Preparation of iron oxide red by sinking iron slag in zinc smelting hematite process
-
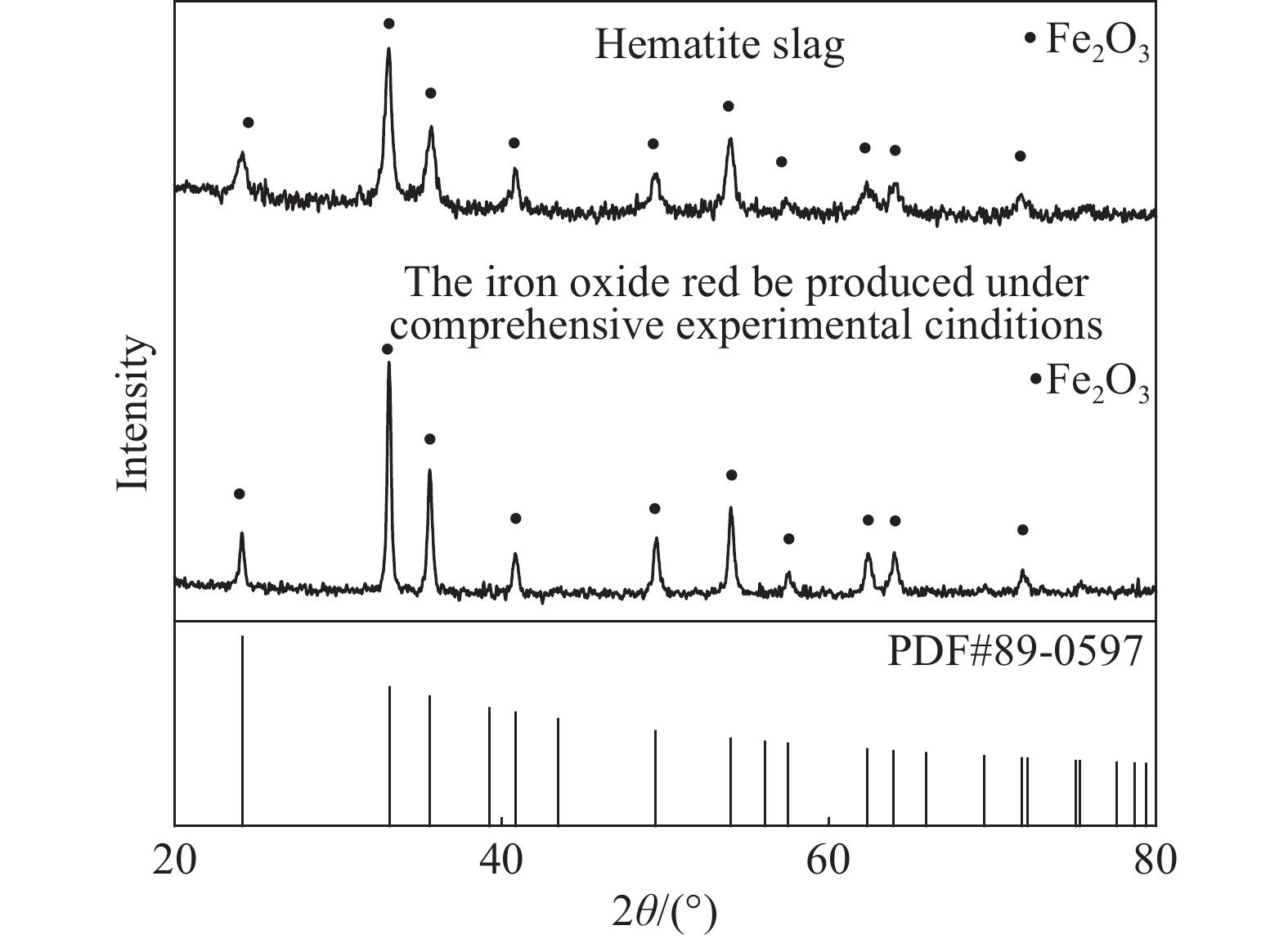
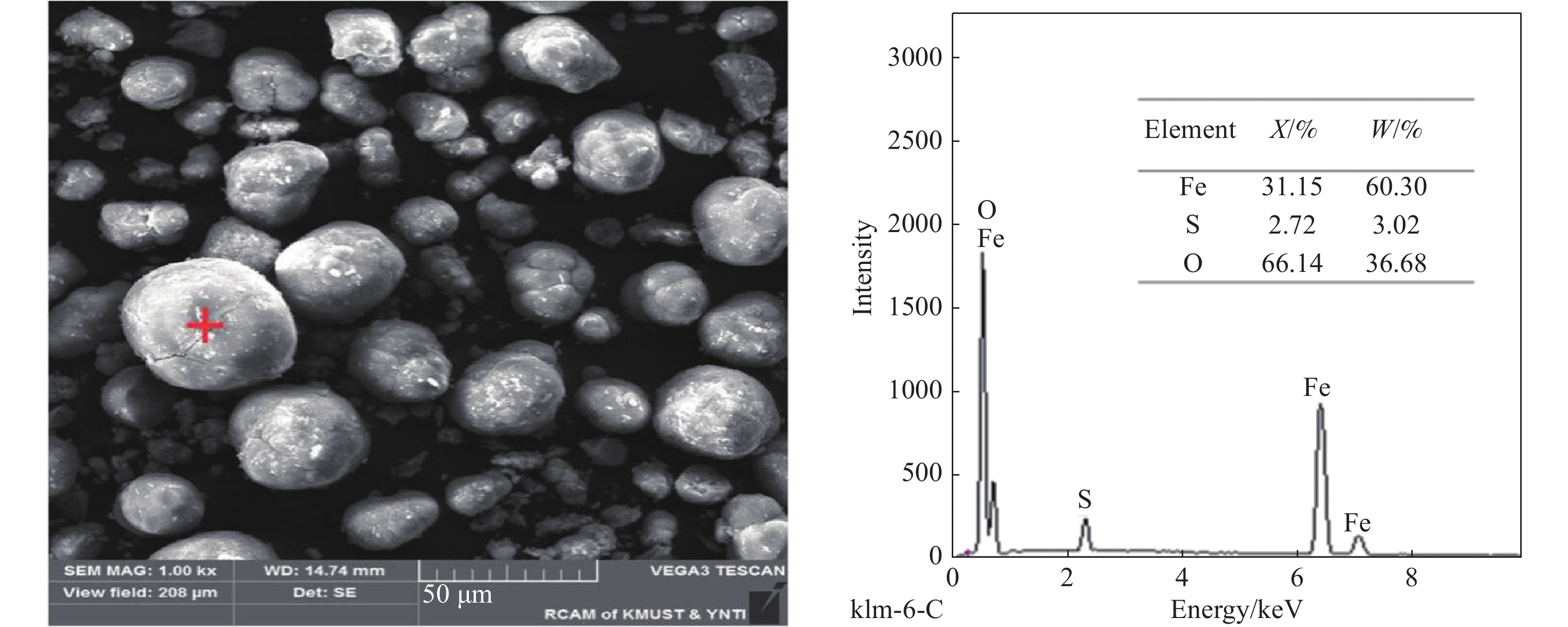
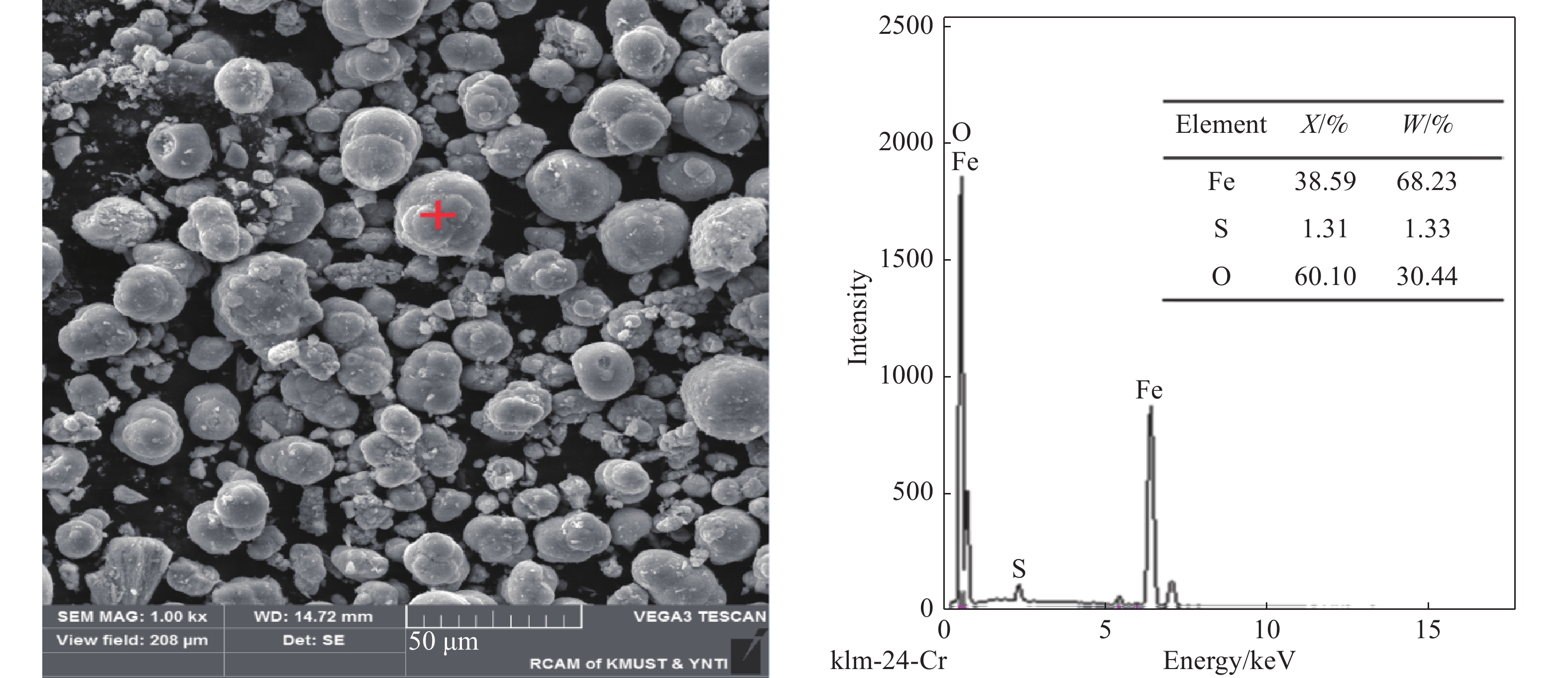
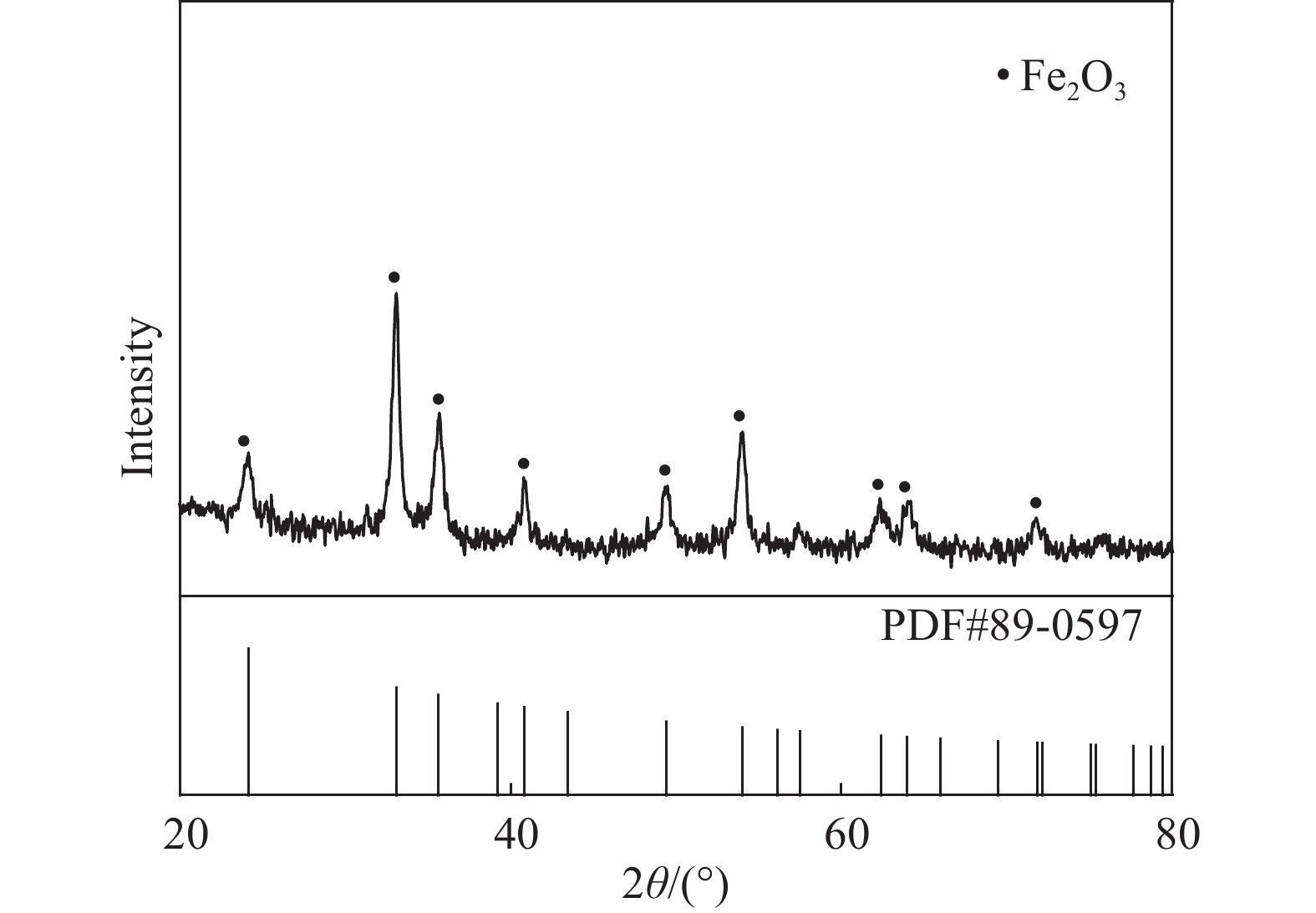
摘要: 針對赤鐵礦渣中存在雜質,影響其綜合回收利用的問題,開展赤鐵礦渣高溫水熱法脫雜,制備鐵紅的研究。研究了不同酸度、溫度、時間和液固比條件,對鐵紅產品中鐵、鋅、硫含量以及鋅、硫脫除率和鐵溶出率的影響。實驗結果表明:pH值為1,溫度220 ℃,保溫時間3 h,液固比6∶1,轉速400 r·min?1條件下,鐵紅產品中鐵質量分數由58.66%上升為66.83%;赤褐鐵類礦物含鐵由占總鐵質量分數94.05%,上升為97.79%;硫質量分數由2.96%下降至0.82%;鋅質量分數由1.03%下降至0.18%。經X射線衍射檢測,與赤鐵礦渣相比,鐵紅產品中氧化鐵信號峰值提高,雜峰減少。通過掃描電鏡/能量散射X射線分析,鐵紅產品表面附著的硫酸鹽等雜質經高溫水熱法處理后明顯減少;實驗前后,赤鐵礦渣與鐵紅產品顆粒形貌與大小沒有發生變化。實驗處理后的鐵紅產品經檢測,滿足國家標準氧化鐵紅含鐵量C級,水溶物和水溶性氯化物及硫酸鹽含量III型,篩余物2型,105 ℃揮發物V2型,來源a型標準。Abstract: In wet zinc smelting process, iron slag generated by hematite process has high iron content, uniform particle size, and stable thermodynamics, which have evident advantages. However, impurities are present in hematite slag, including jarosite, basic ferric sulfate, adsorptive salts, and small amounts of iron carbonate and iron silicate, that limit its comprehensive recovery and utilization. In view of these impurities in hematite slag, in this study, iron oxide red was prepared using a high-temperature hydrothermal method. The effects of different acidity levels, temperatures, preparation times, and liquid–solid ratios on the contents of iron, zinc, and sulfur were studied, as were the removal rates of zinc and sulfur and dissolution rate of iron. The experimental results show that the iron content in the iron oxide red products increases from 58.66% to 66.83% at following parameters: pH 1, temperature 220 ℃, preparation time 3 h, liquid–solid ratio 6∶1, and rotation speed 400 r·min?1. The iron content of the ferrous minerals increases from 94.05% to 97.79%, sulfur content decreases from 2.96% to 0.82%, and zinc content decreases from 1.03% to 0.18%. As determined by X-ray diffraction, compared with hematite slag, the peak value of the iron oxide signal in the iron oxide red products is higher and that of the miscellaneous peak is lower. Scanning electron microscopy analysis/energy dispersive analysis of X-rays show that the amounts of sulfate and other impurities on the surface of the iron oxide red products are significantly reduced after high-temperature hydrothermal treatment. However, the morphologies and sizes of the hematite slag and red iron oxide product particles do not change. After the experimental treatment, the iron oxide red products are determined to meet the national standard: iron oxide red content grade C, water soluble substance and water-soluble chloride and sulfate content type III, sieve residue type 2, 105 ℃ volatile type V2, source type a standard.
-
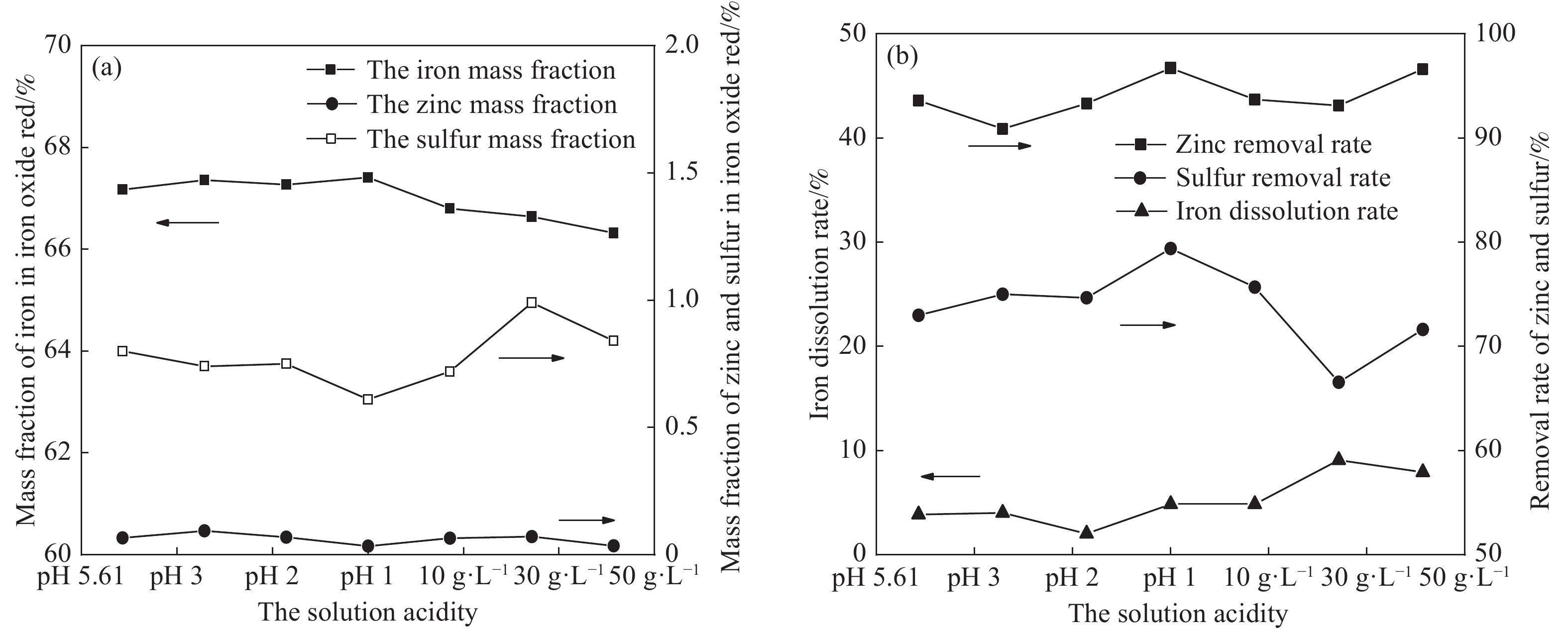
圖 2 不同酸度對鐵紅產品質量,鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率的影響。(a)鐵紅產品中鐵、鋅、硫質量分數;(b)鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率
Figure 2. Effects of different acidity levels on iron oxide red content, impurity removal rate, and iron dissolution rate: (a) iron, zinc, sulfur mass fraction in iron oxide red products; (b) removal rate of zinc and sulfur and iron dissolution rate
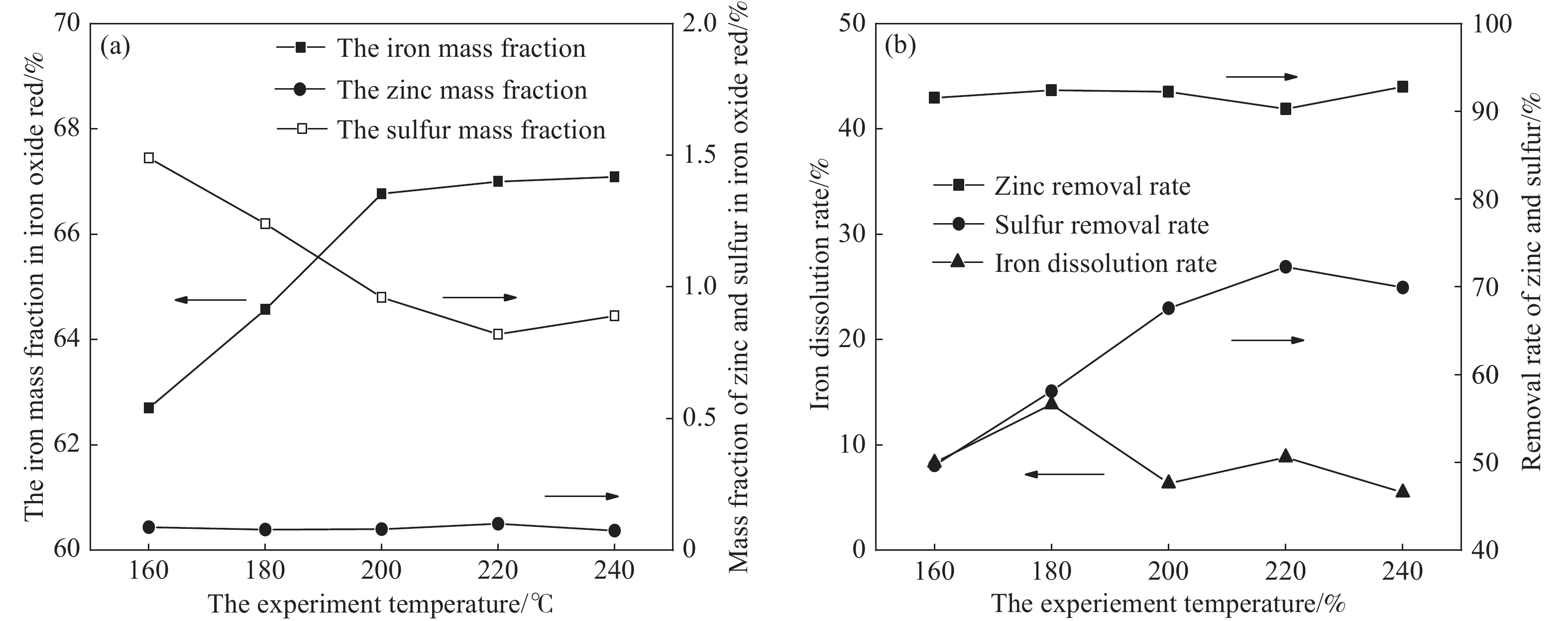
圖 4 不同溫度對鐵紅產品質量,鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率的影響。(a)鐵紅產品中鐵、鋅、硫質量分數;(b)鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率
Figure 4. Effects of different temperatures on iron oxide red product content, impurity removal rate, and iron dissolution rate: (a) iron, zinc, sulfur mass fraction in iron oxide red products; (b) removal rate of zinc and sulfur and iron dissolution rate
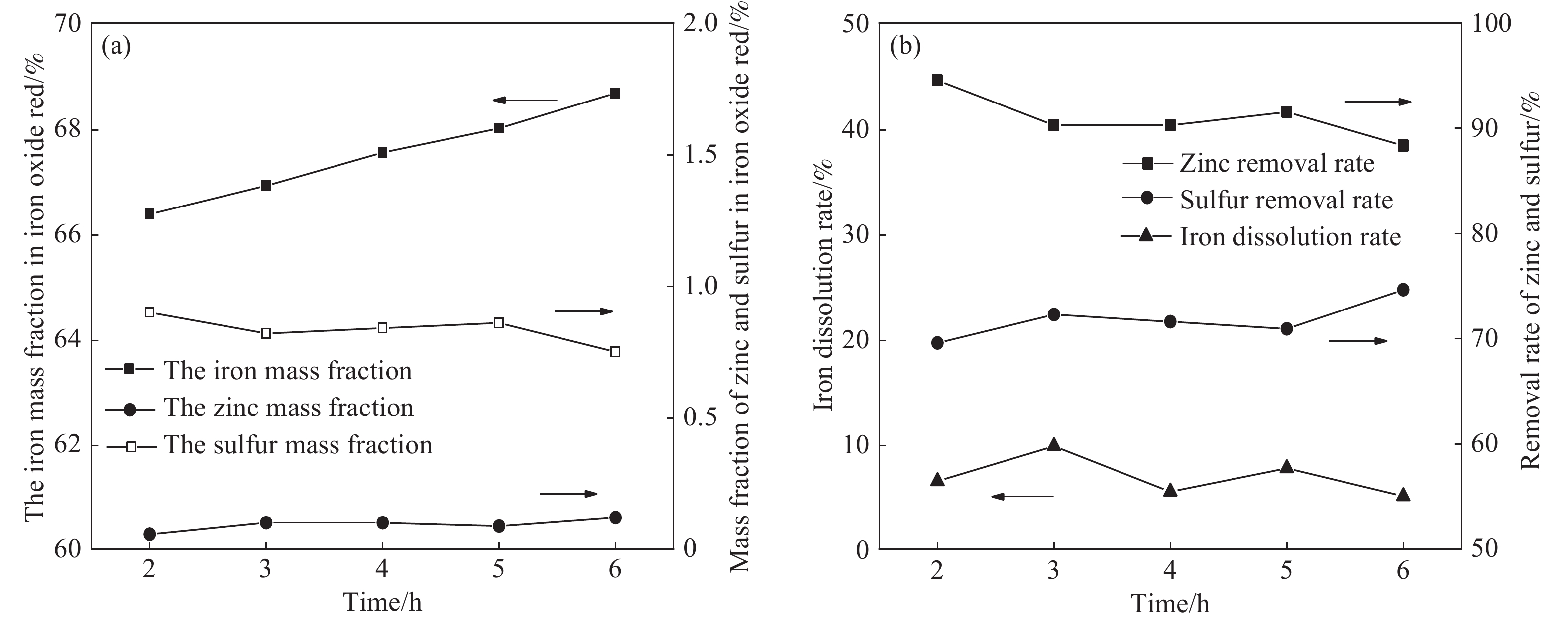
圖 5 不同反應時間對鐵紅產品質量,鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率的影響。(a)鐵紅產品中鐵、鋅、硫質量分數;(b)鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率
Figure 5. Effects of different preparation times on iron oxide red product content, impurity removal rate, and iron dissolution rate: (a) iron, zinc, sulfur mass fraction in iron oxide red products; (b) removal rate of zinc and sulfur and iron dissolution rate
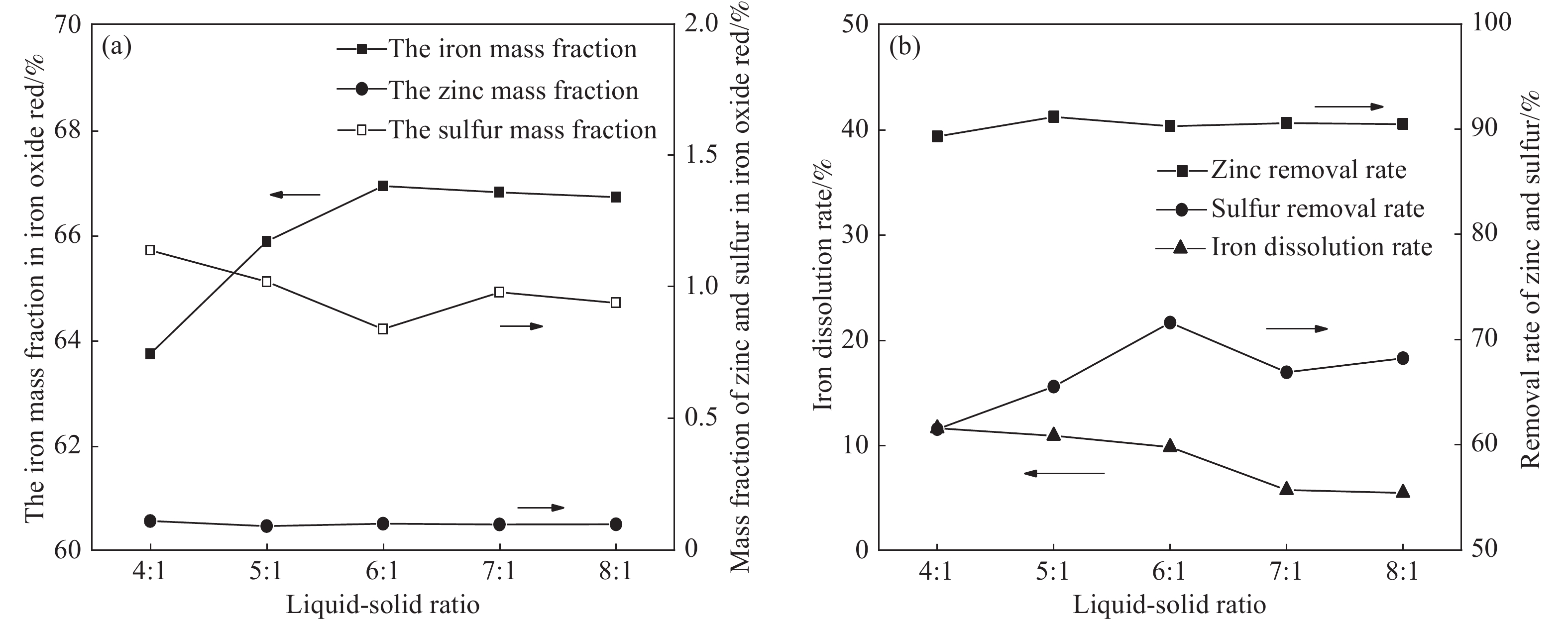
圖 6 不同液固比對鐵紅產品質量,鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率的影響。(a)鐵紅產品中鐵、鋅、硫質量分數;(b)鋅、硫脫除率以及鐵溶出率
Figure 6. Effects of different liquid–solid ratios on iron oxide red product content, impurity removal rate, and iron dissolution rate: (a) iron, zinc, sulfur mass fraction in iron oxide red products; (b) removal rate of zinc and sulfur and iron dissolution rate
表 1 赤鐵礦渣中主要元素含量(質量分數)
Table 1. Content of main elements in hematite
% Fe Zn S K Na 58.66 1.03 2.96 0.028 0.061 表 2 赤鐵礦渣中鐵物相含鐵占比(質量分數)
Table 2. Proportions of iron content in hematite slag
% Iron in magnetic iron minerals Iron in iron carbonate minerals Iron in silicate minerals Iron in sulfate minerals Iron in red brown iron minerals 1.23 0.58 1.74 2.39 94.05 表 3 赤鐵礦渣浸出毒性檢測結果
Table 3. Hematite residue leaching toxicity test results
mg·L?1 Index Fluoride Cyanide Hexavalent chromium Copper Lead Zinc Cadmium Beryllium Standard 100 5 5 100 5 100 1 0.02 Content 0.09 — — 0.253 0.084 75.7 0.045 0.0015 Index Nickel Total chromium Arsenic Selenium Barium Mercury Silver Standard 5 15 5 1 100 0.1 5 Content 0.027 0.012 0.010 0.0072 0.0066 0.0002 — 表 4 檢測最佳條件處理的鐵紅產品與赤鐵礦渣中各鐵物相含鐵質量分數占比
Table 4. Proportion of iron content in the iron phase between the iron red product and the hematite residue under the best condition
Sample types Iron in magnetic iron minerals/% Iron in iron carbonate minerals/% Iron in silicate minerals/% Iron in sulfate minerals/% Iron in red brown iron minerals/% Hematite slag 1.23 0.58 1.74 2.39 94.05 Iron red products <0.75 0.10 0.75 0.58 97.79 表 5 鐵紅產品與赤鐵礦渣中鐵,鋅,硫質量分數對比
Table 5. Comparison of zinc, iron, and sulfur mass fractions in iron oxide red products and hematite slag
% Sample types Fe Zn S Hematite slagIron 58.66 1.03 2.96 Iron oxide red products 66.83 0.18 0.82 www.77susu.com<span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> <span id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <th id="fpn9h"></th> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><strike id="fpn9h"></strike> <th id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"> <span id="fpn9h"><video id="fpn9h"></video></span> <ruby id="fpn9h"></ruby> <strike id="fpn9h"><noframes id="fpn9h"><span id="fpn9h"></span> -
參考文獻
[1] Yang J J, Ding C, Li Y X, et al. Status and analysis of comprehensive utilization of zinc slag by hydrometallurgy. World Nonferrous Met, 2011(6): 44楊建軍, 丁朝, 李永祥, 等. 濕法煉鋅渣綜合利用工藝現狀及分析. 世界有色金屬, 2011(6):44 [2] Fu Y K. Analysis of different treating technology of zinc leaching residue. Sichuan Nonferrous Met, 2003(1): 35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4079.2003.01.010付運康. 鋅浸出渣不同處理工藝淺析. 四川有色金屬, 2003(1):35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4079.2003.01.010 [3] Duan X W, Wang X W, Ye Y H. Discussion on the relationship between various processes in zinc hydrometallurgy. China Nonferrous Metall, 2016, 45(3): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2016.03.003段小維, 王新文, 冶玉花. 鋅濕法冶煉各工序之間關系的探討. 中國有色冶金, 2016, 45(3):10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2016.03.003 [4] Chen S, Kuang L C, Zhang W, et al. The influence of impurities in zinc electrolyte on energy saving of zinc electrolysis is briefly discussed // Low-carbon Development of Non-Ferrous Metal Industry— —National Non-ferrous Metal Industry Low-carbon Economy and Smelting Emissions Reduction Academic Symposium Proceedings. Nanjing, 2010: 152陳順, 匡立春, 張偉, 等. 淺談鋅電解液中雜質對鋅電解節能的影響 // 有色金屬工業低碳發展——全國有色金屬工業低碳經濟及冶煉廢氣減排學術研討會論文集. 南京, 2010: 152 [5] Zhang X J, Huang H, Dong J, et al. Influence of manganese on the electrochemical behavior of an aluminum cathode used in zinc electrowinning. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(7): 800張小軍, 黃惠, 董勁, 等. 鋅電積過程中錳元素對鋁陰極的電化學行為影響. 工程科學學報, 2018, 40(7):800 [6] Wei C, Wang J K. Theory and Application of Zinc Hydrometallurgy. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2003魏昶, 王吉坤. 濕法煉鋅理論與應用. 昆明: 云南科學技術出版社, 2003 [7] Zhang C S, Zhao T. Application of the hematite process for removing iron in the zinc hydrometallurgical production. Hunan Nonferrous Met, 2014, 30(2): 39張成松, 趙婷. 赤鐵礦除鐵法在濕法煉鋅工藝中的應用. 湖南有色金屬學報, 2014, 30(2):39 [8] Peng B, Lin D H, Liu H, et al. Alkaline leaching zinc from high iron-bearing zinc calcine after reduction roasting. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2017, 27(2): 423彭兵, 林冬紅, 劉恢, 等. 高鐵鋅焙砂還原焙燒-堿浸工藝. 中國有色金屬學報, 2017, 27(2):423 [9] Deng Z G, Wei C, Zhang F, et al. Resource utilization and hematite precipitation in zinc hydrometallurgy. Nonferrous Met Eng, 2016, 6(5): 38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2016.05.009鄧志敢, 魏昶, 張帆, 等. 濕法煉鋅赤鐵礦法除鐵及資源綜合利用新技術. 有色金屬工程, 2016, 6(5):38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2016.05.009 [10] Hu Z R, Luo J, Deng Z G, et al. Effects of zinc and iron concentration on iron-removing by hematite precipitation. Nonferrous Met Eng, 2017, 7(6): 54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2017.06.013胡智潤, 羅佳, 鄧志敢, 等. 鋅鐵離子濃度對赤鐵礦法除鐵的影響. 有色金屬工程, 2017, 7(6):54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2017.06.013 [11] Zhang Y L. Study on iron precipitation by goethite method with zinc sulfate solution. Technol Econom Guide, 2016(18): 101張應龍. 硫酸鋅溶液針鐵礦法沉鐵研究. 科技經濟導刊, 2016(18):101 [12] Ma F F. Discussion on vanadium and iron precipitation process in zinc hydrometallurgy. China Nonferrous Metall, 2017, 46(2): 19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2017.02.005馬菲菲. 濕法煉鋅浸出沉礬沉鐵工藝探討. 中國有色冶金, 2017, 46(2):19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2017.02.005 [13] Yang F, Deng Z G, Wei C, et al. Iron-removal by hematite from leaching liquor of high iron sphalerite. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2014, 24(9): 2387楊凡, 鄧志敢, 魏昶, 等. 采用赤鐵礦去除高鐵閃鋅礦浸出液中的鐵. 中國有色金屬學報, 2014, 24(9):2387 [14] He J, Wu S N, Tang M T, et al. Separation of zinc and iron in sulfate system with hydrothermal method and preparation of ferric oxide powder for soft magnetic ferrite use // Seminar on Development of Heavy Nonferrous Metal Metallurgy Technology in Low Carbon Economy— —Proceedings of the Sixth Session of the Committee. Kunming, 2010: 64何靜, 吳勝男, 唐謨堂, 等. 硫酸鹽體系中水熱法分離鋅鐵及制備軟磁鐵氧體用氧化鐵粉 // 低碳經濟條件下重有色金屬冶金技術發展研討會——暨重冶學委會第六屆委員會成立大會論文集. 昆明, 2010: 64 [15] Li C X, Wei C, Deng Z G, et al. Hydrothermal hematite precipitation and conversion behavior of metastable iron phase in FeSO4?H2O system. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2018, 28(3): 628李存兄, 魏昶, 鄧志敢, 等. FeSO4?H2O體系中水熱赤鐵礦沉鐵及亞穩態鐵物相轉變行為. 中國有色金屬學報, 2018, 28(3):628 [16] Yue M, Sun N L, Zou X, et al. The discussion on hydrolysis precipitation of ferric oxide directly from ferric-ion rich zinc leachate. China Nonferrous Metall, 2012, 41(4): 80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2012.04.022岳明, 孫寧磊, 鄒興, 等. 鋅浸出液三價鐵直接水解赤鐵礦法除鐵的探討. 中國有色冶金, 2012, 41(4):80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6103.2012.04.022 [17] Yang F. Study on Iron Removal by Leaching Hematite from High Iron Sphalerite[Dissertation]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015楊凡. 高鐵閃鋅礦浸出液赤鐵礦法除鐵的研究[學位論文]. 昆明: 昆明理工大學, 2015 [18] Yamada T, Kuramochi S, Togashi R. Recent Operations at the Iijima Zinc Refinery // Proceedings of the Lead-Zinc 2000 Symposium. Pittsburgh, 2000: 373 [19] Xu H J, Li R G, Yin G M, et al. Treatment of Desulphurization of Zinc Smelting Hematite Slag: China Patent, 201910133389.X.2019-4-26徐華軍, 李若貴, 印國敏, 等. 濕法煉鋅赤鐵礦渣脫硫的處理方法: 中國專利, 201910133389. X. 2019-4-26 [20] Xu H J, Li R G, Yin G M, et al. Treatment Unit for Desulphurization of Zinc Smelting Hematite Slag: China Patent, 201910133380.9.2019-5-3徐華軍, 李若貴, 印國敏, 等. 濕法煉鋅赤鐵礦渣脫硫的處理裝置: 中國專利, 201910133380.9.2019-5-3 [21] Liu J L. Research on the recovery of zinc and production of iron oxide red from hematite slag. Chin Mater Sci Technol Equip, 2012, 8(6): 81劉俊蘭. 鋅冶煉赤鐵礦渣回收鋅金屬并生產氧化鐵紅可行性研究. 中國材料科技與設備, 2012, 8(6):81 [22] Zhang X Z. Study on Preparation of Transparent Iron Oxide Pigment by Hydrometallurgy Zinc Hematite Slag[Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009張學政. 濕法煉鋅赤鐵礦渣制備透明氧化鐵顏料的研究[學位論文]. 長沙: 中南大學, 2009 [23] Xu J H, Wang X J. Clean production of iron oxide red // Proceedings of 2007 China Sustainable Development Forum. Guangzhou, 2007: 259許金花, 汪曉軍. 氧化鐵紅的清潔生產 // 2007中國可持續發展論壇暨中國可持續發展學術年會論文集. 廣州, 2007: 259 [24] He S P, Gao Q, Yu X T, et al. Preparation of red iron oxide and the use in coatings. Chem Prod Technol, 2011, 18(1): 29何蘇萍, 高倩, 余曉婷, 等. 氧化鐵紅的制備方法及其在涂料中的應用. 化工生產與技術, 2011, 18(1):29 [25] State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB5085.3—2007 Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes— —Identification for Extraction Toxicity. Beijing: China Environment Press, 2007中華人民共和國國家環境保護總局. GB5085.3—2007 危險廢物鑒別標準——浸出毒性鑒別. 北京: 中國環境出版社, 2007 [26] Li H G. Science of Hydro-Metallurgy. 1st Ed. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2002李洪桂. 濕法冶金學. 1版. 長沙: 中南大學出版社, 2002 [27] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 1863—2008 Iron Oxide Pigments. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008中華人民共和國國家質量監督檢驗檢疫總局, 中國國家標準化管理委員會. GB/T 1863—2008 氧化鐵顏料. 北京: 中國標準出版社, 2008 -




 下載:
下載: