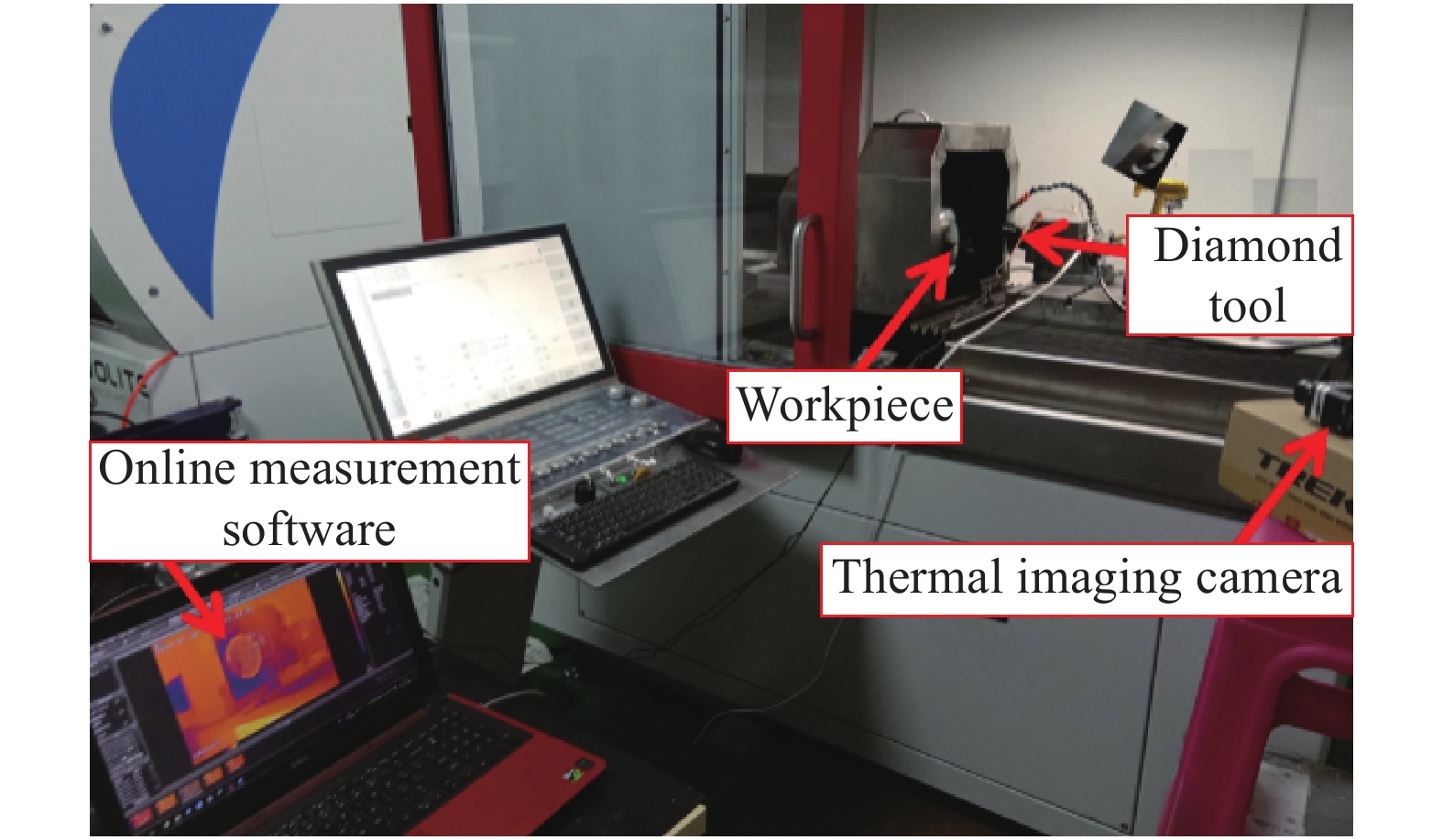
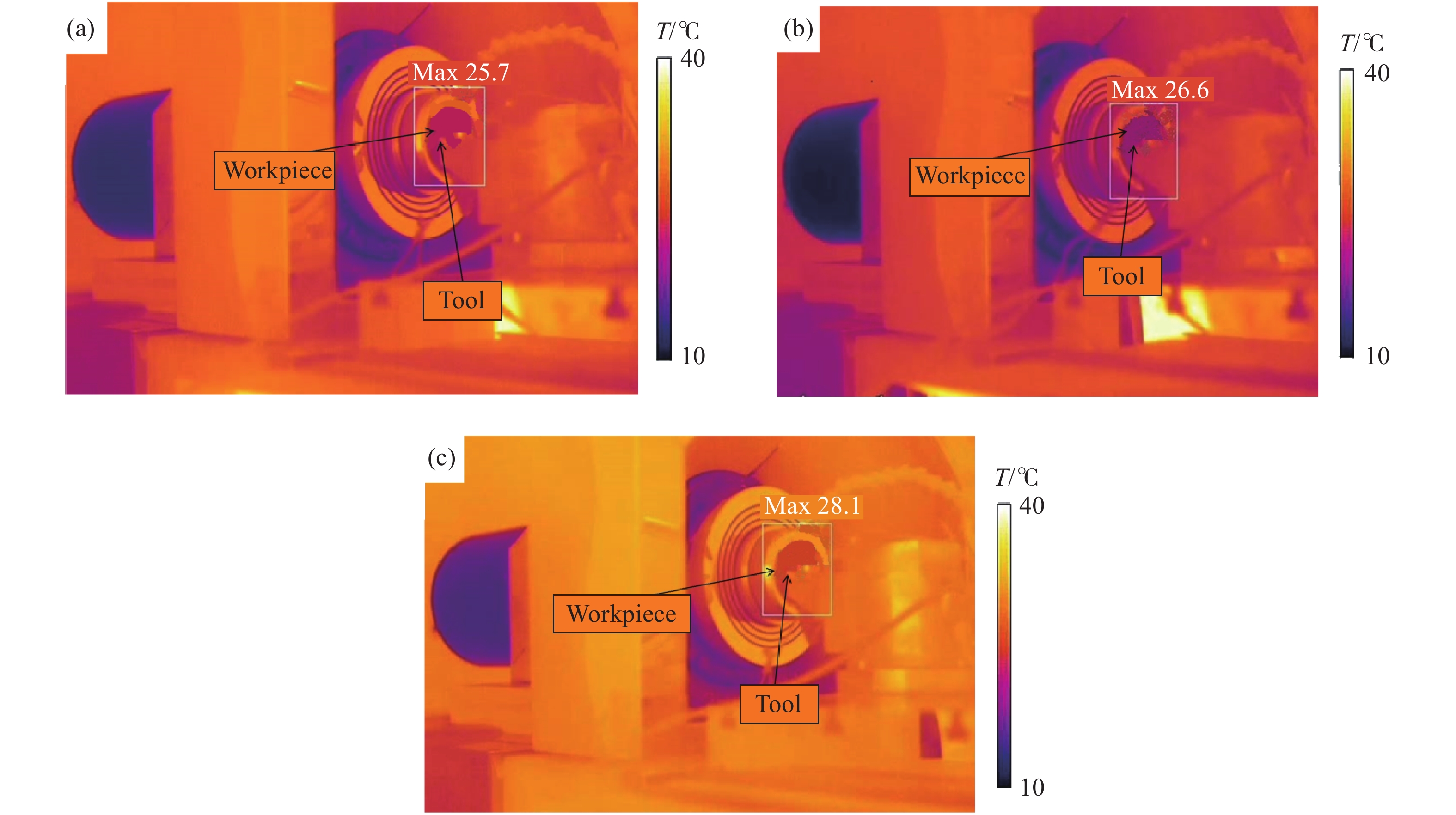
Modeling and experimental analysis of micro-cutting temperature on single crystal germanium
-
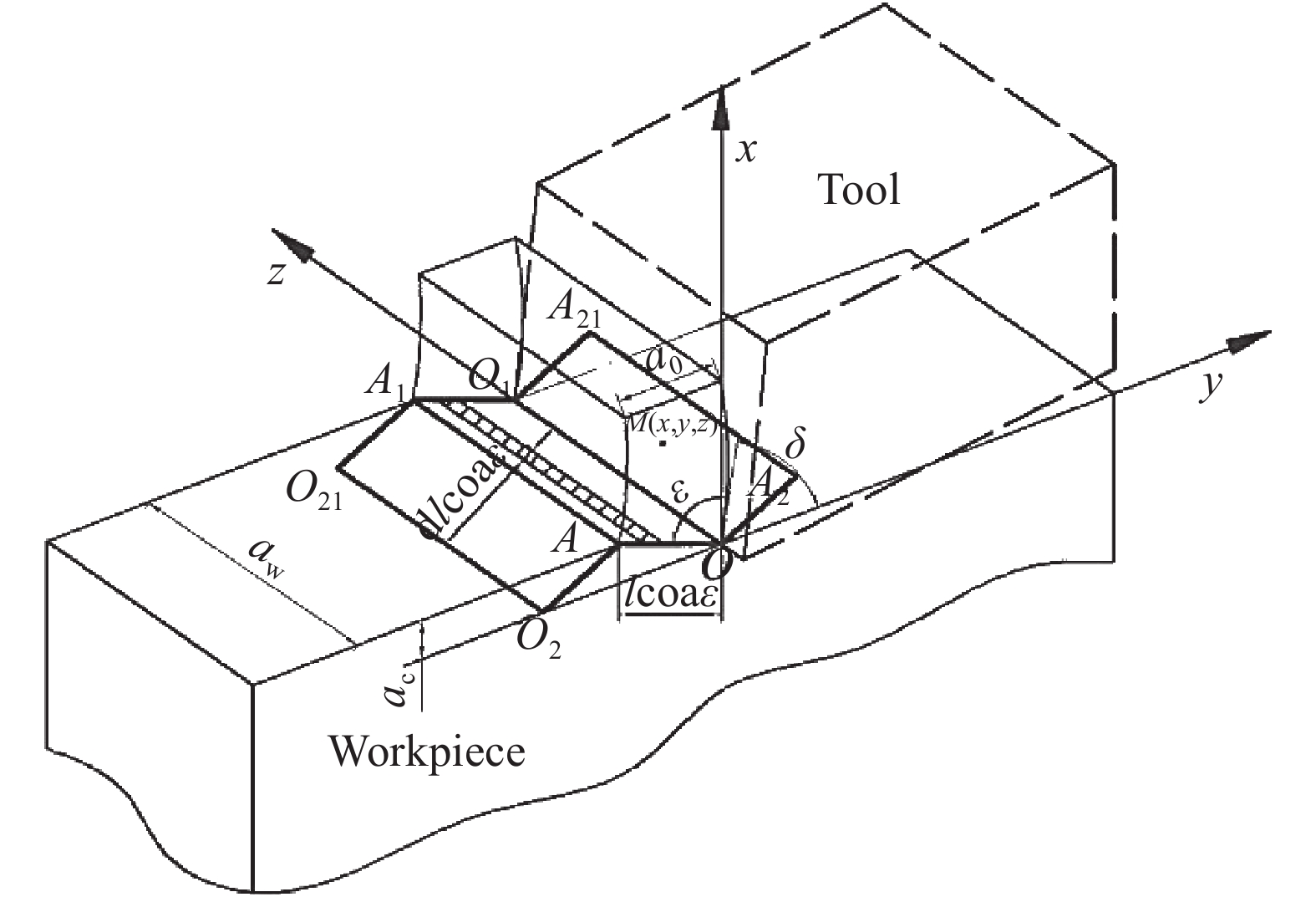
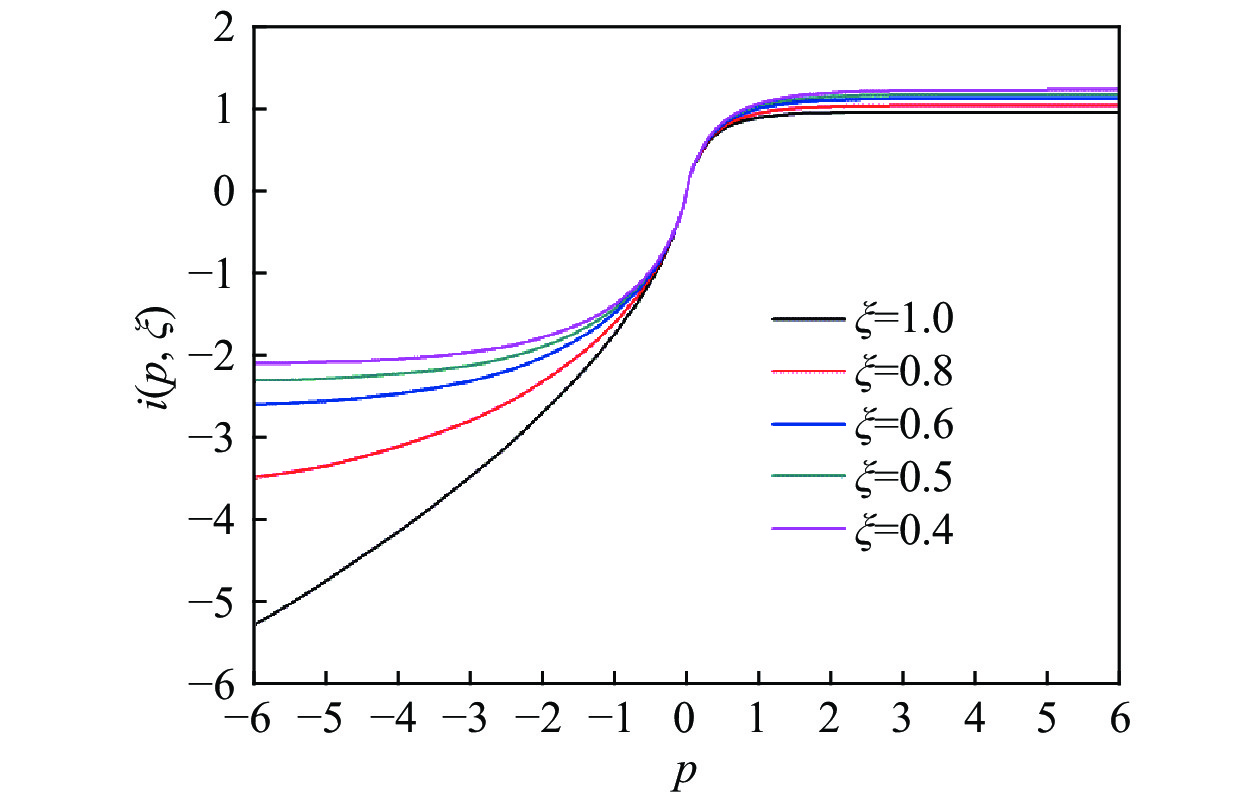
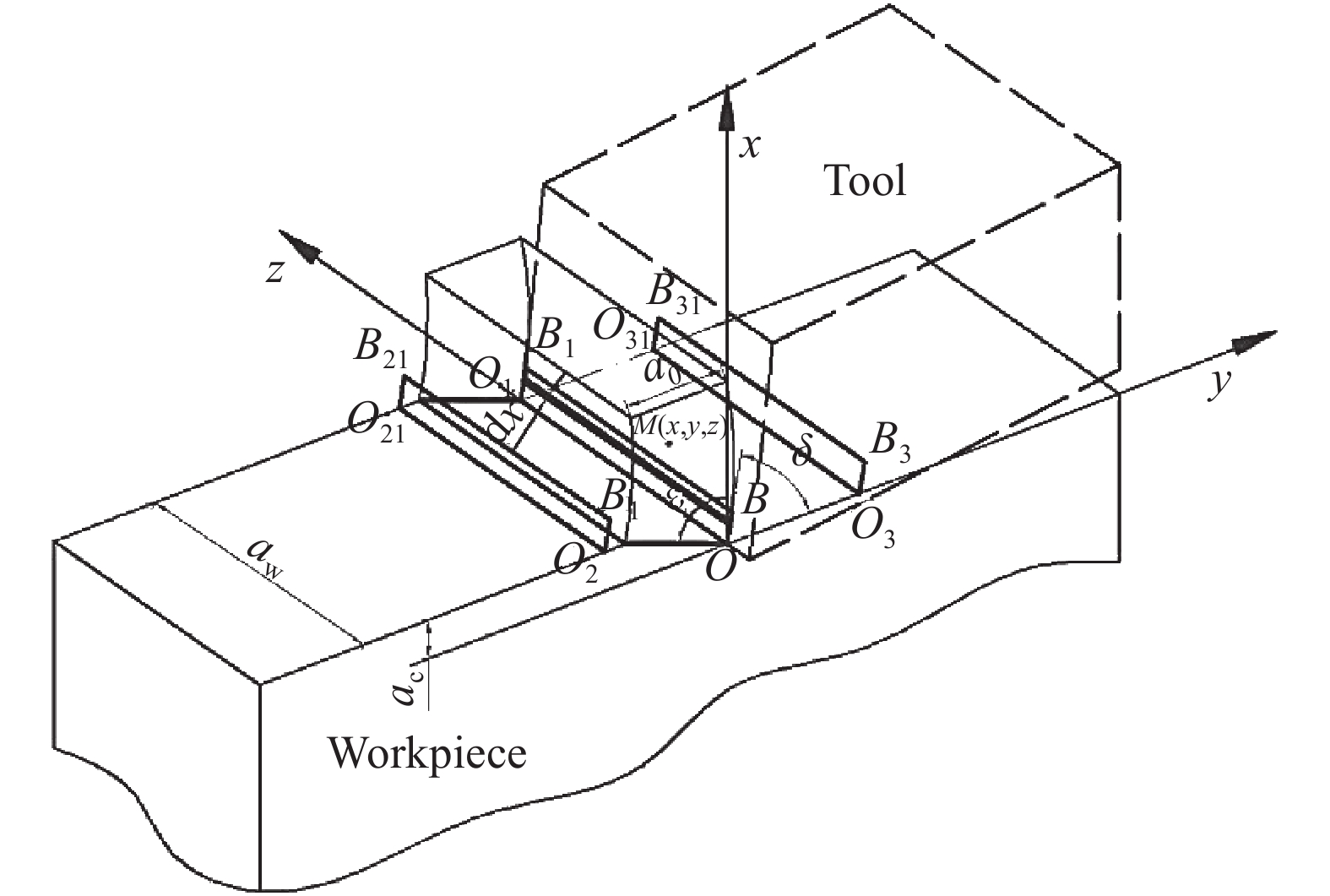
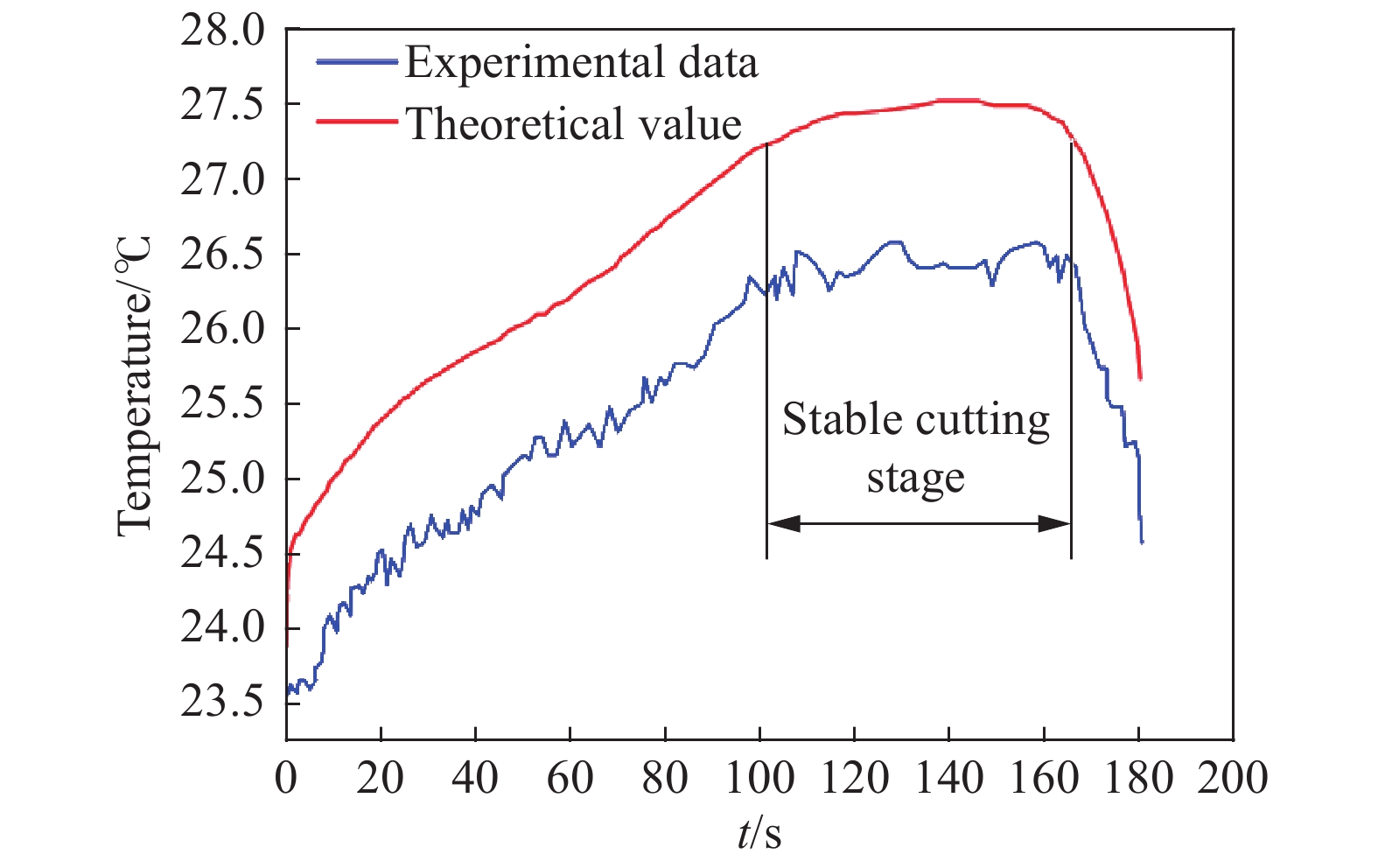
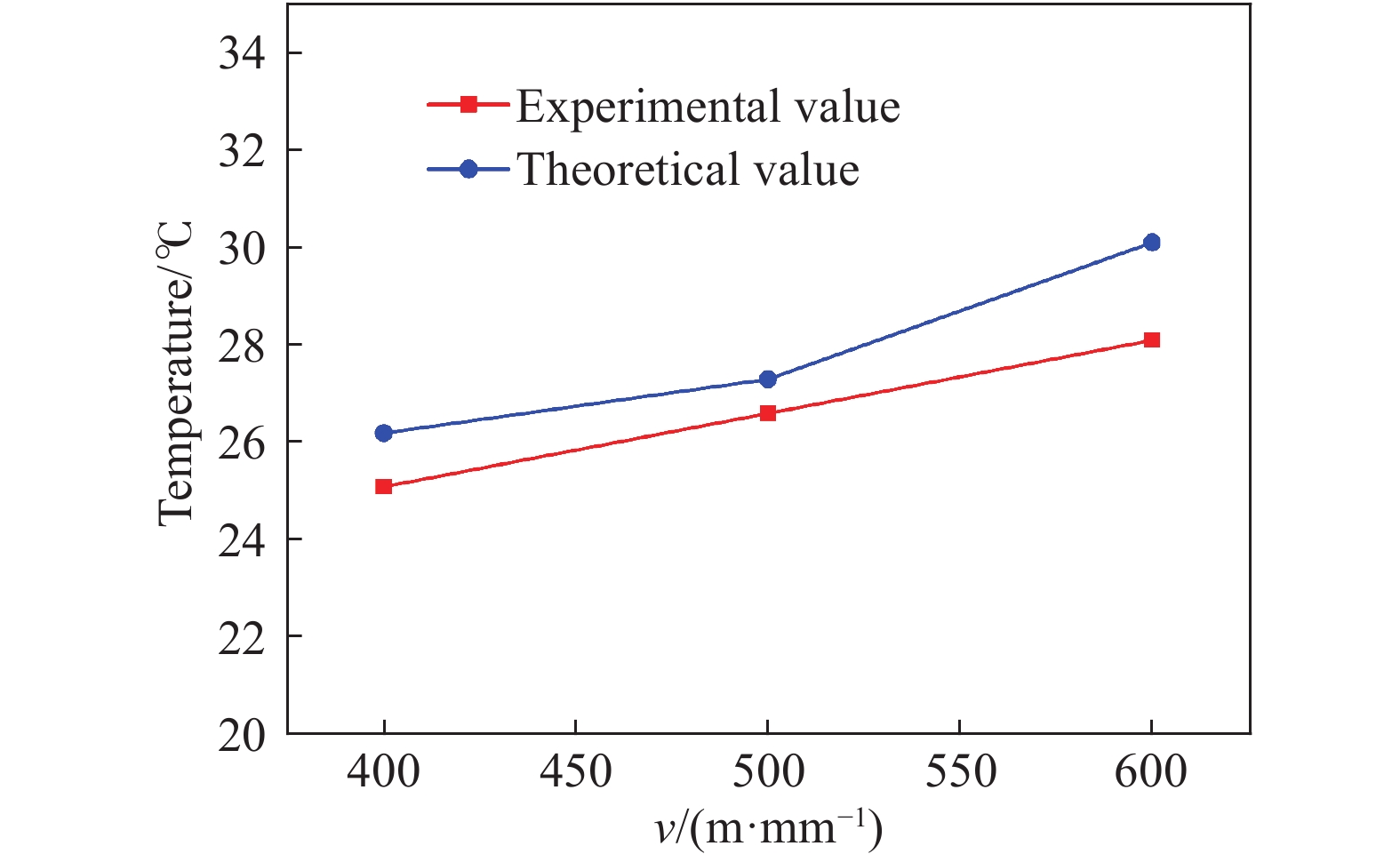
摘要: 針對單晶鍺微切削熱傳導問題,采用移動熱源法分別建立了在剪切滑移面熱源和前刀面摩擦熱源作用下單晶鍺的微切削溫升理論模型,計算了單晶鍺三種切削速度下的最高切削溫度,同時以同類硬脆性材料單晶硅的切削溫度對此模型進行了驗證。通過單點金剛石車削實驗,利用紅外熱像儀對單晶鍺微切削過程中的溫度進行了在線測量。實驗測量結果與模型計算結果對比發現,不同切削速度下,單晶鍺的最高切削溫度變化趨勢一致,切削速度越大溫度越高,其相對誤差在2.56%~6.64%之間;單晶硅的最高切削溫度相對誤差為3.84%。模型能夠對單晶鍺及同類硬脆性材料的溫度場進行較準確的預測,為研究其熱效應提供進一步理論支持。Abstract: Single crystal germanium is an important infrared optical material, which is widely used in defense industry, microelectronics, and other fields. It is extremely difficult to achieve the required surface quality by conventional processing methods due to its hardness and brittleness. Practically, single-point diamond tool is used for micro-cutting. During the micro-cutting process of single crystal germanium, the change of cutting temperature leads to increased tool wear and material surface hardening, which results in poor surface quality and also reduces processing accuracy. Therefore, analyzing the micro-cutting temperature distribution of single crystal germanium has become the key to better understanding its heat transfer mechanism and for improving product quality and efficiency. Aiming to analyze heat transfer mechanism of single crystal germanium micro-cutting, the moving heat source method was used. It establishes the theoretical model with temperature rise during micro-cutting of single crystal germanium under the action of the heat source of the shear slip surface and the friction heat source of the rake face and the chip, respectively. The maximum cutting temperature of germanium at three cutting speeds, and the model was verified with the cutting temperature of homogeneous hard and brittle material single crystal silicon. Through a single-point diamond turning experiment, an infrared thermal imager was used to measure the temperature of the single crystal germanium micro-cutting process online. When experimental measurement results and the model calculation results are compared, it revealed that the maximum cutting temperature of single crystal germanium has displayed same trend under different cutting speeds, which is that the cutting temperature is directly proportional to the cutting speed. The relative error is found to be between 2.56% and 6.64%. The relative error of the maximum cutting temperature is 3.84%. The model can accurately predict the temperature field of single crystal germanium and also for similar hard and brittle materials, providing further theoretical support for analyzing its thermal effects.
-
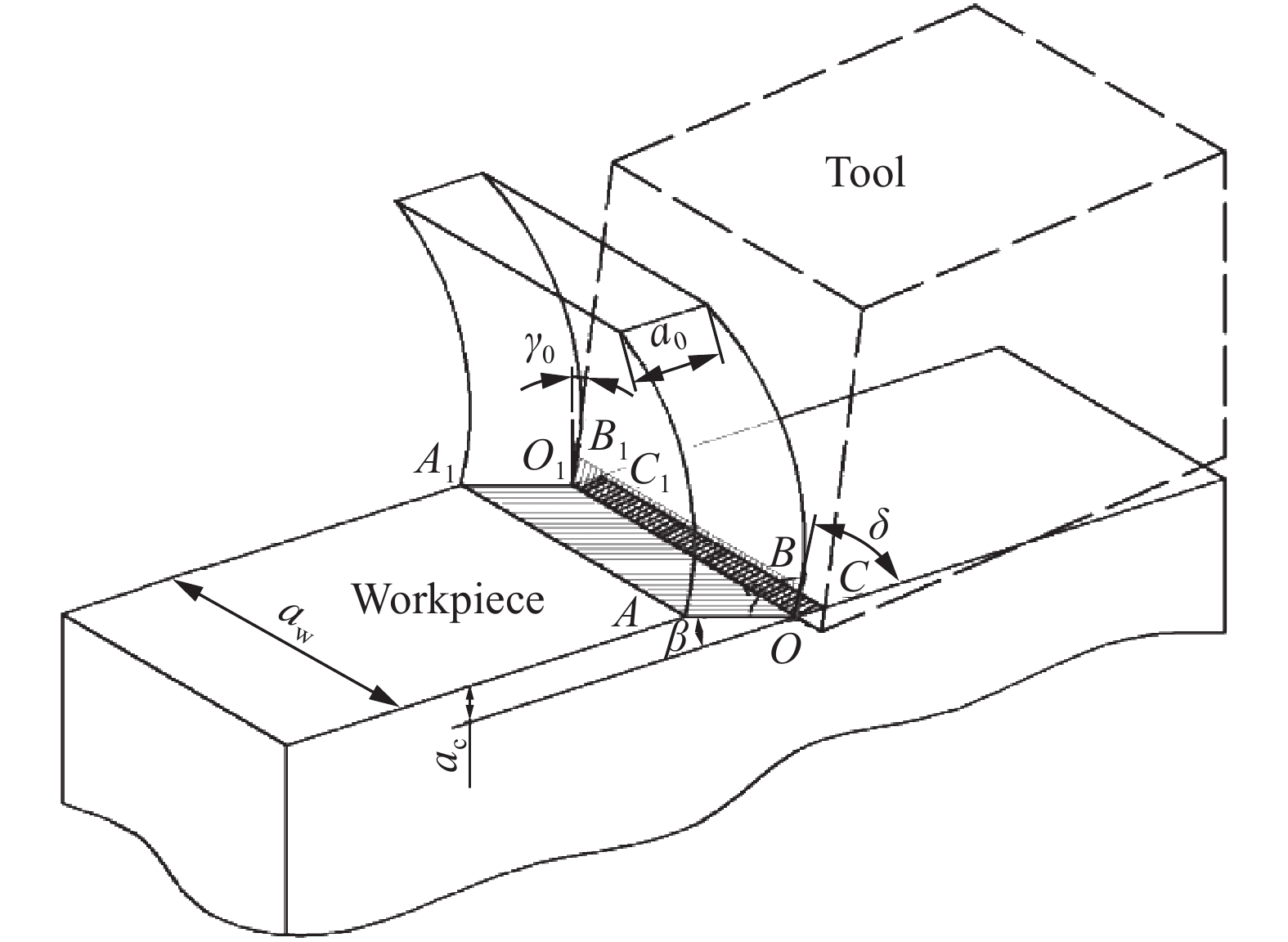
表 1 工件材料及切削參數[22]
Table 1. Workpiece material and cutting parameters
Parameter Value Thermal conductivity/(J·cm?1·s?1·℃?1) 0.013 Density/(g·cm?3) 5.327 Specific heat/(J·g?1·℃?1) 0.31 Shear angle/(°) 30 Wedge angle/(°) 80 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Chae J, Park S S, Freiheit T. Investigation of micro-cutting operations. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2006, 46(3-4): 313 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.05.015 [2] Zhang Z M, Cheng Q, Wang Z C, et al. Nano/Microscale Heat Transfer. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016張卓敏, 程強, 王志超, 等. 微納尺度傳熱. 北京: 清華大學出版社, 2016 [3] Liang Y C, Yang K, Bai Q S, et al. Modeling and experimental analysis of microburr formation considering tool edge radius and tool-tip breakage in microend milling. J Vac Sci Technol B, 2009, 27(3): 1531 doi: 10.1116/1.3046147 [4] Yang X J, Zhao B, Luo L. Experimental research on brittle-ductile transition of single crystal germanium based on nano-scratch. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2018, 47(10): 3228楊曉京, 趙彪, 羅良. 基于納米劃痕的單晶鍺脆塑轉變實驗研究. 稀有金屬材料與工程, 2018, 47(10):3228 [5] Krahmer D M, Hameed S, Egea A J S, et al. Wear and MnS layer adhesion in uncoated cutting tools when dry and wet turning free-cutting steels. Metals, 2019, 9(5): 556 doi: 10.3390/met9050556 [6] Tao W Q. Numerical Heat Transfer. 2nd Ed. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, 2001陶文銓. 數值傳熱學. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大學出版社, 2001 [7] Ulutan D, Lazoglu I, Dinc C. Three-dimensional temperature predictions in machining processes using finite difference method. J Mater Process Technol, 2009, 209(2): 1111 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.03.020 [8] Dai Y J, Wu X H, Tao W Q. Weighted least-squares collocation method (WLSCM) for 3-D heat conduction problems in irregular domain. J Eng Thermophys, 2011, 32(7): 1173戴艷俊, 吳學紅, 陶文銓. 三維不規則區域熱傳導問題無網格方法的數值模擬. 工程熱物理學報, 2011, 32(7):1173 [9] Hou Z B, He S J, Li S X. Heat Conduction Within a Solid. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, 1984侯鎮冰, 何紹杰, 李恕先. 固體熱傳導. 上海: 上海科學技術出版社, 1984 [10] Dessoly V, Melkote S N, Lescalier C. Modeling and verification of cutting tool temperatures in rotary tool turning of hardened steel. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2004, 44(14): 1463 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.05.007 [11] Tanveer A, Marla D, Kapoor S G. A thermal model to predict tool temperature in machining of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with an atomization-based cutting fluid spray system. J Manuf Sci Eng, 2017, 139(7): 071016 doi: 10.1115/1.4036123 [12] Zhang J J, Liu Z Q, Du J. Modelling and prediction of tool-chip interface temperature in hard machining of H13 steel with PVD coated tools. Int J Mach Mach Mater, 2015, 17(5): 381 [13] Mamedov A, Lazoglu I. Thermal analysis of micro milling titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. J Mater Process Technol, 2016, 229: 659 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.10.019 [14] Silva G C, Malveira B M, Carneiro J R G, et al. Wear and thermal analysis of WC inserts in turning operations by fuzzy modeling. Procedia CIRP, 2017, 58: 523 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.266 [15] Guo K W, Dai S J, Yue J F. An analytical solution for the temperature field with variable thermal conductivity. J Eng Thermophys, 2017, 38(8): 1724郭開文, 代少軍, 岳建鋒. 一類變導熱系數下三維溫度場解析模型. 工程熱物理學報, 2017, 38(8):1724 [16] Zhang S J, Liu Z Q, Liu J G. Calculating transient temperature distribution of single-coated tool in high speed cutting. J Mech Eng, 2010, 46(1): 187 doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.01.187張士軍, 劉戰強, 劉繼剛. 用解析法計算高速切削單涂層刀具瞬態溫度分布. 機械工程學報, 2010, 46(1):187 doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.01.187 [17] Wang S F, An C H, Zhang F H, et al. Thermal field distribution in fly-cutting of KDP crystal and its influence on chip morphology. Opt Precis Eng, 2016, 24(8): 1948 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1948汪圣飛, 安晨輝, 張飛虎, 等. 磷酸二氫鉀晶體飛切過程中溫度場的分布及其對切屑形貌的影響. 光學精密工程, 2016, 24(8):1948 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1948 [18] Zhan G, He L, Jiang H W, et al. Performance comparison and prediction of cutting energy of new cemented carbide micro-pit turning tool. Chin J Eng, 2017, 39(8): 1207占剛, 何林, 蔣宏婉, 等. 新型硬質合金微坑車刀切削能對比研究與預測. 工程科學學報, 2017, 39(8):1207 [19] Yue C X, Du J B, Liu X L, et al. Modeling research on transient temperature field of rake face on end mills considering time-varying heat intensity and time-varying distribution ratio. J Mech Eng, 2019, 55(9): 206 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.09.206岳彩旭, 都建標, 劉獻禮, 等. 考慮時變性熱強度和時變性熱量分配比的銑刀前刀面瞬態溫度場建模研究. 機械工程學報, 2019, 55(9):206 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.09.206 [20] Hu C, Zhuang K J, Weng J, et al. Three-dimensional analytical modeling of cutting temperature for round insert considering semi-infinite boundary and non-uniform heat partition. Int J Mech Sci, 2019, 155: 536 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.03.019 [21] Zhang H J. Non-quasi-steady analysis heat conduction from a moving heat source (Ⅲ). J Eng Thermophys, 1991, 12(3): 294張洪濟. 移動熱源熱傳導的非準穩態分析(Ⅲ). 工程熱物理學報, 1991, 12(3):294 [22] Wakaki M, Keiei K, Shibuya T. Physical Properties and Data of Optical Materials. Translated by Zhou H X, Cheng Y F. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010Wakaki M, Keiei K, Shibuya T. 光學材料手冊. 周海憲, 程云芳, 譯. 北京: 化學工業出版社, 2010 [23] Xia X G, Zhang Y. Effects of germanium single-crystal anisotropy in SPDT. New Technol New Process, 2014(2): 110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5311.2014.02.034夏曉光, 張宇. 鍺單晶的各向異性對單點金剛石切削的影響. 新技術新工藝, 2014(2):110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5311.2014.02.034 [24] Sawangsri W, Cheng K. Investigation on partitioned distribution of cutting heat and cutting temperature in micro cutting. Int J Mech Manuf Syst, 2016, 9(2): 173 [25] Komanduri R, McGee J, Thompson R A, et al. On a methodology for establishing the machine tool system requirements for high-speed/high-throughput machining. J Eng Ind, 1985, 107(4): 316 doi: 10.1115/1.3186004 [26] Jiang F L, Liu Z Q, Yang F Z, et al. Investigations on tool temperature with heat conduction and heat convection in high-speed slot milling of Ti6Al4V. In J Adv Manuf Technol, 2018, 96(5-8): 1847 doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-1733-3 -




 下載:
下載: