized scheme of sequence casting based on "furnace-caster matching" principle. China Metall, 2019, 29(4): 22余相灼, 楊建平, 李想, 等. 基于“爐機對應”原則的連澆優化方案. 中國冶金, 2019, 29(4):22 [9] Feng K, He D F, Xu A J, et al. End temperature prediction of molten steel in LF based on CBR-BBN. Steel Res Int, 2016, 87(1): 79 doi: 10.1002/srin.201400512 [10] Bao Y P, Li X, Wang M. A novel method for endpoint temperature prediction in RH. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2019, 46(4): 343 doi: 10.1080/03019233.2017.1392104 [11] Fu G Q, Liu Q, Wang Z, et al. Grey box model for predicting the LF end-point temperature of molten steel. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(7): 948付國慶, 劉青, 汪宙, 等. LF精煉終點鋼水溫度灰箱預報模型. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(7):948 [12] Fredman T P. Heat transfer in steelmaking ladle refractories and steel temperature: a literature review. Scand J Metall, 2000, 29(6): 232 doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0692.2000.d01-28.x [13] Wu X D, Zhou D, Zheng J Z. Research on thermal status of 300 t ladle in the process of steel-making and continues casting. Steelmaking, 2009, 25(4): 49吳曉東, 周丹, 鄭建忠. 煉鋼–連鑄過程300 t鋼包熱狀態測試研究. 煉鋼, 2009, 25(4):49 [14] Mazzetti-Succi V. Insulation board investigation and trials in 300 tonne steel ladles at Arcelormittal Dofasco // Proceedings of the Unified International Technical Conference on Refractories. Victoria, 2014: 703 [15] Zhou J A, Xie J B, Wang B, et al. New insight into investigation of thermal transfer of molten steel inside a ladle with vacuum shell. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2017, 128(1): 481 doi: 10.1007/s10973-016-5853-4 [16] Fredman T P, Saxen H. Model for temperature profile estimation in the refractory of a metallurgical ladle. Metall Mater Trans B, 1998, 29(3): 651 doi: 10.1007/s11663-998-0100-4 [17] Zabadal J R S, Vilhena M T M B, Leite S Q B. Heat transfer process simulation by finite differences for online control of ladle furnaces. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2004, 31(3): 227 doi: 10.1179/030192304225012150 [18] Lu B Y, Meng X N, Zhu M Y. Numerical analysis for the heat transfer behavior of steel ladle as the thermoelectric waste-heat source. Catal Today, 2018, 318: 180 doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.10.038 [19] Song G W, Tama B A, Park J, et al. Temperature control optimization in a steel-making continuous casting process using a multimodal deep learning approach. Steel Res Int, 2019, 90(12): 1900321 doi: 10.1002/srin.201900321 [20] Zhang Z, Cao L L, Lin W H, et al. Improved prediction model for BOF end-point manganese content based on IPSO-RELM method. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(8): 1052張壯, 曹玲玲, 林文輝, 等. 基于IPSO-RELM轉爐冶煉終點錳含量預測模型. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(8):1052 [21] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436 doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [22] Xia J L, Ahokainen T. Transient flow and heat transfer in a steelmaking ladle during the holding period. Metall Mater Trans B, 2001, 32(4): 733 doi: 10.1007/s11663-001-0127-2 [23] Xia J L, Ahokainen T. Thermal stratification in a steel ladle. Can Metall Q, 2001, 40(4): 479 doi: 10.1179/cmq.2001.40.4.479 [24] Volkova O, Janke D. Modelling of temperature distribution in refractory ladle lining for steelmaking. ISIJ Int, 2003, 43(8): 1185 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.43.1185 [25] Bj?rn G, M?rten G, Du S C. Thermal modelling of the ladle preheating process. Steel Res Int, 2011, 82(12): 1425 doi: 10.1002/srin.201100198 [26] Tripathi A, Saha J K, Singh J B, et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer phenomenon in steel making ladle. ISIJ Int, 2012, 52(9): 1591 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.52.1591 [27] Huang Y F, Xiong W, Fan Z Y. Effect of ladle thermal state on the LF endpoint temperature of molten steel // Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering. Shenzhen, 2016: 533 [28] Phanomchoeng G, Chantranuwathana S, Charunyakorn P. On-line ladle lining temperature estimation by using bounded Jacobian nonlinear observer. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2016, 23(8): 792 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30122-4 [29] Gong H C, Xu A J, Yuan F, et al. The analysis about effect of ladle thermal status on liquid steel temperature drop and algorithm optimization. Steelmaking, 2016, 32(6): 19龔華超, 徐安軍, 袁飛, 等. 鋼包熱狀態對鋼水溫降影響因素分析算法優化. 煉鋼, 2016, 32(6):19 [30] Wang M. Study on Improvement of Thermal Properties of Ladle with New Refractory Materials[Dissertation]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2017王淼. 新型耐火材料改善鋼包熱特性的研究[學位論文]. 沈陽: 東北大學, 2017 [31] Yuan F. Temperature Simulation and Optimization Research on the Processes of the Ladle Regenerative Preheating and Turnover[Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018袁飛. 鋼包蓄熱式烘烤及周轉過程溫度模擬和優化研究[學位論文]. 北京: 北京科技大學, 2018 [32] Santos M F, Moreira M H, Campos M G G, et al. Enhanced numerical tool to evaluate steel ladle thermal losses. Ceram Int, 2018, 44(11): 12831 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.092 [33] Hou A D, Jin S L, Harmuth H, et al. A method for steel ladle lining optimization applying thermomechanical modeling and Taguchi approaches. JOM, 2018, 70(11): 2449 doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-3063-1 [34] Wang E H, Chen J H, Hou X M. Current research and latest developments on refractories used as ladle linings. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(6): 695王恩會, 陳俊紅, 侯新梅. 鋼包工作襯用耐火材料的研究現狀及最新進展. 工程科學學報, 2019, 41(6):695 [35] Yan W, Wu G Y, Ma S B, et al. Energy efficient lightweight periclase-magnesium alumina spinel castables containing porous aggregates for the working lining of steel ladles. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2018, 38(12): 4276 doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.05.002 [36] Gruber D, Harmuth H. Thermomechanical behavior of steel ladle linings and the influence of insulations. Steel Res Int, 2014, 85(4): 512 doi: 10.1002/srin.201300129 [37] Liu Q, Zhao P, Wu X D, et al. Control strategy for ladle running. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2005, 27(2): 235 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.02.025劉青, 趙平, 吳曉東, 等. 鋼包的運行控制. 北京科技大學學報, 2005, 27(2):235 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.02.025 [38] Wang B, Wang B, Mu Y Q, et al. Optimization and control of ladle operation for special steel plants. Appl Mech Mater, 2014, 602-605: 899 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.602-605.899 [39] Huang B F, Tian N Y, Shi Z, et al. Steel ladle exchange models during steelmaking and continuous casting process. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2017, 24(6): 617 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30093-6 [40] Cai J, Wang H B, He D F, et al. Affecting factors of the turnover rate of steel ladle in steelmaking plants. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(8): 1072蔡峻, 汪紅兵, 賀東風, 等. 煉鋼廠鋼包周轉率的影響因素. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(8):1072 [41] Cai J, Wang H B, Xu A J, et al. Simulation on influencing factors of rate of hot steel ladle in steelmaking plant. J Iron Steel Res, 2014, 26(1): 27蔡峻, 汪紅兵, 徐安軍, 等. 煉鋼廠鋼包紅包出鋼率的影響因素仿真. 鋼鐵研究學報, 2014, 26(1):27 [42] Zhao T H, Xu A J, Cai J. Survey on steel ladle management system. Ind Heat, 2015, 44(2): 12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2015.02.004趙天恒, 徐安軍, 蔡峻. 煉鋼廠鋼包管理系統研究綜述. 工業加熱, 2015, 44(2):12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2015.02.004 [43] Liu J. Research on Ladle Tracking and Scheduling in Steelworks[Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2009劉建. 煉鋼廠鋼包跟蹤與調度研究[學位論文]. 杭州: 杭州電子科技大學, 2009 [44] Liu W, Chai T Y. Steelmaking continuous casting ladle matching method based on rule-learning. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2018, 39(11): 1521劉煒, 柴天佑. 基于規則學習的煉鋼–連鑄鋼包選配方法. 東北大學學報: 自然科學版, 2018, 39(11):1521 [45] Liu W, Pang X F, Chai T Y. Research on the dephosphorization ladle scheduling algorithm of steelmaking?refining?continuous casting process. Control Eng China, 2019, 26(4): 790劉煒, 龐新福, 柴天佑. 煉鋼–精煉–連鑄脫磷鋼包調度算法研究. 控制工程, 2019, 26(4):790 [46] Tan Y Y, Wei Z, Wang S, et al. Optimization algorithm for ladle scheduling based on the VRPTW-AT model. J Syst Eng, 2013, 28(1): 94 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2013.01.013譚園園, 魏震, 王森, 等. 基于VRPTW-AT模型的鋼包優化調度方法. 系統工程學報, 2013, 28(1):94 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2013.01.013 [47] Tan Y Y, Cheng T C E, Ji M. A multi-objective scatter search for the ladle scheduling problem. Int J Prod Res, 2014, 52(24): 7513 doi: 10.1080/00207543.2014.939238 [48] Xiao Y. Research on Ladle Scheduling Based on UML and Plant Simulation in Steel Plant[Dissertation]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012肖陽. 基于UML與Plant Simulation的鋼包周轉調度研究[學位論文]. 重慶: 重慶大學, 2012 [49] Zhang T. Study on Optimical Method of Steelmaking-Continuous Casting Production Planning Involved in Ladle Turn-around[Dissertation]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2009張濤. 涉及鋼包周轉的煉鋼–連鑄生產作業計劃優化方法研究[學位論文]. 重慶: 重慶大學, 2009 [50] Zhang Y. A Scatter Search Algorithm for A Steelmaking?Continuous Casting Schedule Problem with Combination of Ladle Allocation[Dissertation]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2018張媛. 考慮鋼包分配的煉鋼?連鑄調度問題研究[學位論文]. 沈陽: 沈陽工業大學, 2018 [51] Cai J, Wang H B, Xu A J, et al. Molten steel temperature on-line compensation system based on steel ladle tracking. Metall Ind Autom, 2013, 37(5): 37蔡峻, 汪紅兵, 徐安軍, 等. 基于鋼包跟蹤的鋼水溫度在線補償系統. 冶金自動化, 2013, 37(5):37 [52] Kuyama S, Tomiyama S. A crane guidance system with scheduling optimization technology in a steel slab yard. ISIJ Int, 2016, 56(5): 820 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-466 [53] Maschietto G N, Ouazene Y, Ravetti M G, et al. Crane scheduling problem with non-interference constraints in a steel coil distribution centre. Int J Prod Res, 2017, 55(6): 1607 doi: 10.1080/00207543.2016.1193249 [54] Liu Q, Tian N Y, Wang Y Q, et al. Important role of crane schedule in optimizing mass flow control of steel plant. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 1998, 20(1): 36劉青, 田乃媛, 王英群, 等. 天車調度在優化鋼廠物流管制中的重要作用. 北京科技大學學報, 1998, 20(1):36 [55] Xu L. Study on Simulation Method of Crane Scheduling in Workshop of Steel-making Plant Based on Cellular Automata[Dissertation]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2007徐樂. 基于元胞自動機的鋼廠車間天車調度仿真方法研究[學位論文]. 重慶: 重慶大學, 2007 [56] Ma C B, Zhu D F, Wang H, et al. Simulation model for crane scheduling in workshop of steel-making plant based on MAS // 2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling. Taiyuan, 2010: V5-404 [57] Liu W, Sun L L, Ding J L, et al. Study on ladle schedule of steel making process using heuristic scheduling algorithm. IFAC Proc Vol, 2011, 44(1): 8211 doi: 10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.02306 [58] Sun L L, Liu W, Chai T Y, et al. Crane scheduling of steel-making and continuous casting process using the mixed-Timed Petri net modelling via CPLEX optimization. IFAC Proc Vol, 2011, 44(1): 9482 doi: 10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.00170 [59] Xie X, Li Y P, Zhou H B, et al. Variable neighborhood search based multi-objective dynamic crane scheduling // Proceedings of 2012 International Conference on Measurement, Information and Control. Harbin, 2012: 457 [60] Yu X. Research on Crane Scheduling of Steelmaking?Refining?Continuous Casting Production Process[Dissertation]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2012俞俠. 煉鋼–精煉–連鑄生產過程天車調度問題研究[學位論文]. 沈陽: 東北大學, 2012 [61] Zhu D F, Wang H, Wang J J, et al. Simulation of crane scheduling systems for steel plant based on Petri Nets and UML. J Kunming Univ Sci Technol Sci Technol, 2013, 38(3): 5朱道飛, 王華, 王建軍, 等. 基于Petri網和UML的鋼廠天車調度系統仿真. 昆明理工大學學報: 自然科學版, 2013, 38(3):5 [62] Zheng Z, Zhou C, Chen K. Crane scheduling simulation model based on immune genetic algorithms. Syst Eng —Theory Pract, 2013, 33(1): 223 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2013.01.028鄭忠, 周超, 陳開. 基于免疫遺傳算法的車間天車調度仿真模型. 系統工程理論與實踐, 2013, 33(1):223 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2013.01.028 [63] Wang X, Liu S X, Wang J. Memetic algorithm for crane scheduling problem with spatial and temporal constraints. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 2014, 35(2): 190王旭, 劉士新, 王佳. 求解具有時空約束的天車調度問題Memetic算法. 東北大學學報: 自然科學版, 2014, 35(2):190 [64] Jiang H Y. Optimization and Simulation on Crane Scheduling of Steelmaking–Continuous Casting Production Process[Dissertation]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2016姜海遠. 煉鋼–連鑄車間天車調度的仿真與優化[學位論文]. 青島: 青島理工大學, 2016 [65] Gao X Q, Li P, Long J Y, et al. Multi-objective modelling and solving for crane scheduling with spatio-temporal constraints in casting workshop. Syst Eng —Theory Pract, 2017, 37(9): 2373 doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2017)09-2373-11高小強, 李盼, 龍建宇, 等. 時空約束下連鑄車間天車調度的多目標建模與求解. 系統工程理論與實踐, 2017, 37(9):2373 doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2017)09-2373-11 [66] Li J, Xu A J, Zang X S. Simulation-based solution for a dynamic multi-crane-scheduling problem in a steelmaking shop. Int J Prod Res, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1687952 [67] Pang X F, Liu W, Li H B, et al. Crane scheduling method in steelmaking?continuous casting process. Inform Control, 2019, 48(6): 745龐新富, 劉煒, 李海波, 等. 煉鋼–連鑄生產過程運輸設備天車調度方法. 信息與控制, 2019, 48(6):745 [68] Yang J P, Zhang J S, Guan M, et al. Fine description of multi-process operation behavior in steelmaking?continuous casting process by a simulation model with crane non-collision constraint. Metals, 2019, 9(10): 1078 doi: 10.3390/met9101078 [69] Liu Q, Tian N Y, Yin R Y. Operation principle and control strategy for steelmaking workshop system. Chin J Process Eng, 2003, 3(2): 171 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2003.02.015劉青, 田乃媛, 殷瑞鈺. 煉鋼廠系統的運行原則與調控策略. 過程工程學報, 2003, 3(2):171 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2003.02.015 [70] Liu Q, Huang X W, Fu P Y. Production mode optimization of a steelmaking workshop system. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2005, 27(6): 736 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.06.024劉青, 黃星武, 富平原. 煉鋼廠系統生產模式優化. 北京科技大學學報, 2005, 27(6):736 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.06.024 [71] Yin R Y. Theory and Methods of Metallurgical Process Integration. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013殷瑞鈺. 冶金流程集成理論與方法. 北京: 冶金工業出版社, 2013 [72] Liu Q, Yin J, Tian X Z, et al. Matching of productive capacity among working procedures and allocating of continuous casting machines for quality steel in a converter plant. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2007, 29(8): 845 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053x.2007.08.021劉青, 尹佳, 田新中, 等. 轉爐煉鋼廠工序產能和品種鋼鑄機配置. 北京科技大學學報, 2007, 29(8):845 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053x.2007.08.021 [73] Dong J G, Zheng Y Y, Jiang X F. Production line practice of Baosteel // Proceedings of 2015 Continuous Casting Equipment Technical Innovation and Refined Production Technology Exchange Meeting. Xi’an, 2015: 30董金剛, 鄭貽裕, 蔣曉放. 寶鋼產品專線化生產實踐//2015連鑄裝備的技術創新和精細化生產技術交流會. 西安, 2015: 30 [74] Dong J G. Comparison and application of steelmaking production patterns // Proceedings of the 12th CSM Steel Congress. Beijing, 2019: 1董金剛. 煉鋼生產模式比較及應用//第12屆中國鋼鐵年會. 北京, 2019: 1 [75] Mu Y Q, Yin J, Xie F M, et al. Research on matching between furnaces and casters in special steel plants. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(1): 126穆衍清, 尹佳, 謝飛鳴, 等. 特殊鋼廠爐機匹配研究. 北京科技大學學報, 2013, 35(1):126 [76] Gu Z X, Xu A J, Chang J B, et al. Optimization of the production organization pattern in Tangshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2014, 21(Suppl 1): 17 [77] Lu Y M, Tian N Y, Xu A J, et al. Establishment of the BOF-caster matching model for the process producing rods and wires. Metall Ind Autom, 2009(Suppl 2): 832蘆永明, 田乃媛, 徐安軍, 等. 棒線材生產流程爐機匹配模型的建立. 冶金自動化, 2009(增刊?2): 832 [78] Lu Y M, Wang F, He D F, et al. Establishment of the BOF-caster matching model for the steelmaking plant producing plates and strips. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2009, 31(9): 1189蘆永明, 王鋒, 賀東風, 等. 全板帶型鋼廠爐機匹配模型的建立. 北京科技大學學報, 2009, 31(9):1189 [79] Chen R B, Qi H. Matching between converters and continuous casters. J Cent South Univ Sci Technol, 2011, 42(6): 1650陳若冰, 齊歡. 煉鋼–連鑄流程的爐機匹配. 中南大學學報: 自然科學版, 2011, 42(6):1650 [80] Liu Q, Yin J, Wang B, et al. Research on rational collocation of LF in medium and small size BOF process // AISTech 2009-Proceedings of the Iron and Steel Technology Conference. St. Louis, 2009: 995 [81] Zheng Z, Xu Z J, Gao X Q, et al. Simulation-based research on the production operation mode in steel plant // Proceedings of the 11th CSM Steel Congress. Beijing, 2017: 1鄭忠, 徐兆俊, 高小強, 等. 鋼廠生產運行模式的仿真研究//第11屆中國鋼鐵年會. 北京, 2017: 1 [82] Yuan S P, Li T K, Wang B L. Improved fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective steelmaking?continuous production scheduling. Comput Integr Manuf Syst, 2019, 25(1): 115袁帥鵬, 李鐵克, 王柏琳. 多目標煉鋼–連鑄生產調度的改進帶精英策略的快速非支配排序遺傳算法. 計算機集成制造系統, 2019, 25(1):115 [83] Liu Q, Yang J P, Wang B L, et al. Genetic optimization model of steelmaking?continuous casting production scheduling based on the “furnace?caster coordinating” strategy. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(5): 645劉倩, 楊建平, 王柏琳, 等. 基于“爐–機對應”的煉鋼–連鑄生產調度問題遺傳優化模型. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(5):645 [84] Liu Q, Liu Q, Yang J P, et al. Progress of research on steelmaking–continuous casting production scheduling. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(2): 144劉青, 劉倩, 楊建平, 等. 煉鋼?連鑄生產調度的研究進展. 工程科學學報, 2020, 42(2):144 -




 下載:
下載: