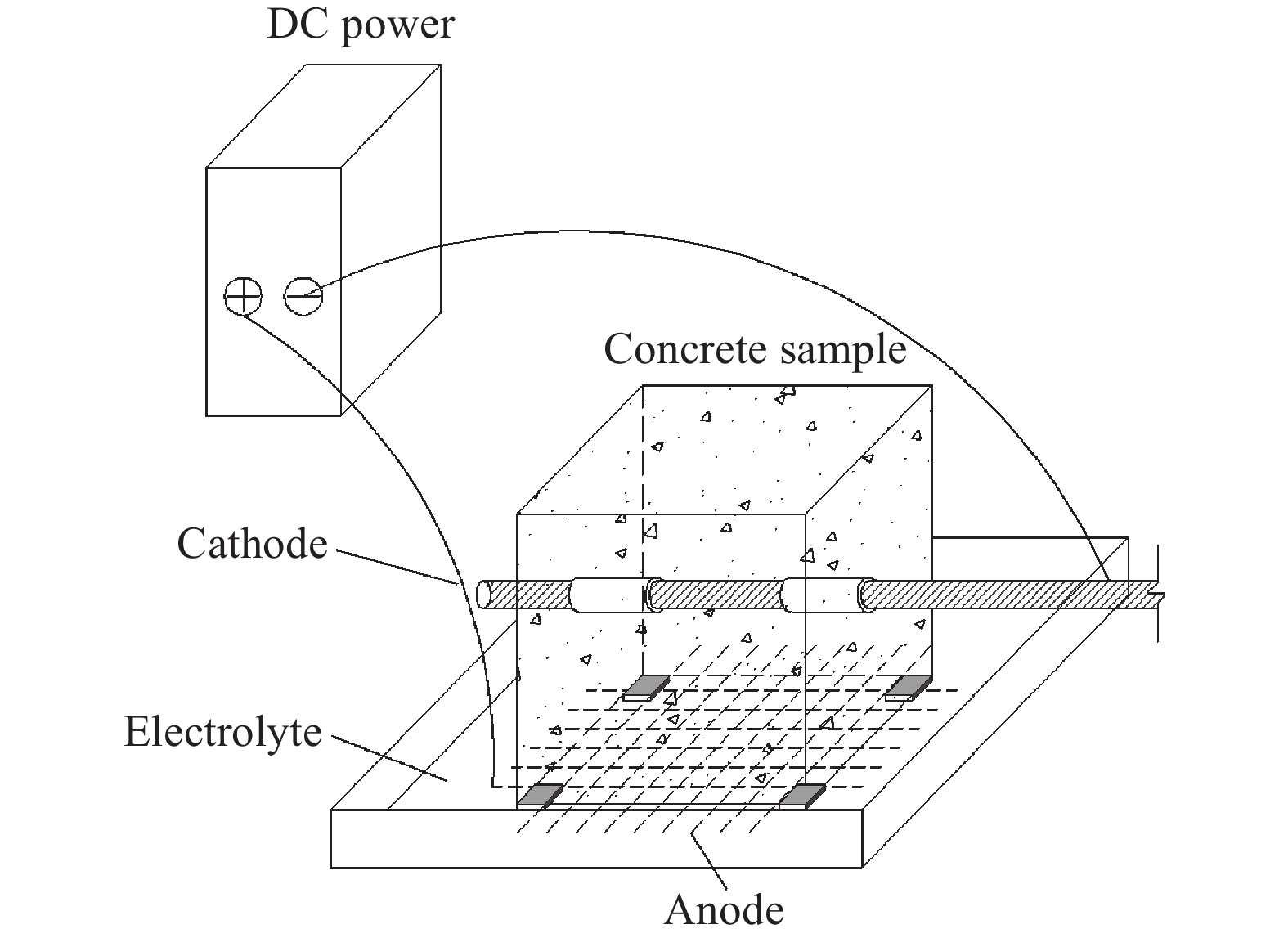
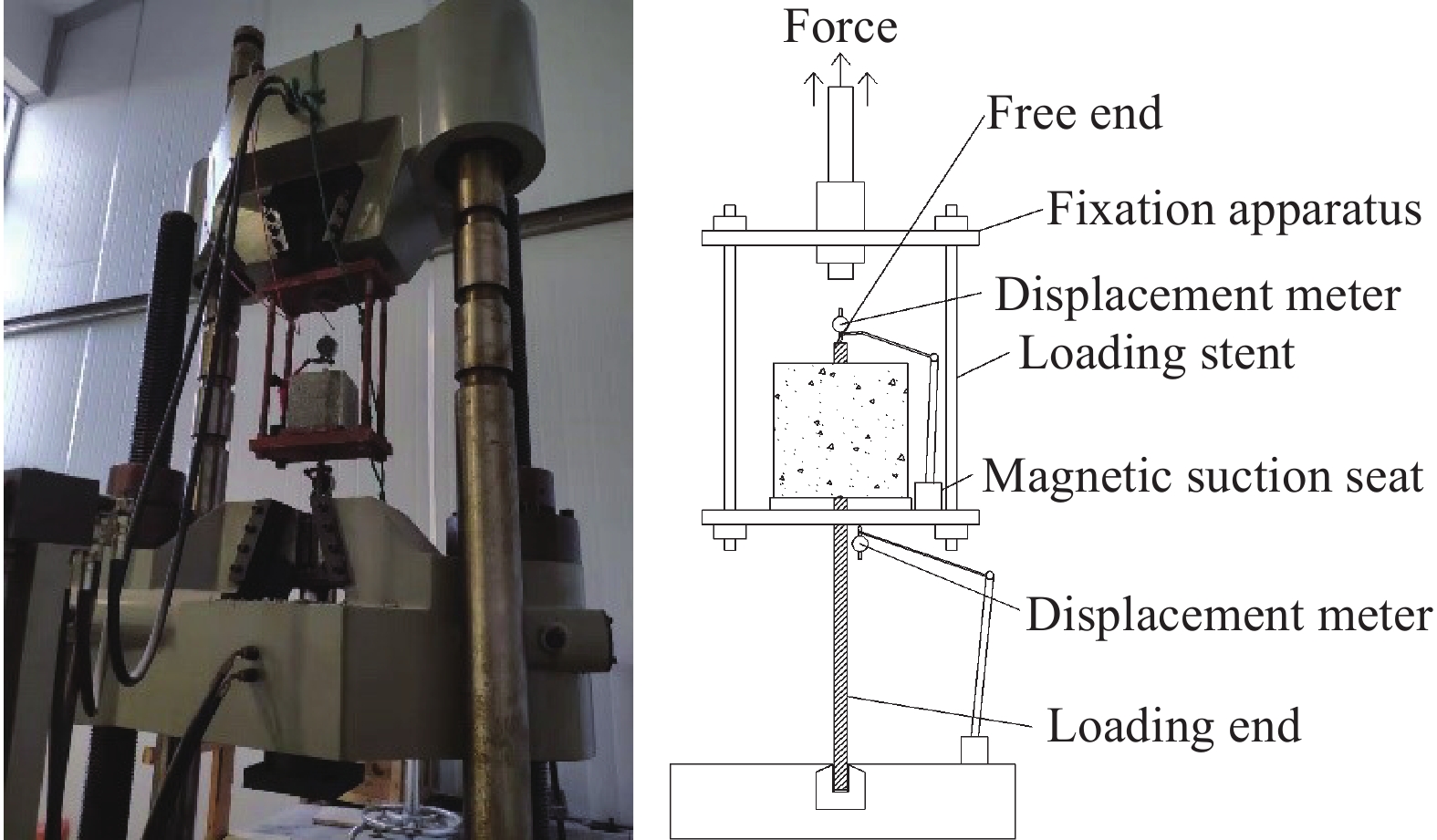
Evolutionary regularity of bond property for reinforced concrete after electrochemical rehabilitation
-
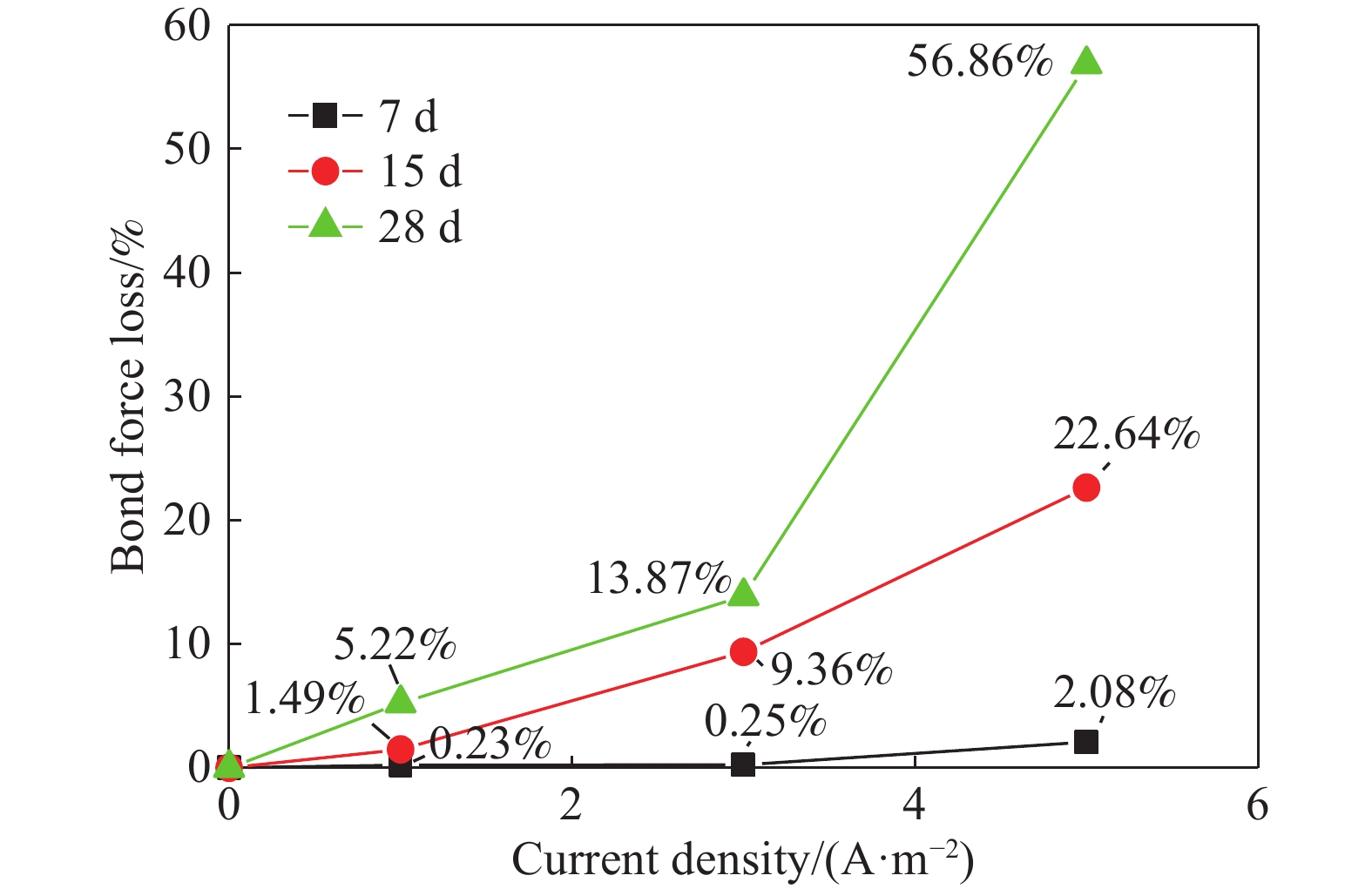
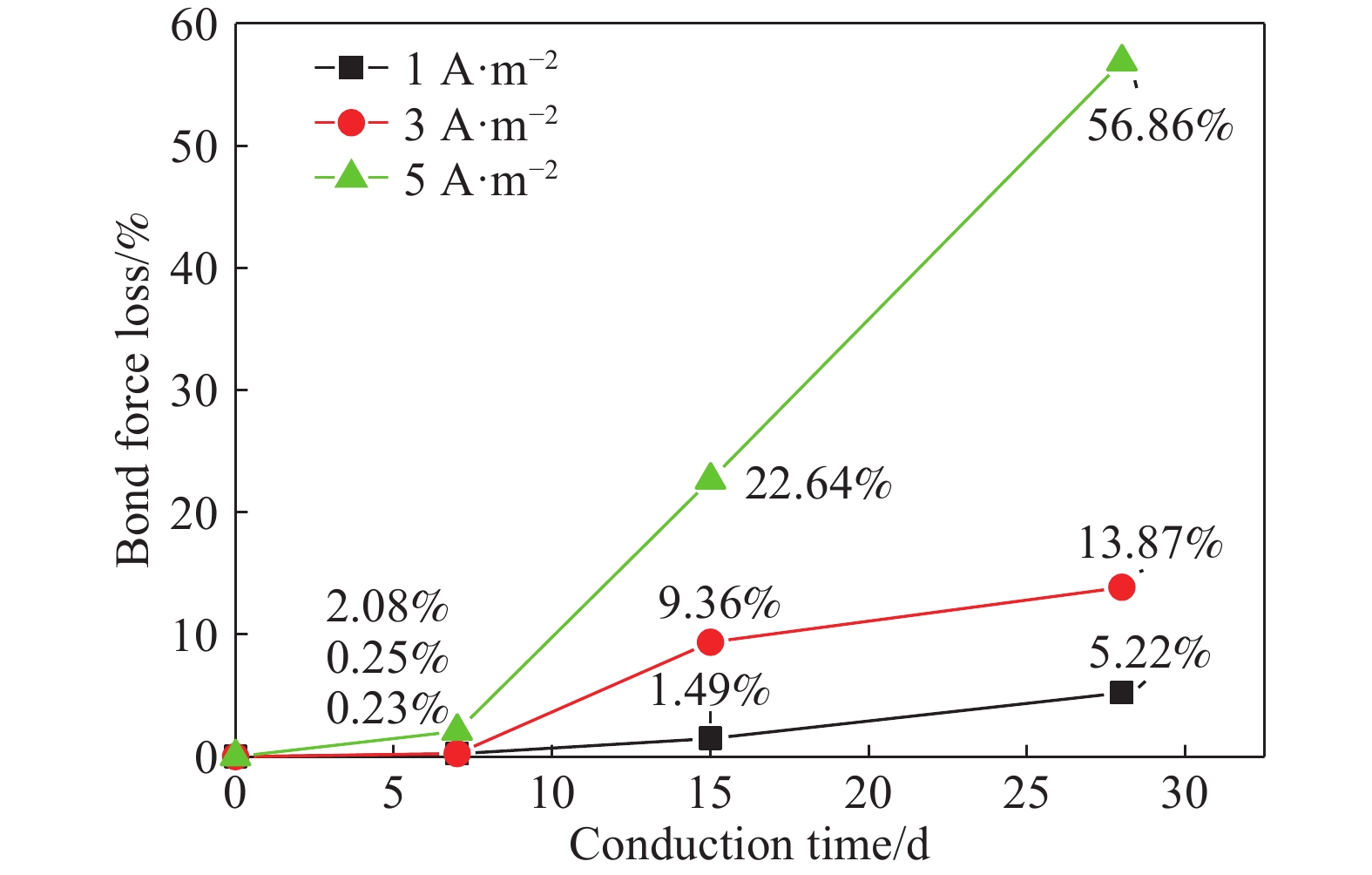
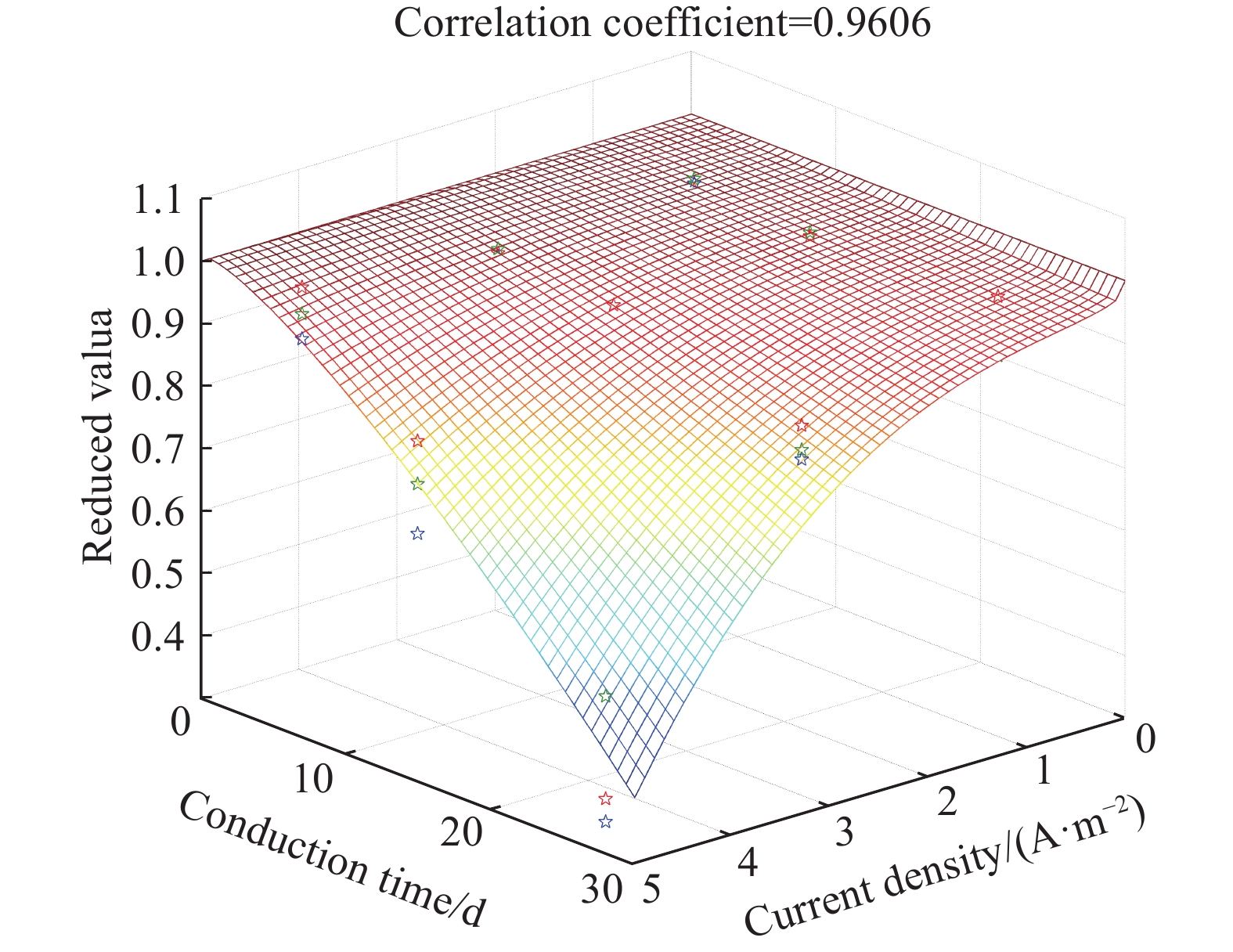
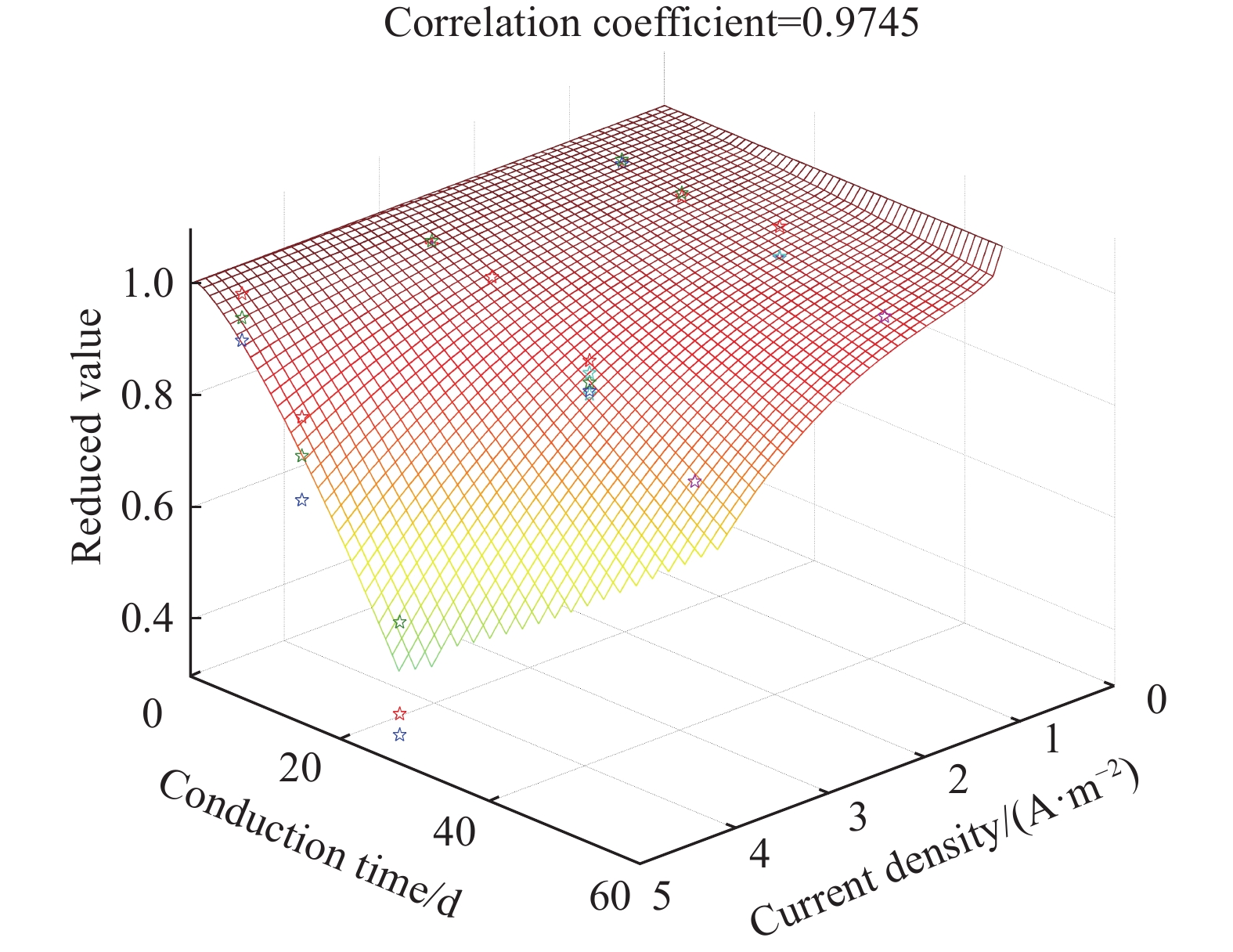
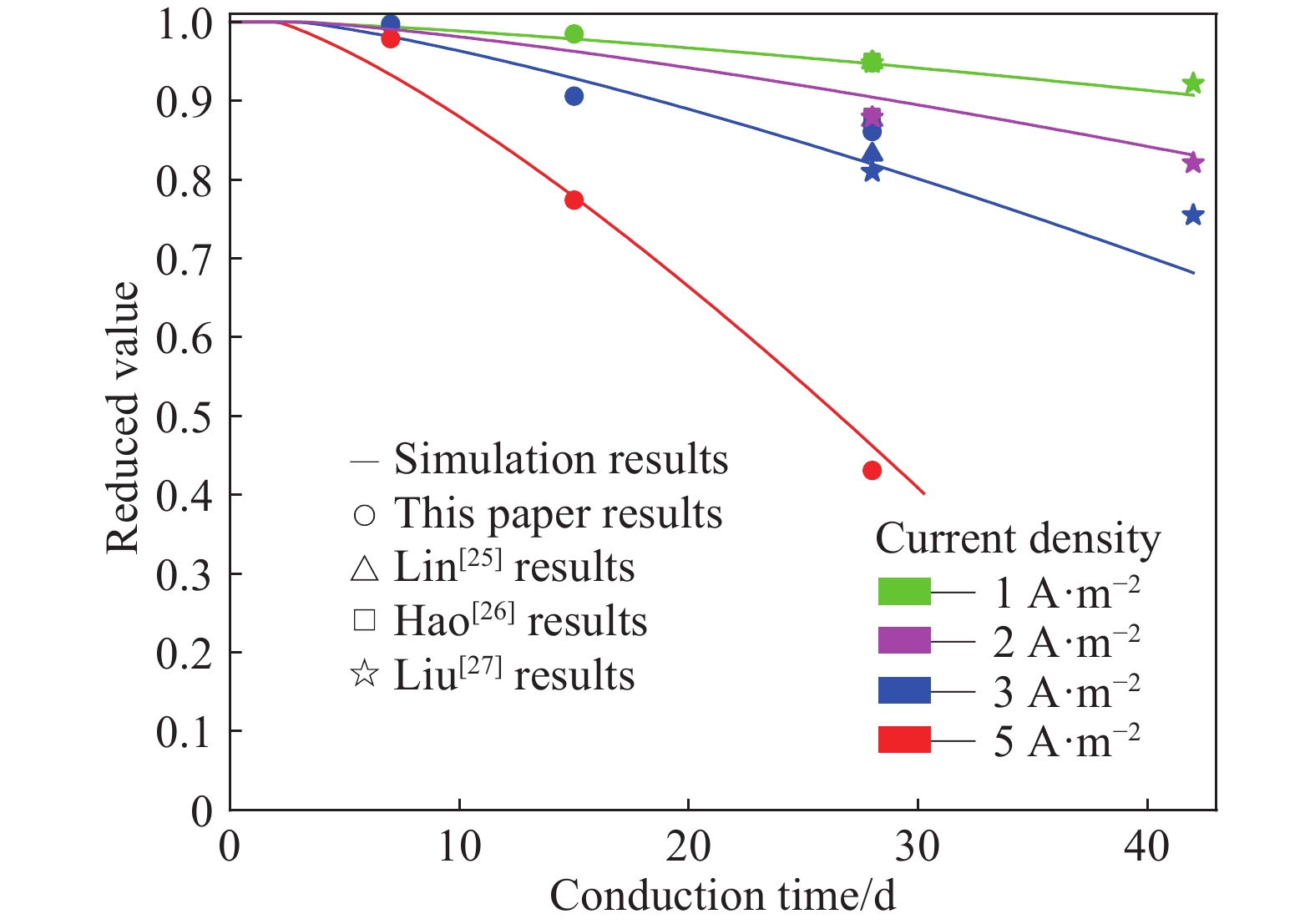
摘要: 針對電化學修復技術導致修復后結構內鋼筋混凝土黏結性能退化問題,通過中心拉拔實驗獲取電化學修復后鋼筋混凝土黏結滑移曲線,研究電化學修復參數(電流密度和通電時間)對鋼筋混凝土黏結性能的影響規律,通過實驗結果進行模型參數分析,建立基于電流密度和通電時間兩個控制變量的黏結強度劣化模型。研究結果表明:電通量較小的情況下,鋼筋混凝土黏結性能損失較小;不控制通電參數的電化學修復技術導致黏結強度下降明顯,采用5 A·m–2的電流開展28 d的恒電流通電,試件的最大黏結力損失量高達56.9%;本文提出的劣化模型可以定量表征電化學修復后試件黏結強度折減情況,模型的數值模擬結果與本文及其他文獻的實驗結果均有較好的一致性,相關系數分別為0.9606和0.9745。Abstract: Reinforcement corrosion, due to the presence of chloride ions, is a major cause of the degradation of reinforced concrete structures. Nowadays, electrochemical rehabilitation (ER) is becoming a common technique for repairing reinforced structures. Due to the transmission properties of the micro-pores in concrete, chloride ions can be transferred to the outside of the concrete through the pores under the driven force of electric field. Compared with other conventional technologies, ER presents many advantages, such as high efficiency and little influence on the environment and surroundings. However, previous studies indicate that ER exhibits negative effect on the interfacial bonding properties of steel concrete. As the main influence factor for ER, varying current densities may consequently change the bond loss between steel and concrete. In addition, large current density significantly reduces interfacial bond. However, current studies lack relevant quantitative research results and fail to propose an effective method to solve the problem after electrochemical repair since aiming at electrochemical rehabilitation will most likely result in the bond deterioration of reinforced concrete. In this study, the bond-slip curves were obtained through central pull-out specimens after ER with various electrochemical parameters, and the relationship between the electrochemical parameters (current density and conduction time) and the bond behaviors were investigated. Finally, a degradation model of bond strength considering the influences of the two parameters mentioned was established. Results show that the bond strength decreases significantly with high current density and long conduction time. Using a current density of 5 A·m–2, reduction of the max bond force increased up to 22.6% and 56.9% under a conduction time of 15 and 28 d, respectively. The proposed model can be used to quantitatively characterize the reduction of bond strength after electrochemical rehabilitation. Good consistency of results was observed after comparing the evaluated results with that of the experiment.
-
表 1 C30混凝土配合比
Table 1. Mix proportion of C30 concrete specimen
kg·m–3 Water Cement Sand Gravel 202 382 751 1157 表 2 實驗試件分組情況表
Table 2. Electrochemical parameters design
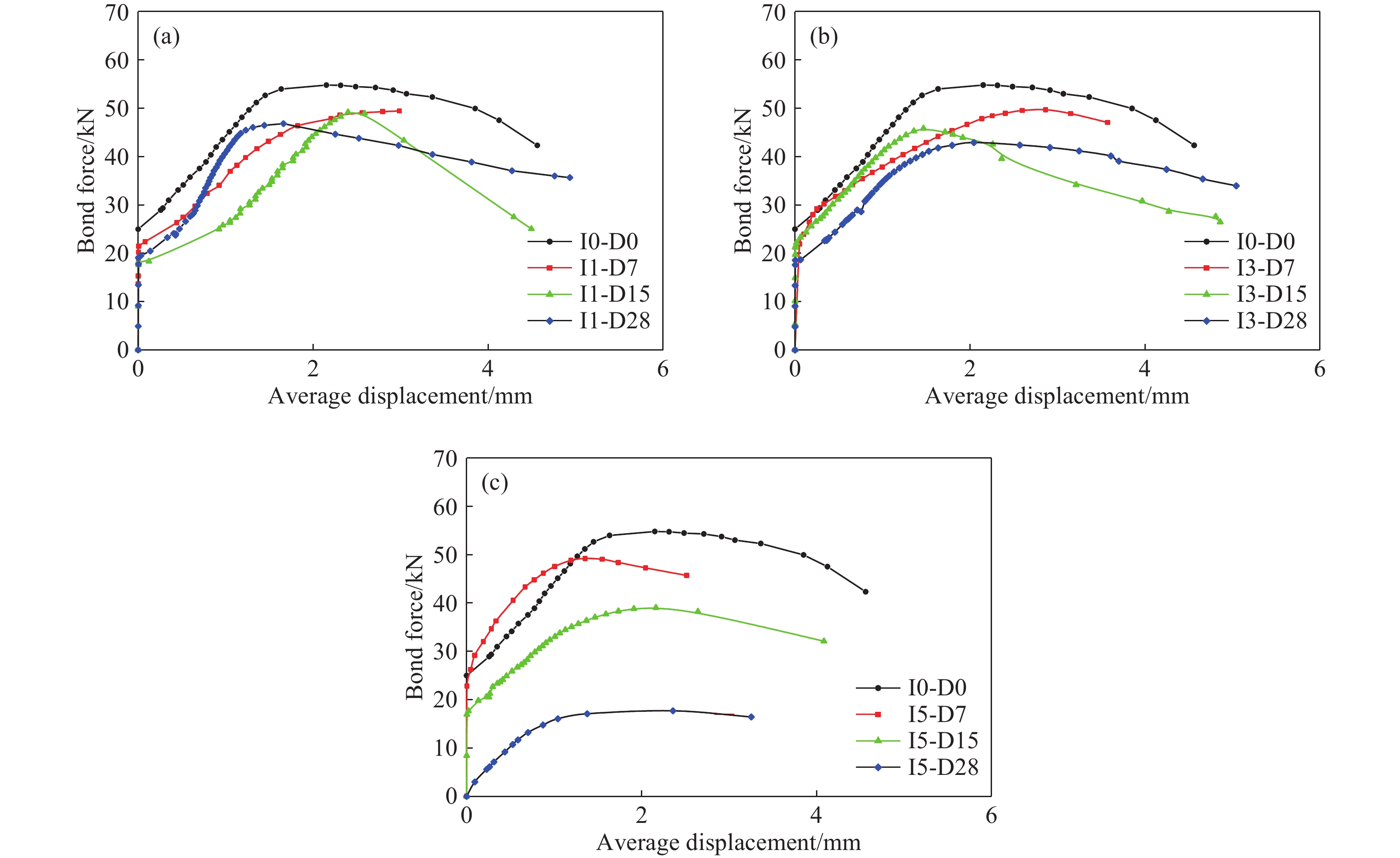
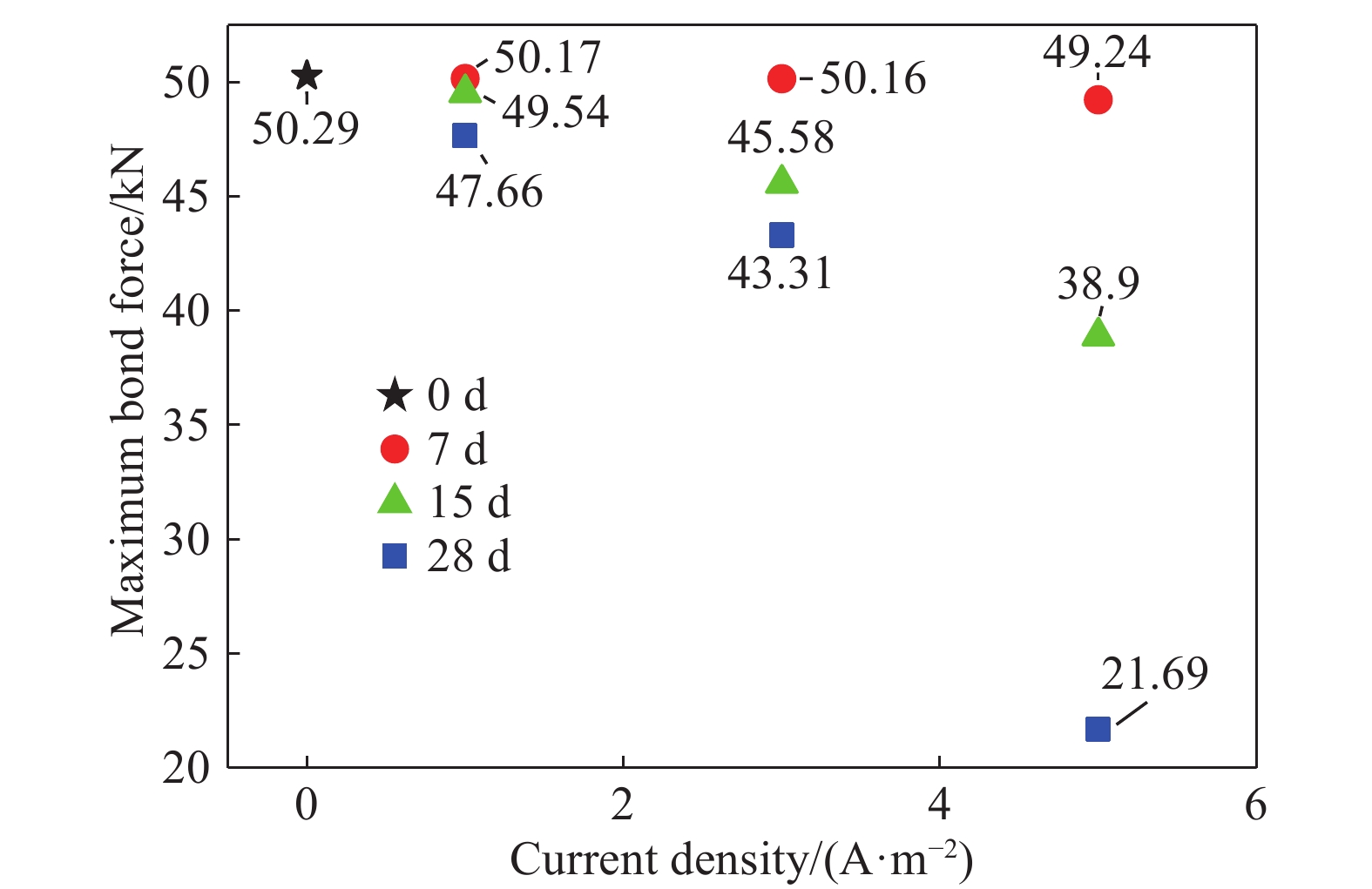
Sample Current density / (A·m–2) Conduction time / d I1-D7 1 7 I1-D15 1 15 I1-D28 1 28 I3-D7 3 7 I3-D15 3 15 I3-D28 3 28 I5-D7 5 7 I5-D15 5 15 I5-D28 5 28 表 3 拉拔實驗最大黏結力
Table 3. Maximum force of pull-out test
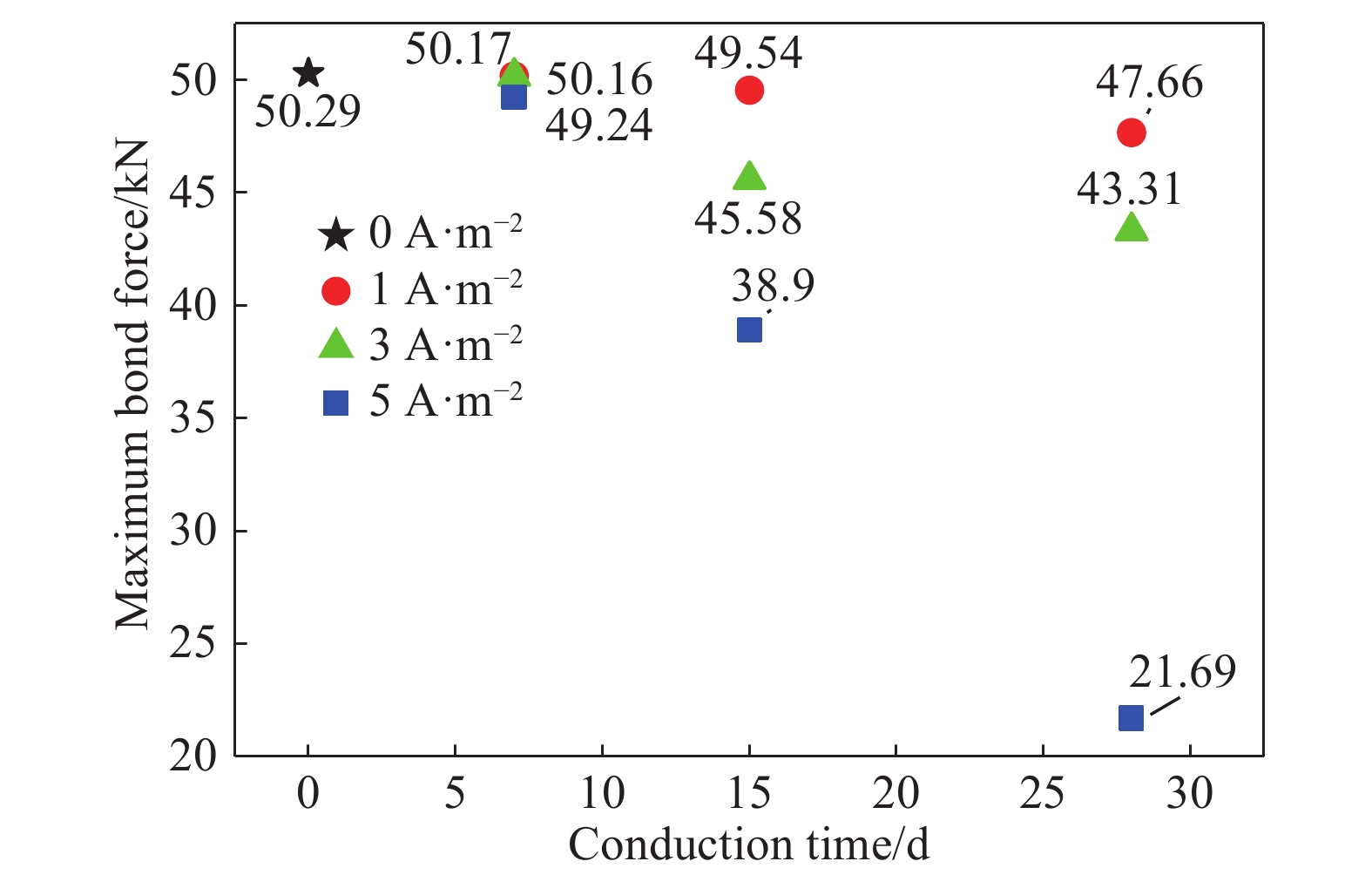
Sample Maximum force/kN Average force/kN Average
bond stress/
MPaAverage reduced value Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 I0-D0 44.34 54.72 51.80 50.29 16.34 1.000 I1-D7 50.16 50.58 49.76 50.17 16.30 0.998 I1-D15 49.21 49.86 49.54 49.54 16.10 0.985 I1-D28 46.81 45.69 50.49 47.66 15.49 0.948 I3-D7 49.06 49.68 51.74 50.16 16.04 0.997 I3-D15 42.41 48.50 45.83 45.58 12.45 0.906 I3-D28 42.15 42.91 44.86 43.31 14.07 0.861 I5-D7 47.18 49.20 51.34 49.24 16.00 0.979 I5-D15 35.11 39.06 42.54 38.90 12.64 0.774 I5-D28 17.71 27.80 19.57 21.69 7.70 0.431 表 4 擬合值與實驗值對比
Table 4. Comparison between analysis results and experimental results
Reference Sample Practical reduced value Formula reduced value Reference Sample Practical reduced value Formula reduced value This paper I0-D0 1.000 1.000 Lin et al.
(25 ℃)[25]I1-D28 0.949 0.947 I1-D7 0.998 0.994 I2-D28 0.876 0.905 I1-D15 0.985 0.979 I3-D28 0.832 0.820 I1-D28 0.948 0.947 Hao et al.
(Nature corrosion)[26]I1-D28 0.950 0.947 I3-D7 0.997 0.981 I2-D28 0.880 0.905 I3-D15 0.906 0.929 I3-D28 0.870 0.820 I3-D28 0.861 0.820 Liu et al.[27] I1-D28 0.948 0.947 I5-D7 0.979 0.933 I1-D42 0.922 0.907 I5-D15 0.774 0.778 I2-D28 0.879 0.905 I5-D28 0.431 0.462 I2-D42 0.821 0.831 I3-D28 0.810 0.820 I3-D42 0.755 0.682 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Peng H D, Liu D W, Dai B, et al. Experimental research on load-shear performance of interface between new and old concrete with corroded planting bar. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(1): 23彭懷德, 劉敦文, 戴兵, 等. 銹蝕植筋下新老混凝土面壓剪試驗研究. 工程科學學報, 2018, 40(1):23 [2] Shi J J, Sun W, Geng G Q. Steel corrosion in simulated concrete pore solutions using a galvanostatic pulse method. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(6): 727施錦杰, 孫偉, 耿國慶. 恒電流脈沖法研究鋼筋在模擬混凝土孔溶液中的腐蝕行為. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(6):727 [3] Vera R, Villarroel M, Carvajal A M, et al. Corrosion products of reinforcement in concrete in marine and industrial environments. Mater Chem Phys, 2009, 114(1): 467 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.09.063 [4] Shi J J, Sun W, Geng G Q, et al. Corrosion resistance of fine-grained rebar in simulated concrete pore solutions by means of electrochemical methods. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2011, 33(12): 1471施錦杰, 孫偉, 耿國慶, 等. 電化學方法研究混凝土模擬液中細晶粒鋼的耐蝕性. 北京科技大學學報, 2011, 33(12):1471 [5] Zhu Y X, Zhu X C, Luo D K, et al. Influences of electrochemical desalination on the behavior of reinforced concrete. Port Waterway Eng, 2002(5): 8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2002.05.003朱雅仙, 朱錫昶, 羅德寬, 等. 電化學脫鹽對鋼筋混凝土性能的影響. 水運工程, 2002(5):8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2002.05.003 [6] Xu J Z, Ding Z, Xing F. Research status of electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) on steel reinforced concrete. Concrete, 2008(9): 22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2008.09.008徐建芝, 丁鑄, 邢峰. 鋼筋混凝土電化學脫鹽修復技術研究現狀. 混凝土, 2008(9):22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2008.09.008 [7] Guo Y X. Study on Electrochemical Chloride Extraction and Post Performance of Reinforced Concrete [Dissertation]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2010郭育霞. 鋼筋混凝土電化學除氯及除氯后性能研究[學位論文]. 大連: 大連理工大學, 2010 [8] Glass G K, Buenfeld N R. The inhibitive effects of electrochemical treatment applied to steel in concrete. Corros Sci, 2000, 42(6): 923 doi: 10.1016/S0010-938X(99)00121-3 [9] Liu Y, Du R G, Lin C J. Progress in electrochemical treatment applied to reinforced concrete. Corros Sci Prot Technol, 2008, 20(2): 125劉玉, 杜榮歸, 林昌健. 鋼筋混凝土結構的電化學處理及其研究進展. 腐蝕科學及防護技術, 2008, 20(2):125 [10] Gao X J, Zheng X M, Yang Y Z. Influence of electrochemical parameters on chloride extraction efficiency. J Shenyang Univ Technol, 2010, 32(5): 579高小建, 鄭秀梅, 楊英姿. 電化學參數對混凝土除氯效率的影響. 沈陽工業大學學報, 2010, 32(5):579 [11] Zhu P, Zheng L, Wang X X, et al. Parameters optimization of electrochemical chloride extraction and exploratory research on its engineering application. China Concr Cem Prod, 2010(2): 4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2010.02.002祝頻, 鄭靚, 王新祥, 等. 電化學除鹽工藝參數優化及工程應用探索. 混凝土與水泥制品, 2010(2):4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2010.02.002 [12] Rodrigo de Almeida Souza L, de Medeiros M H F, Pereira E, et al. Electrochemical chloride extraction: Efficiency and impact on concrete containing 1% of NaCl. Constr Build Mater, 2017, 145: 435 doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.010 [13] Guo Y X, Gong J X. Study on electrochemical chloride extraction of reinforced concrete. J Taiyuan Univ Technol, 2011, 42(6): 588郭育霞, 貢金鑫. 鋼筋混凝土電化學除氯的試驗研究. 太原理工大學學報, 2011, 42(6):588 [14] Nguyen T H, Nguyen T A, Le V K, et al. Effect of electrochemical chloride extraction treatment on the corrosion of steel rebar in chloride contaminated mortar. Anti-Corros Methods Mater, 2016, 63(5): 377 doi: 10.1108/ACMM-12-2014-1473 [15] Lei Z H, Qu F, Sun H R, et al. Research on electrochemical chloride extraction of reinforced concrete structures. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2018, 37(9): 2834雷智昊, 屈鋒, 孫浩然, 等. 鋼筋混凝土結構電化學除氯研究. 硅酸鹽通報, 2018, 37(9):2834 [16] Ihekwaba N M, Hope B B, Hansson C M. Pull-out and bond degradation of steel rebars in ECE concrete. Cem Concr Res, 1996, 26(2): 267 doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00210-3 [17] Zheng X M, Li G J, Zhi X L. Effect of electrochemical chloride extraction on adhesion strength between steel bars and concrete. Concrete, 2011(6): 46鄭秀梅, 李廣軍, 支秀蘭. 電化學除鹽對鋼筋與混凝土間力的影響. 混凝土, 2011(6):46 [18] Chang J J. Bond degradation due to the desalination process. Constr Build Mater, 2003, 17(4): 281 doi: 10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00113-7 [19] Buenfeld N R, Broomfield J P. Influence of electrochemical chloride extraction on the bond between steel and concrete. Mag Concr Res, 2000, 52(2): 79 doi: 10.1680/macr.2000.52.2.79 [20] Orellan J C, Escadeillas E, Arliguie G. Electrochemical chloride extraction: efficiency and side effects. Cem Concr Res, 2004, 34(2): 227 doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.07.001 [21] Liang Y, Luo X Y, Xiao X Q, et al. Experimental study on bond-slip performance of corroded reinforced concrete. Ind Constr, 2012, 42(10): 95梁巖, 羅小勇, 肖小瓊, 等. 銹蝕鋼筋混凝土黏結滑移性能試驗研究. 工業建筑, 2012, 42(10):95 [22] Yuan G L, Guo C, Lv Z T. Experimental study on bond property of reinforced concrete at high temperatures. Ind Constr, 2006, 36(2): 57 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8993.2006.02.017袁廣林, 郭操, 呂志濤. 高溫下鋼筋混凝土黏結性能的試驗與分析. 工業建筑, 2006, 36(2):57 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8993.2006.02.017 [23] Zhou Z J, Huo J S, Jin B. Experimental study on bond behavior and damage mechanism analysis of reinforcing steel to concrete interface after elevated temperature. J Exp Mech, 2018, 33(2): 209 doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-16-283周子健, 霍靜思, 金寶. 高溫后鋼筋與混凝土黏結性能試驗與損傷機理分析. 實驗力學, 2018, 33(2):209 doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-16-283 [24] Wang X L, Zha X X, Zhang X C. Bond behavior of FRP rebar and concrete at elevated temperature. J Harbin Inst Technol, 2013, 45(6): 8王曉璐, 查曉雄, 張旭琛. 高溫下FRP筋與混凝土的黏結性能. 哈爾濱工業大學報, 2013, 45(6):8 [25] Lin H, Li Y, Yaqiang Li Y Q. A study on the deterioration of interfacial bonding properties of chloride-contaminated reinforced concrete after electrochemical chloride extraction treatment. Constr Build Mater, 2019, 197: 228 doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.196 [26] Hao T Y, Lin H, Li Y, et al. Effects of electrochemical chloride extraction on the bonding properties of corroded reinforced concrete by the anode of magnesium phosphate cement bonding carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP). IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng, 2019, 544: 012031 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/544/1/012031 [27] Liu B. Study on chloride distribution and bonding properties of concrete structures after Electrochemical chloride extraction [Dissertation]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2008劉斌. 砼結構電化學除鹽離子分布及黏結性能研究[學位論文]. 煙臺: 煙臺大學, 2008 -




 下載:
下載: